Question: 2. Consider the following problem. Given a simple, undirected graph G - (V. E), with edges weights we 0, integer k, and integer l, where
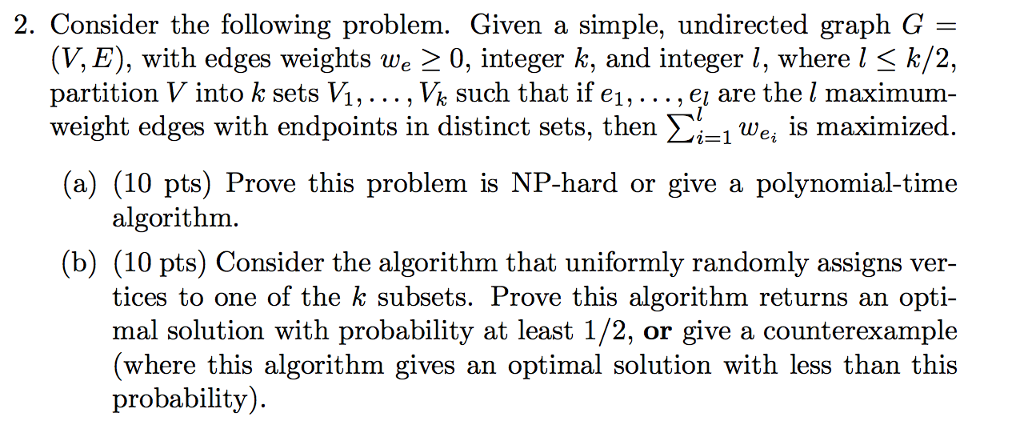
2. Consider the following problem. Given a simple, undirected graph G - (V. E), with edges weights we 0, integer k, and integer l, where l-k/2. partition V into k sets VM,... , V% such that if e1,..., ei are the I maximum weight edges with endpoints in distinct sets, then _1 we, is maximized (a) (10 pts) Prove this problem is NP-hard or give a polynomial-time algorithm (b) (10 pts) Consider the algorithm that uniformly randomly assigns ver- tices to one of the k subsets. Prove this algorithm returns an opti- mal solution with probability at least 1/2, or give a counterexample (where this algorithm gives an optimal solution with less than this probability) 2. Consider the following problem. Given a simple, undirected graph G - (V. E), with edges weights we 0, integer k, and integer l, where l-k/2. partition V into k sets VM,... , V% such that if e1,..., ei are the I maximum weight edges with endpoints in distinct sets, then _1 we, is maximized (a) (10 pts) Prove this problem is NP-hard or give a polynomial-time algorithm (b) (10 pts) Consider the algorithm that uniformly randomly assigns ver- tices to one of the k subsets. Prove this algorithm returns an opti- mal solution with probability at least 1/2, or give a counterexample (where this algorithm gives an optimal solution with less than this probability)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


