Question: CAPM predicts that a security's risk premium increases in proportion to its beta of the security, not its volatility. Justify this statement using Figures 10.6
CAPM predicts that a security's risk premium increases in proportion to its beta of the security, not its volatility. Justify this statement using Figures 10.6 and 10.7
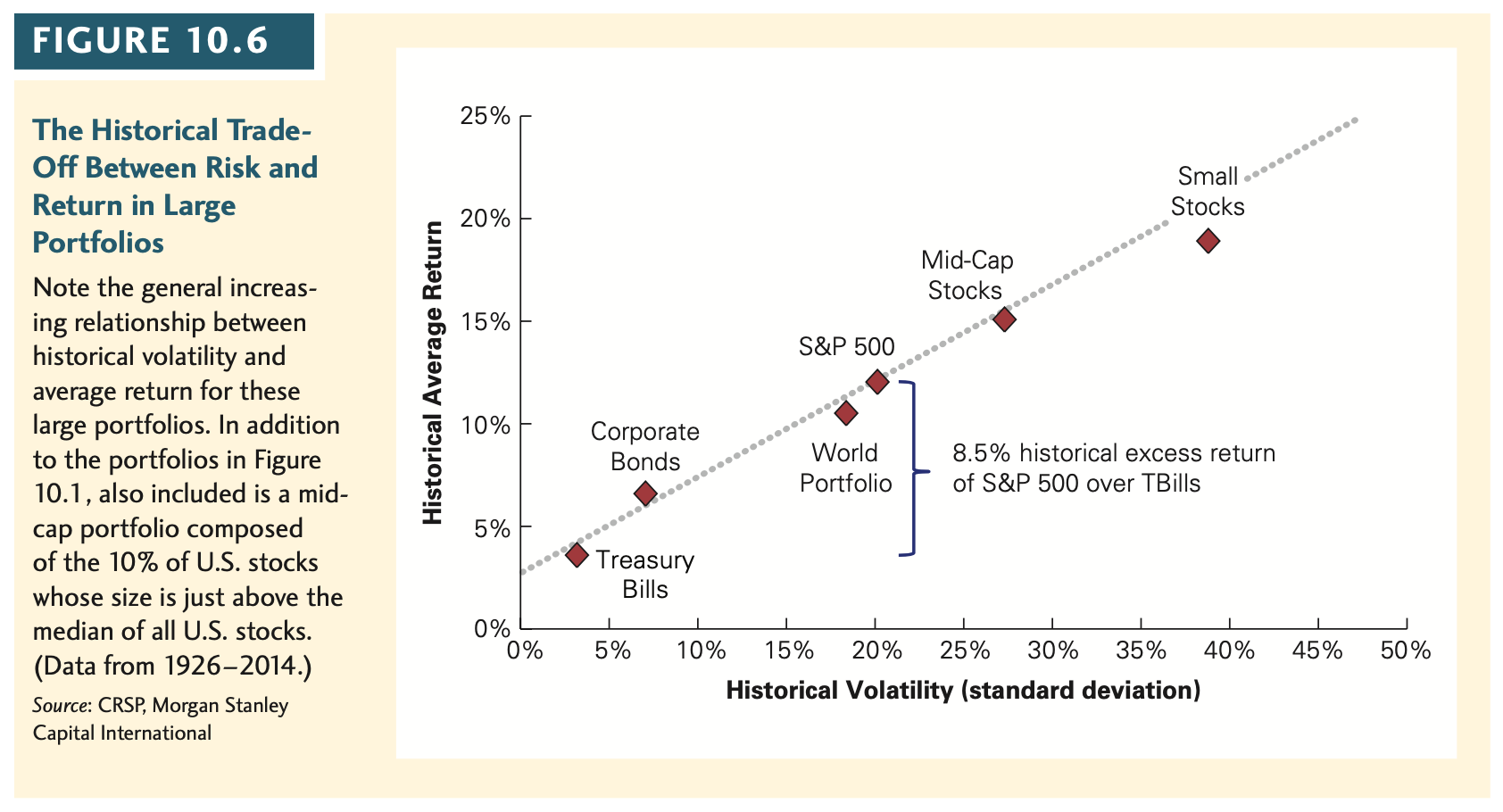
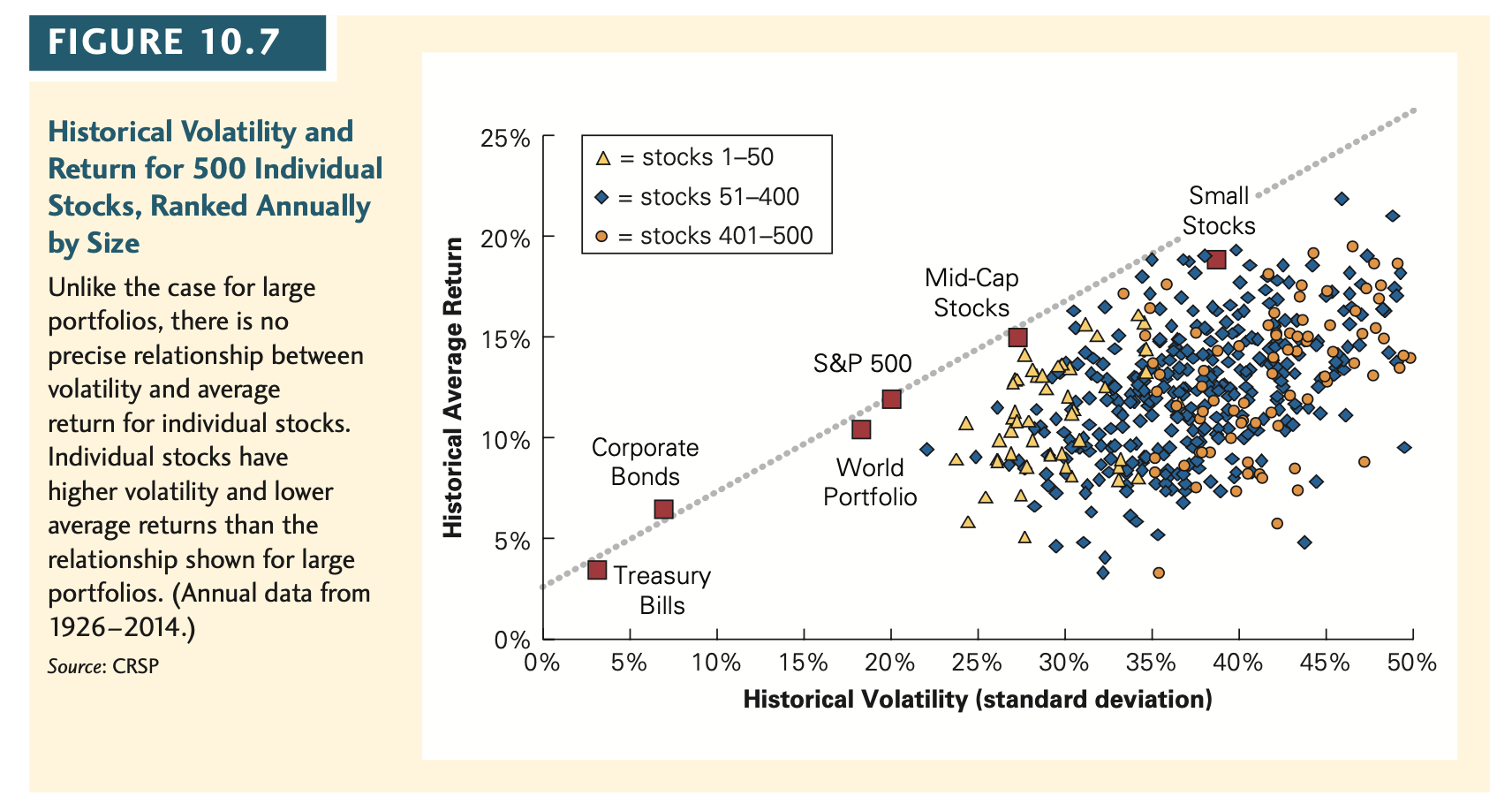
FIGURE 10.6 25% Small Stocks 20% Mid-Cap Stocks 15% S&P 500 The Historical Trade- Off Between Risk and Return in Large Portfolios Note the general increas- ing relationship between historical volatility and average return for these large portfolios. In addition to the portfolios in Figure 10.1, also included is a mid- cap portfolio composed of the 10% of U.S. stocks whose size is just above the median of all U.S. stocks. (Data from 19262014.) Source: CRSP, Morgan Stanley Capital International Historical Average Return 10% Corporate Bonds World Portfolio 8.5% historical excess return of S&P 500 over TBills 5% Treasury Bills 0% 0% 5% 45% 50% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% Historical Volatility (standard deviation) FIGURE 10.7 25% A = stocks 1-50 OOOOOOOOOO = stocks 51-400 stocks 401-500 Small Stocks 20% O = Mid-Cap Stocks 15% S&P 500 Historical Volatility and Return for 500 Individual Stocks, Ranked Annually by Size Unlike the case for large portfolios, there is no precise relationship between volatility and average return for individual stocks. Individual stocks have higher volatility and lower average returns than the relationship shown for large portfolios. (Annual data from 19262014.) Source: CRSP Historical