Question: Consider the heat equation with boundary conditions with initial value Uxx = Ut u (0,t) = 0 (1,t) = 0 u (x, 0) =
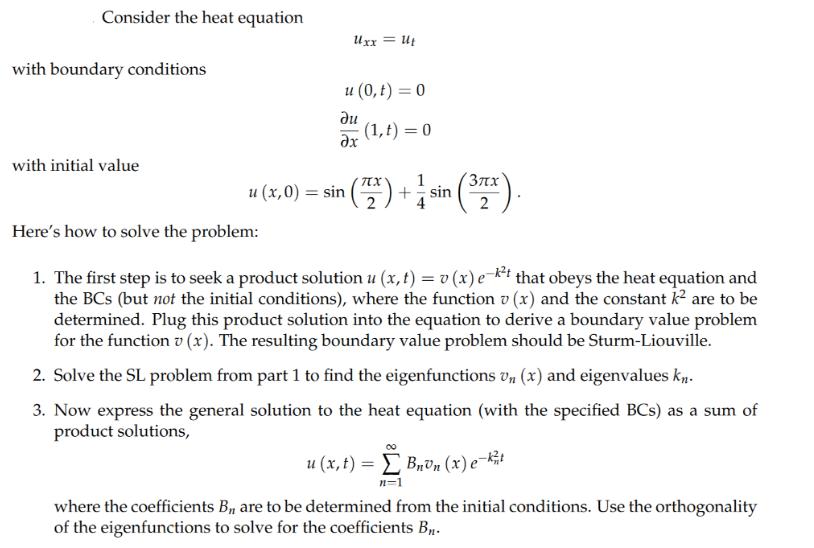
Consider the heat equation with boundary conditions with initial value Uxx = Ut u (0,t) = 0 (1,t) = 0 u (x, 0) = sin (). 1 += sin 4 3x 2 Here's how to solve the problem: 1. The first step is to seek a product solution u(x,t) = v(x) et that obeys the heat equation and the BCs (but not the initial conditions), where the function (x) and the constant k are to be determined. Plug this product solution into the equation to derive a boundary value problem for the function v (x). The resulting boundary value problem should be Sturm-Liouville. 2. Solve the SL problem from part 1 to find the eigenfunctions Un (x) and eigenvalues kn. 3. Now express the general solution to the heat equation (with the specified BCs) as a sum of product solutions, u(x,t) = Bon (x) e-k where the coefficients B, are to be determined from the initial conditions. Use the orthogonality of the eigenfunctions to solve for the coefficients B.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


