Question: Problem 6 - 7 A Gross profit comparisons and cost flow assumptions - perpetual LO 2 , 3 Ontario Skateboard Company has the following inventory
Problem A Gross profit comparisons and cost flow assumptionsperpetual LO
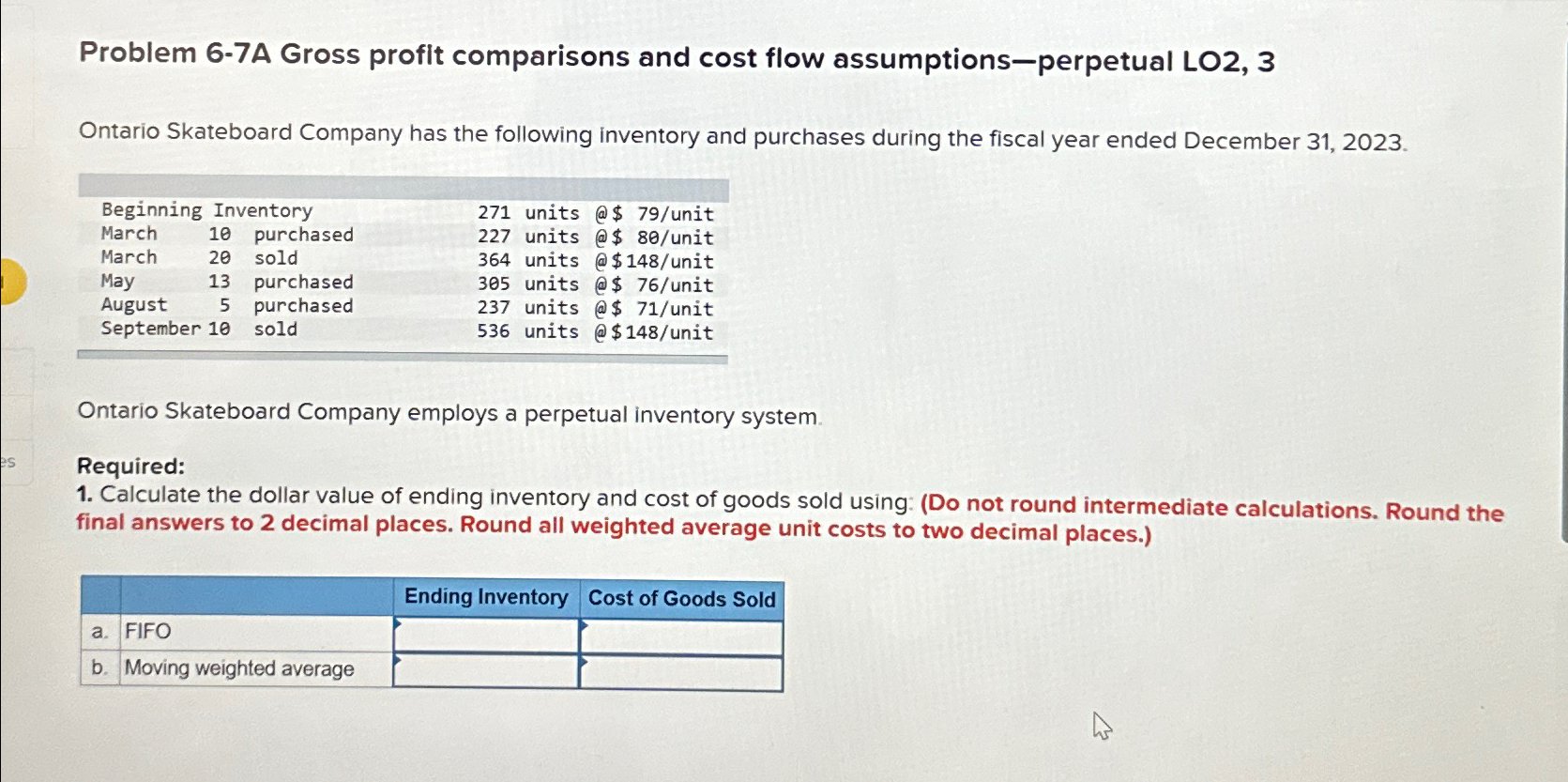
Ontario Skateboard Company has the following inventory and purchases during the fiscal year ended December
tableBeginning Irentory,units,@$ unitMarchpurchased,units,@$unitMarchsold,units,@$unitMaypurchased,units,@$ unitAugustpurchased,units,@$unitSeptember sold,units,@$unit
Ontario Skateboard Company employs a perpetual inventory system.
Required:
Calculate the dollar value of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round the final answers to decimal places. Round all weighted average unit costs to two decimal places.
tableaFIFO,Ending Inventory,Cost of Goods SoldbMoving weighted average,,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


