Question: 1. (i) Calculate the current efficiency for the two EW experiments. You will need the average current for each test, which is total charge passed
1. (i) Calculate the current efficiency for the two EW experiments. You will need the
average current for each test, which is total charge passed over the total plating time
in seconds.
(ii) Calculate the energy consumption in kWh/tonne Cu plated for each test. (1 kWh
= 3.6 x 106 J.)
(iii) What effect did iron in the electrolyte have on current efficiency and energy
consumption? Which is easier to reduce, Cu+2 or Fe+3? (Provide E° values to validate your answer.) Which is easier to oxidize, Fe+2 or H2O? Explain the effect of iron in the electrolyte on current efficiency and energy consumption, i.e. what are the processes occurring at the cathode and at the anode and how do they affect the two quantities?
2. The reduction potential for light's solution on Pt is 0.673 V relative to standard
H+/H2. Assume that this is about equal to E°Fe+3/Fe+2. (The E° for Fe+3/Fe+2 in sulfuric acid solution is 0.68 V, so the assumption is not too bad.) What was the measured potential of the ferric/ferrous half reaction on Pt relative to the Cu+2/Cu reference electrode? Estimate the potential for the Cu+2/Cu reference electrode relative to standard H+/H2. (Note - this is actually not the standard Cu+2/Cu potential, though it should be close.)
3. Was it possible to measure the voltage of the S2O82-/SO42- half reaction on Pt? Explain why or why not.
4. (i) What gas formed on the surface of the Zn metal submerged in the ZnSO4/H2SO4 solution? Is this gas formation due to a reduction or an oxidation of the reactant that forms the gas? Whatis the balanced chemical reaction for process and calculate ∆E°.
(ii) After adding the CuSO4·5H2O a dark coloured material formed on the zinc surface.
What was this material? What is the balanced reaction for its formation. State the relevant standard half reaction potentials and calculate ∆E° (It should be positive.)
(iii) Zinc metal is not thermodynamically stable in dilute sulfuric acid solution. Explain why. What effect did copper sulfate have on the rate of gas evolution? Explain why this occurred? (A diagram of what is occurring on the electrode surface would be helpful.)
5. For the oxygen evolution test in Cu EW: (i) How did the anode-reference electrode potential difference change upon adding cobalt sulfate? Provide a quantitative answer. How is cobalt influencing the oxygen evolution overpotential?
(ii) If a copper EW cell voltage is 1.9 V and CoSO4 addition lowers this cell voltage by 100 mV, calculate the effect on the energy consumption. (Recall that electrical energy is voltage x charge passed through that potential difference.)
(iii) The voltage vs. log j plot should be almost linear at higher current densities. Fit
this part of the curve to a straight line. Calculate the anode voltage at 320 A/m2
current density. If the open circuit potential is about 1.05 V estimate the oxygen
evolution overvoltage at 320 A/m2 current density. If cell voltage is 2.0 V, what
fraction of the total energy consumption is due to the oxygen evolution overpotential?
(iv) The overvoltage for the Cu+2/Cu half reaction is roughly 0.05 V. Assume that the thermodynamic cell voltage is approximately equal to ∆E° (Cu+2/Cu - O2/H2O).
Referring to the conditions of part (iii) what would the voltage drop due to electrical
resistances be in this circuit? (A significant contributor to this is the solution
resistance where the current is carried by migration of ions.)
(v) A new anode material on the market uses platinum group metal oxides to catalyze the oxygen evolution half reaction. If the overvoltage for the preceding question is lowered to 0.30 V calculate the effect on energy consumption in percent.
