Question: = 20 +212 +...+ an-101-1 4. [Root finding by solving an eigenvalue problem, 3+3pts] An efficient way to find individual roots of a polynomial is
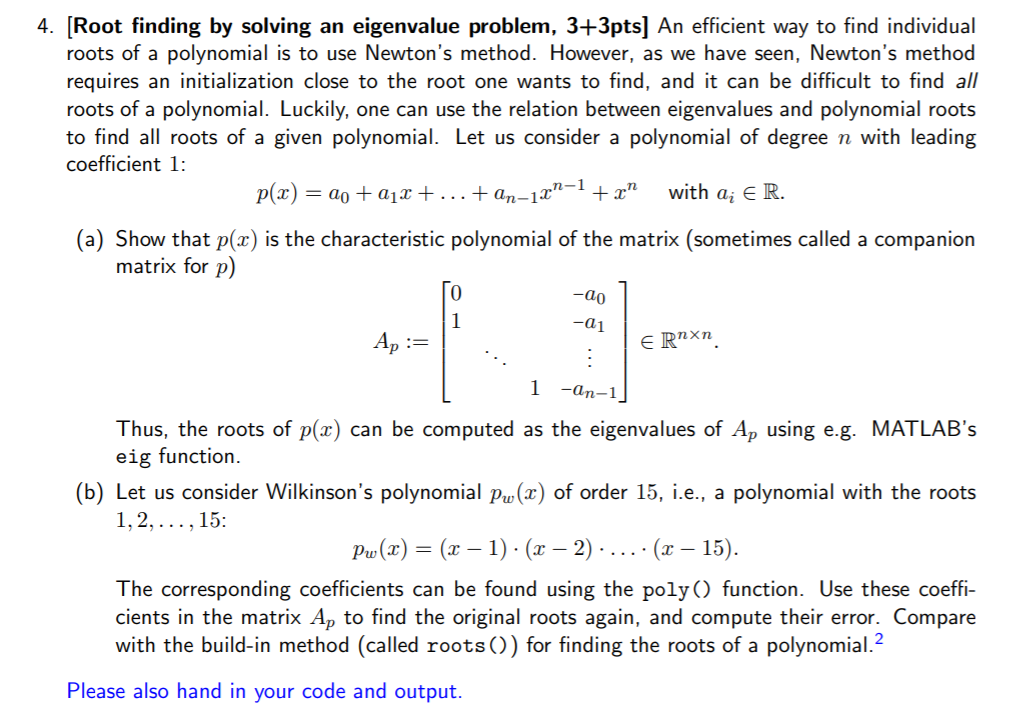
= 20 +212 +...+ an-101-1 4. [Root finding by solving an eigenvalue problem, 3+3pts] An efficient way to find individual roots of a polynomial is to use Newton's method. However, as we have seen, Newton's method requires an initialization close to the root one wants to find, and it can be difficult to find all roots of a polynomial. Luckily, one can use the relation between eigenvalues and polynomial roots to find all roots of a given polynomial. Let us consider a polynomial of degree n with leading coefficient 1: p(x) +2 with a; ER. (a) Show that p(x) is the characteristic polynomial of the matrix (sometimes called a companion matrix for p) TO -00 -01 Ap := ERnxn 1 -an-1 Thus, the roots of p(x) can be computed as the eigenvalues of Ap using e.g. MATLAB's eig function. (b) Let us consider Wilkinson's polynomial pu() of order 15, i.e., a polynomial with the roots 1, 2, ..., 15: pw(x) = (x - 1). (x - 2) ..... .. (x 15). The corresponding coefficients can be found using the poly() function. Use these coeffi- cients in the matrix Ap to find the original roots again, and compute their error. Compare with the build-in method (called roots()) for finding the roots of a polynomial.2 Please also hand in your code and output. = 20 +212 +...+ an-101-1 4. [Root finding by solving an eigenvalue problem, 3+3pts] An efficient way to find individual roots of a polynomial is to use Newton's method. However, as we have seen, Newton's method requires an initialization close to the root one wants to find, and it can be difficult to find all roots of a polynomial. Luckily, one can use the relation between eigenvalues and polynomial roots to find all roots of a given polynomial. Let us consider a polynomial of degree n with leading coefficient 1: p(x) +2 with a; ER. (a) Show that p(x) is the characteristic polynomial of the matrix (sometimes called a companion matrix for p) TO -00 -01 Ap := ERnxn 1 -an-1 Thus, the roots of p(x) can be computed as the eigenvalues of Ap using e.g. MATLAB's eig function. (b) Let us consider Wilkinson's polynomial pu() of order 15, i.e., a polynomial with the roots 1, 2, ..., 15: pw(x) = (x - 1). (x - 2) ..... .. (x 15). The corresponding coefficients can be found using the poly() function. Use these coeffi- cients in the matrix Ap to find the original roots again, and compute their error. Compare with the build-in method (called roots()) for finding the roots of a polynomial.2 Please also hand in your code and output
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


