Question: Exercise 1.7: JAVA: Convert the following C code to Java (code pasted below) C code: struct LNode { int data; LNode* next; }; struct LList
Exercise 1.7: JAVA: Convert the following C code to Java (code pasted below)
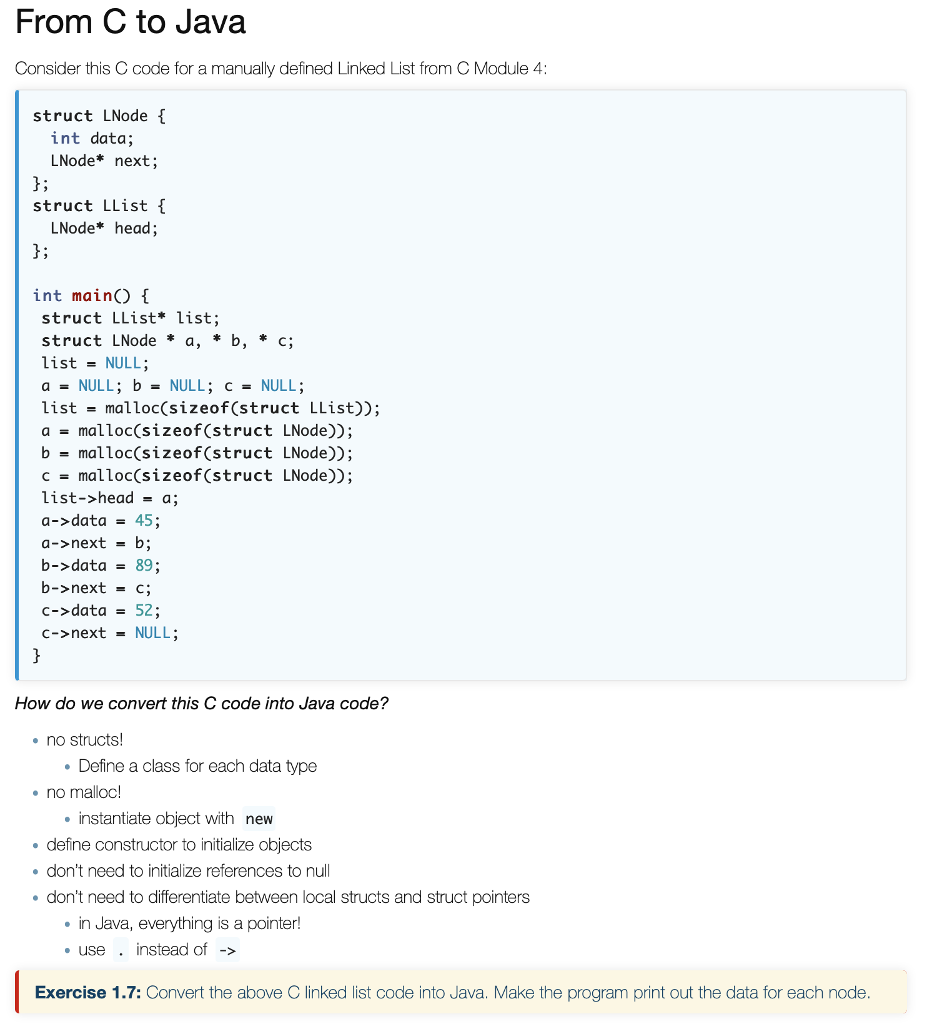
C code:
struct LNode {
int data;
LNode* next;
};
struct LList {
LNode* head;
};
int main() {
struct LList* list;
struct LNode * a, * b, * c;
list = NULL;
a = NULL; b = NULL; c = NULL;
list = malloc(sizeof(struct LList));
a = malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
b = malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
c = malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
list->head = a;
a->data = 45;
a->next = b;
b->data = 89;
b->next = c;
c->data = 52;
c->next = NULL;
}
From C to Java Consider this C code for a manually defined Linked List from C Module 4 struct LNode i int data; LNode* next; struct LList LNode* head; int mainO struct LList* list; struct LNode a, * b, * c; list = NULL; a-NULL; b= NULL; c= NULL; list - malloc(sizeof(struct LList)); a = malloc(sizeof(struct LNode)) ; bmalloc(sizeof(struct LNode)); c = malloc(sizeof(struct LNode)) ; List->heada a->data 45; a->next - b; b->data - 89; b->next = c; c->data 52 ; c->next = NULL; How do we convert this C code into Java code? no structs! Define a class for each data type no malloc! instantiate object with new define constructor to initialize objects don't need to initialize references to null don't need to differentiate between local structs and struct pointers in Java, everything is a pointer! use instead of -> Exercise 1.7: Convert the above C linked list code into Java. Make the program print out the data for each node
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


