Question: An enzyme reversibly binds substrate and irreversibly converts the substrate to product. However, when the substrate is further protonated, it can no longer bind to
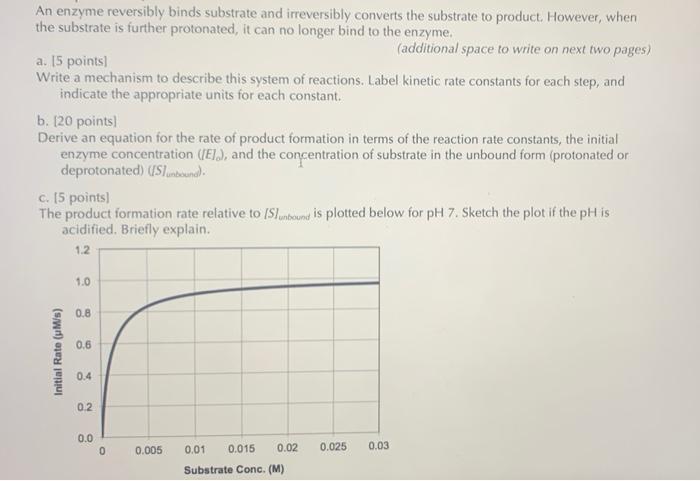
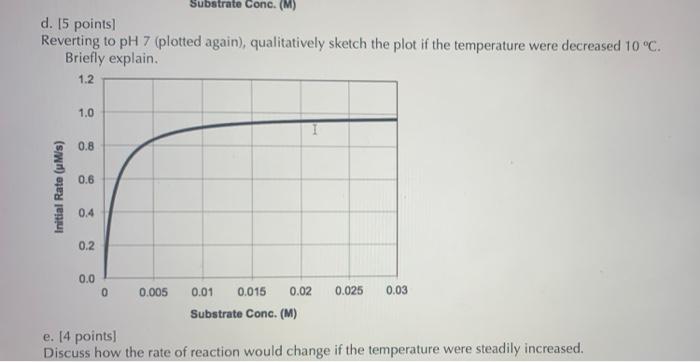
An enzyme reversibly binds substrate and irreversibly converts the substrate to product. However, when the substrate is further protonated, it can no longer bind to the enzyme (additional space to write on next two pages) a. 15 points) Write a mechanism to describe this system of reactions. Label kinetic rate constants for each step, and indicate the appropriate units for each constant. b. 120 points) Derive an equation for the rate of product formation in terms of the reaction rate constants, the initial enzyme concentration (El), and the concentration of substrate in the unbound form (protonated or deprotonated) (Sunbound). C. 15 points) The product formation rate relative to (Slunteunt is plotted below for pH 7. Sketch the plot if the pH is acidified. Briefly explain. 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 Initial Rate (MS) 0.4 0.2 0.0 0 0.005 0.025 0.03 0.01 0.015 0.02 Substrate Conc. (M) Substrate Conc. (M) d. 15 points) Reverting to pH 7 (plotted again), qualitatively sketch the plot if the temperature were decreased 10 C. Briefly explain. 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 Initial Rate (M/s) 0.4 0.2 0.0 0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03 Substrate Conc. (M) e. 14 points) Discuss how the rate of reaction would change if the temperature were steadily increased
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


