Question: G Gmal YouTube Maps Chapter 6 Lab 10 Problem 6-7A Gross profit comparisons and cost flow assumptions-perpetual LO2, 3 Ontario Skateboard Company has the following
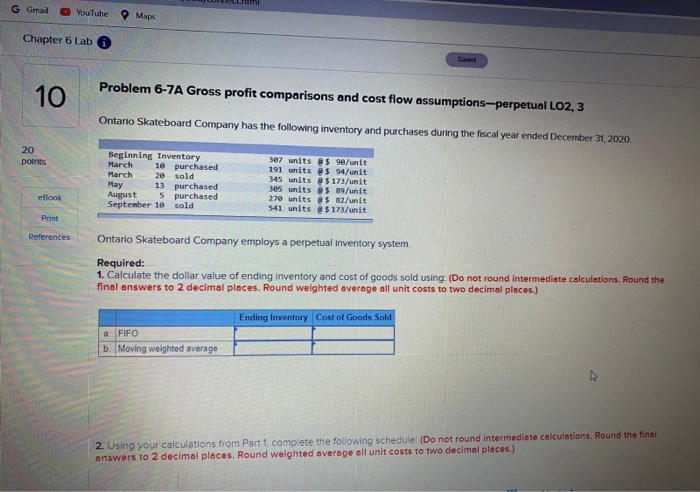
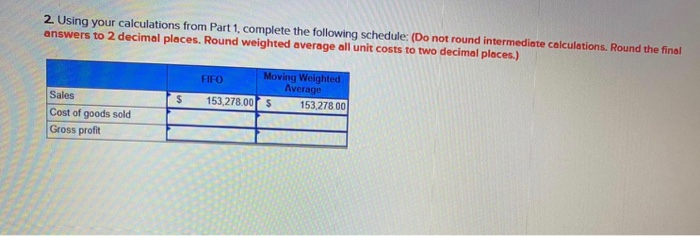
G Gmal YouTube Maps Chapter 6 Lab 10 Problem 6-7A Gross profit comparisons and cost flow assumptions-perpetual LO2, 3 Ontario Skateboard Company has the following inventory and purchases during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020. Beginning Inventory March 10 purchased March 2e sold May 13 purchased August 5 purchased September 10 sold 307 units O$ 90/unit 191 units $ 94/unit 345 units $173/unit 305 units $ 89/unit 270 units @ $ 52/unit 541 units $ 173/unit eBook References Ontario Skateboard Company employs a perpetual inventory system Required: 1. Calculate the dollar value of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using: (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round the final answers to 2 decimal places. Round weighted average all unit costs to two decimal places.) Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold a FIFO b. Moving weighted average 2 Using your calculations from Part 1, complete the following schedule: (Do not found intermediate calculations. Round the final answers to 2 decimal places. Round weighted average all unit costs to two decimal places.) 2. Using your calculations from Part 1, complete the following schedule: (Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round the final answers to 2 decimal places. Round weighted average all unit costs to two decimal places.) FEO Moving Weighted Average 153,278.005 153 278.00 S Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit L
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