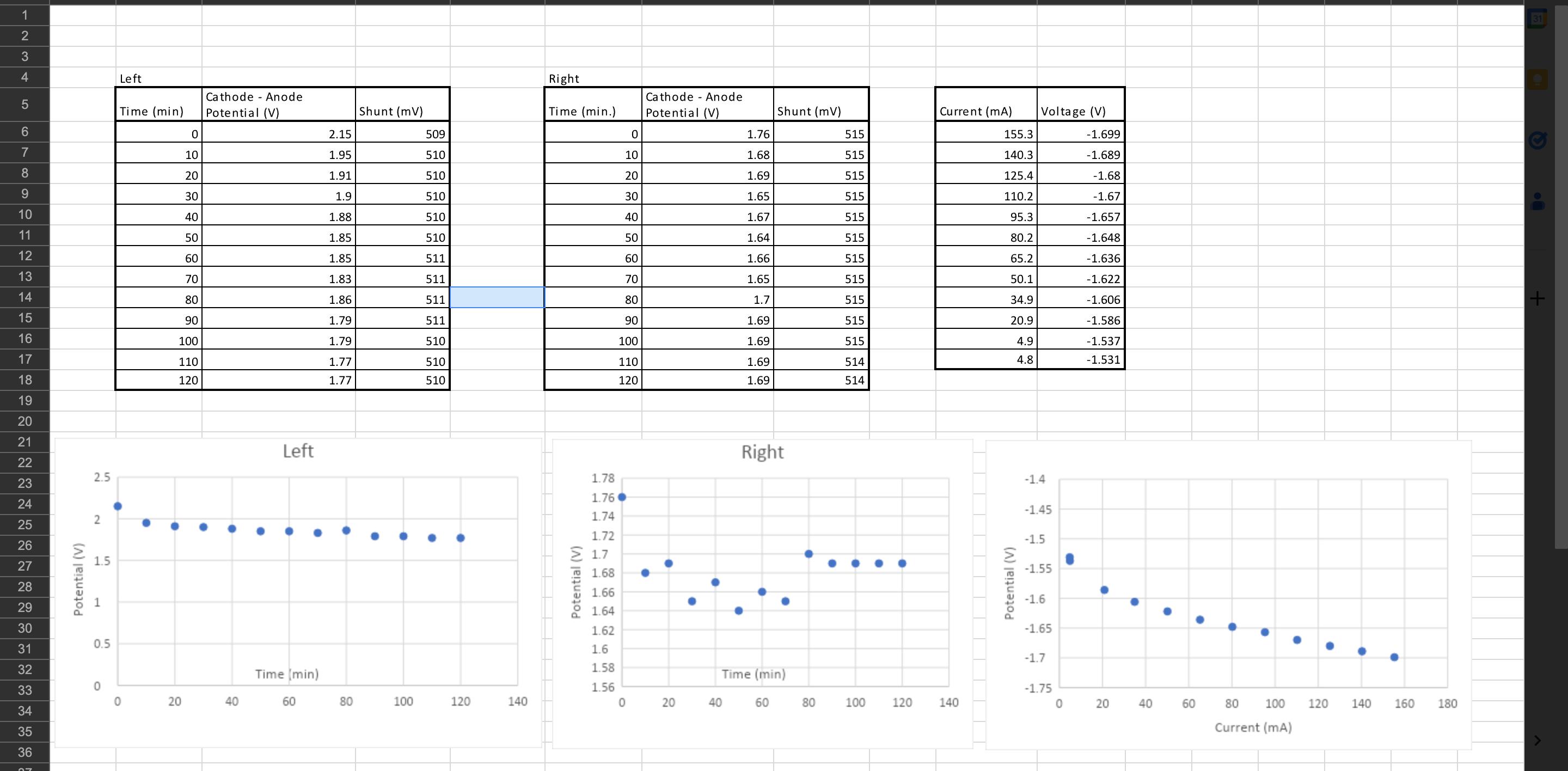
Image transcription text
CO NO 4 Left Right 5 Cathode - Anode Time (min) Cathode - Anode Potential (V) Shunt (mv) Time(min.) Potential (V) Shunt (mv) 6 Current (mA) Voltage (V) 0 2.15 509 1.76 515 155. 1.699 10 1.95 510 10
1.68 515 8 140.3 1.689 20 1.91 510 20 1.69 9 515 125.4 1.68 30 1.9 510 30 10 1.65 515 110.2 1....