Average Return 10% Corporate Bonds World Portfolio 5% Treasury Bills 0% 0% 5% 45% 50% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% Historical Volatility (standard deviation) FIGURE 10.6 25% Small Stocks 20% Mid-Cap Stocks 15% S&P 500 The Historical Trade- Off Between Risk and Return in Large Portfolios Note the general increas- ing relationship between historical volatility and average return for these large portfolios. In addition to the portfolios in Figure 10.1, also included is a mid- cap portfolio composed of the 10% of U.S. stocks whose size is just above the median of all U.S. stocks. (Data from 19262014.) Source: CRSP, Morgan Stanley Capital International Historical Average Return 10% Corporate Bonds World Portfolio 8.5% historical excess return of S&P 500 over TBills 5% Treasury Bills 0% 0% 5% 45% 50% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% Historical Volatility (standard deviation) FIGURE 10.7 25% A = stocks 1-50 OOOOOOOOOO = stocks 51-400 stocks 401-500 Small Stocks 20% O = Mid-Cap Stocks 15% S&P 500 Historical Volatility and Return for 500 Individual Stocks, Ranked Annually by Size Unlike the case for large portfolios, there is no precise relationship between volatility and average return for individual stocks. Individual stocks have higher volatility and lower average returns than the relationship shown for large portfolios. (Annual data from 19262014.) Source: CRSP Historical Average Return 10% Corporate Bonds World Portfolio 5% Treasury Bills 0% 0% 5% 45% 50% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% Historical Volatility (standard deviation)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


