Question: Help please Lab Acid-Base Properties Report Sheet 1. Amino acid used for titration Alanine ml. 0.35 M NAOH Addol 130 10.01 1.84 140 0.01 15.0
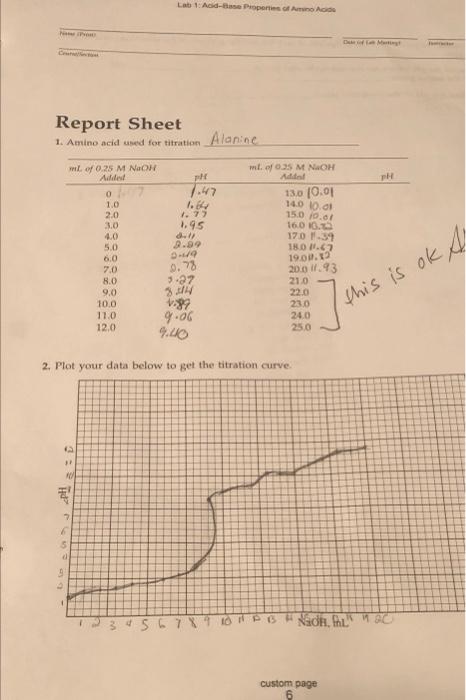


Lab Acid-Base Properties Report Sheet 1. Amino acid used for titration Alanine ml. 0.35 M NAOH Addol 130 10.01 1.84 140 0.01 15.0 19.01 16.0 16.0 17.0 7.39 ml of 0.25 M NON Added pH 0 7.47 1.0 2.0 1.77 3.0 1.95 4.0 . 5.0 29.99 6:0 7.0 8.0 3.27 9.0 3.4 10.0 1.89 11.0 9.06 12,0 4.00 . 0.78 18.0 1.62 19.0.2 20.0 11.93 210 22.0 230 24.0 25.0 this is ok A 2. Plot your data below to get the titration curve pll 3:0 7 5 be 23456789 PB Nadh, fhus C custom page Lab 1: Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids he ay 3. a. Indicate the positions of the midpoints of each leg and the position of the inflection point on your graph. b. Record the pK values for the carboxylic acid group and for the amino group Record the pH of the isoelectric point to sh Tod c. 199tis hoger 1. stration. The pH at Lab 1 Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids POST-LABORATORY QUESTIONS 1. Look up the structure in your textbook of the amino acid you titrated. Write the structure you expect at pH (a) 25 and (b) 12. 2. Compare your isoelectric point value (pl value) with the value of the amino acid listed in your textbook. How does it compare? Into which class does your amino acid fall? 3. Which data point can you obtain with greater accuracy from your graph-the pk values from the "legs or the isoelectric point from the point of inflection? Explain your answer. 4. From the pK, value you obtained in your experiment, calculate the equilibrium constant, K. pK= -log K 5. You are at the isoelectric point for a solution of leucine. If the number of negatively charged carboxylate groups, -COO, is 1 x 10", how many positively charged amino groups, --NH3, would there be
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


