Question: A flat, charged surface with a surface potential do that is positively charged. The surface is adjacent to an aqueous solution with a concentration

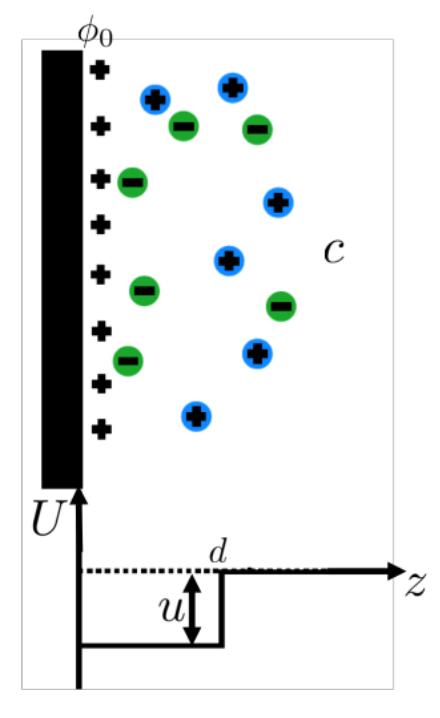
A flat, charged surface with a surface potential do that is positively charged. The surface is adjacent to an aqueous solution with a concentration c of monovalent salts, which have an attraction to the surface. This attraction is a potential well of depth u that extends a distance d into the solution, as shown in the figure below. In a sufficiently dilute solution of concentration c, the Poisson-Boltzmann equation is: V2(x) = c/e [eep(x)- e-Bep(x)] (1) How would this be altered in the presence of the potential well described above? (2) What is the Debye-Hckel expression for a distance z d? (Remember that the electrostatic potential should be continuous at d.) (3) How does the presence of the surface potential affect the charge distribution? (4) Will such a potential promote or decrease the charge stabilization of a charged colloidal system? Why? U d ul] C Z
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 In the presence of the potential well the PoissonBoltzmann equation will be modified to include the effect of the potential well on the electric fie... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


