Question: An analyst determined benzoic acid concentration in lemonade using liquid chromatography (HPLC). She prepared calibration solutions from a high-purity standard substance and recorded chromatograms of
An analyst determined benzoic acid concentration in lemonade using liquid chromatography (HPLC).
She prepared calibration solutions from a high-purity standard substance and recorded chromatograms of these solutions. The benzoic acid peak areas on the chromatograms were as shown in the table:
| C (mg/l) | A (mAUs) |
| 2.05 | 383.7 |
| 4.05 | 779.7 |
| 6.02 | 1174.1 |
| 7.97 | 1551.6 |
| 9.96 | 1968.5 |
The standard uncertainties of the calibration graph slope and intercept can be assumed equal to their standard deviations as found from regression analysis.
The lemonade under question was degassed and diluted. For dilution 2.3 ml of lemonade was pipetted into a 100 ml volumetric flask, which was thereafter made up to the mark with purified water. The uncertainty components of the pipette volume are: calibration (0.05 ml), repeatability of pipetting (0.03 ml) and temperature (maximum difference from pipette calibration temperature was 3C). The uncertainty components of the volumetric flask volume are: calibration (0.11 ml), repeatability of filling the flask (0.09 ml) and temperature (maximum difference from flask calibration temperature was 3C).
Chromatogram of the lemonade solution was recorded and the peak area of benzoic acid Asample was 969.3 mAUs. The standard uncertainty of sample peak area repeatability can be estimated as 2 % of the sample peak area. The standard uncertainty of Asample due to possible drift of the chromatograph and baseline irregularity can be estimated as 14.1 mAUs. The uncertainty of Asample due to possible overlap with some co-eluting component can be estimated as 2.4% of the peak area. The measurement model is the following:
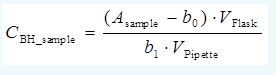
This uncertainty calculation can be carried out either using linear regression with intercept taken into account (as done in section 9.7) or with intercept forced to zero (then it is also removed from the model equation). For carrying out the calculations either the Kragten approach can be used (as used in section 9.7) or the analytical calculation approach with equation 4.12 (section 4.2), i.e. the same approach as used in self-test 9A. With the analytical approach the intercept has to be forced to zero. The correct answers from these calculations differ to some extent, but all are considered correct. However, because of the peculiarities of the Moodle system, only the correct results corresponding to Kragten approach with intercept (using the model that is displayed in the question text) are displayed.
Please find the benzoic acid concentration in lemonade with units mg/l. Please give the result with one decimal place. (A larger than usual number of decimals after the comma have been deliberately given in correct answer in order to enable the participants check their calculations)
CBH_sample=b1VPipette(Asampleb0)VFlask
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


