Question: Consider the function Magic, whose pseudocode is illustrated in Algorithm 1. The algorithm takes a graph as an input and outputs either true or false.

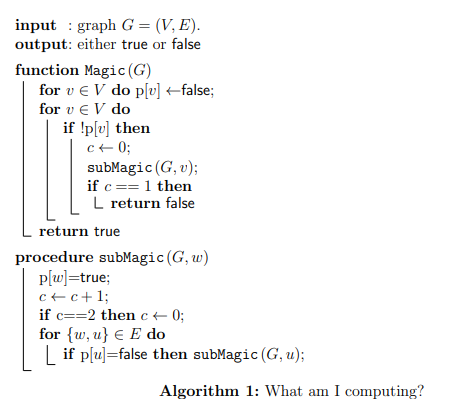
Consider the function Magic, whose pseudocode is illustrated in Algorithm 1. The algorithm takes a graph as an input and outputs either true or false. The algorithm also uses a global array p that holds a Boolean value for every v EV and a global integer variable c. Given a graph G, then the function Magic returns true if: the graph G is connected, the graph G has an even number of vertices, the graph G has an even number of edges, all components of G have exactly two vertices, all components of G have an even number of edges, all components of G have an even number of vertices. input : graph G = (V, E). output: either true or false function Magic (G) for v V do p[u] false; for v EV do if !p[u] then C+0; subMagic (G,u); if c==1 then L return false return true procedure subMagic (G,w) p[w]=true; ctc+1; if c==2 then c0; for {w, u} E do | if p[u]=false then subMagic (G,u); Algorithm 1: What am I computing
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


