Question: Bit fields in ARM opcodes cannot be overloaded, or repurposed to hold immediate values ALU status bits should be cleared using the STC instruction (status
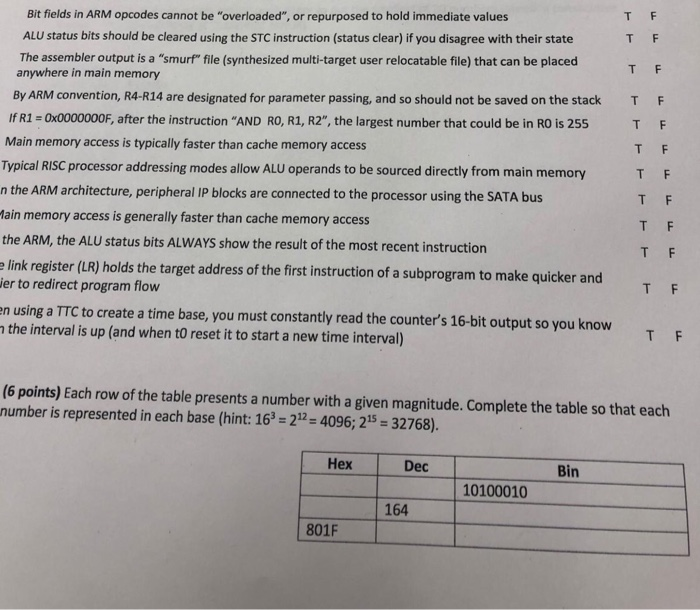
Bit fields in ARM opcodes cannot be "overloaded", or repurposed to hold immediate values ALU status bits should be cleared using the STC instruction (status clear) if you disagree with their state The assembler output is a "smurf" file (synthesized multi-target user relocatable file) that can be placed anywhere in main memory By ARM convention, R4-R14 are designated for parameter passing, and so should not be saved on the stack T If R1 -Ox0000000F, after the instruction "AND RO, R1, R2", the largest number that could be in RO is 255 T Main memory access is typically faster than cache memory access Typical RISC processor addressing modes allow ALU operands to be sourced directly from main memory n the ARM architecture, peripheral IP blocks are connected to the processor using the SATA bus ain memory access is generally faster than cache memory access the ARM, the ALU status bits ALWAYS show the result of the most recent instruction elink register (LR) holds the target address of the first instruction of a subprogram to make quicker and F F ier to redirect program flow n using a TTC to create a time base, you must constantly read the counter's 16-bit output so you know the interval is up (and when to reset it to start a new time interval) (6 points) Each row of the table presents a number with a given magnitude. Complete the table so that each number is represented in each base (hint: 16 21 4096; 215-32768). Hex Dec Bin 10100010 164 801F
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