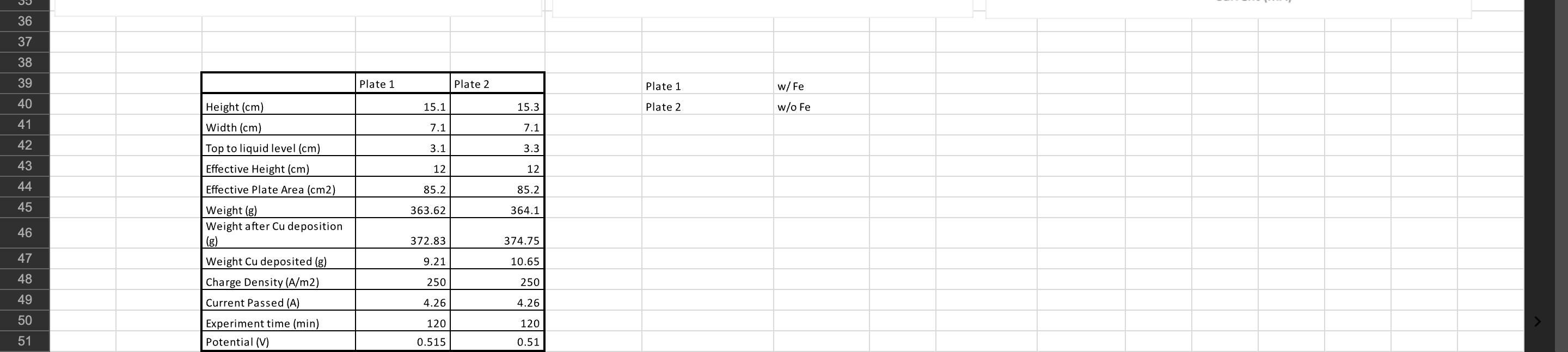
Image transcription text
36 37 38 39 Plate 1 Plate 2 Plate 1 w/ Fe 40 Height (cm) 15.1 15.3 Plate 2 w/o Fe 41 Width (cm) 7.1 7.1 42Top to liquid level (cm) 3.1 3.3 43 Effective Height (cm) 12 12 44 Effective Plate Area (cm2) 35.2 85.2 45
Weight (8) 363.62 364.1 46 Weight after Cu deposition 372.83 374.75 47 Weight Cu deposi...
1 31 2 3 4 Left Right Cathode Anode Cathode Anode 5 Time (min) Potential (V) Shunt (mV) Time (min.) Potential (V) Shunt (mV) Current (mA) Voltage (V) 6 0 2.15 509 0 1.76 515 155.3 -1.699 7 10 1.95 510 10 1.68 515 140.3 -1.689 8 20 1.91 510 20 1.69 515 125.4 -1.68 9 30 1.9 510 30 1.65 515 110.2 -1.67 10 40 1.88 510 40 1.67 515 95.3 -1.657 11 50 1.85 510 50 1.64 515 80.2 -1.648 12 60 1.85 511 60 1.66 515 65.2 -1.636 13 70 1.83 511 70 1.65 515 50.1 -1.622 14 80 1.86 511 80 1.7 515 34.9 -1.606 + 15 90 1.79 511 90 1.69 515 20.9 -1.586 16 100 1.79 510 100 1.69 515 4.9 -1.537 17 110 1.77 510 110 1.69 514 4.8 -1.531 18 120 1.77 510 120 1.69 514 19 20 21 Left 22 2.5 23 24 2 25 26 Right 1.78 1.76 1.74 1.72 27 28 29 Potential (V) 1.7 1.5 1.68 -1.55 1.66 1 -1.6 1.64 30 1.62 -1.65 0.5 31 1.6 -1.7 32 Time (min) 1.58 Time (min) 33 0 1.56 -1.75 0 20 40 40 60 34 60 80 100 120 140 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 35 Current (mA) -1.4 -1.45 -1.5 36 17
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


