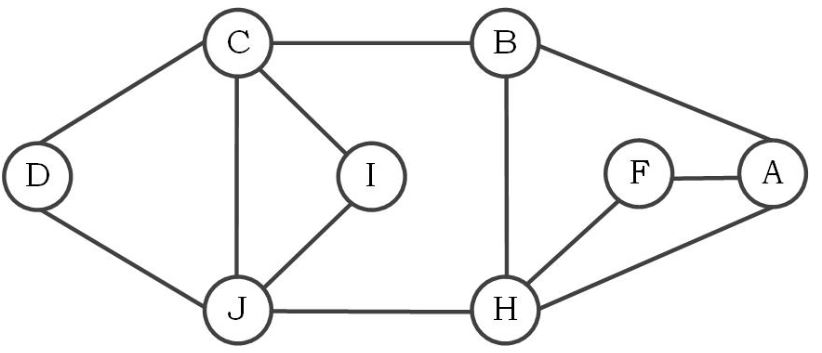
Question: An undirected graph G is shown in the figure below. Assume that the adjacency lists are in alphabetical order. Apply breadth - first search (
An undirected graph G is shown in the figure below.
Assume that the adjacency lists are in alphabetical order. Apply breadthfirst search BFS on graph G starting from vertex A
Answer the following questions after BFS is completed
a What is the value of Cd
b What is the value of Jd
c What is the value of Cpi
d What is the value of Jpi
Preliminaries
We start from a source vertex, s
Discover vertices in the graph
Three possible color values of a vertex
white, not discovered yet
gray, discovered but not explored
black, discovered and explored
Initially, all vertices are white
The source vertex is discovered first
PredecessorParent
While exploring gray node u we check the adjacency list uAdj
If v on uAdj is white, we say v is discovered by u We also say u is the parent or predecessor of v This is denoted by vpiu
BFSG s
for each vertex u E GV s
ucolor WHITE;
ud inf; upi NIL;
scolor GRAY;
sd ; spi NIL
Q
EnqueueQ s
while Q
u DEQUEUEQ
for each vertex v E GAdju
if vcolor WHITE
vcolor GRAY
vd ud
vpi u
EnqueueQ v
ucolor BLACK
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


