Question: Homework 2 In this homework you are going to implement PCA from scratch We are going to use the following dataset for our examples *****
Homework 2
In this homework you are going to implement PCA from scratch
We are going to use the following dataset for our examples
*****
Dataset
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(0) X = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean = np.array([2,3]), cov = np.array([[2,1],[1,1]]),size = 100) plt.plot(X[:,0],X[:,1],"*b") plt.grid()
****
Problem 1
First normalize the each variable (column) by subtracting its mean and dividing by it standart deviation as follows:
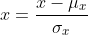
your function should take input matrix X as input and should return normalized matrix, mean and standart deviation vector as output
def normalize_data(X): pass
# Problem 1 example X_norm, mu, sigma = normalize_data(X)
print(X_norm[0]) print(mu) print(sigma) plt.plot(X_norm[:,0],X_norm[:,1],"*b") plt.grid()
[-1.74865957 -1.32485349] [1.95492653 3.07587784] [1.43707517 1.03112934]
Problem 2
Find the eiegnvalues and eiegnvectors of the covariance matrix. You can use np.cov() function for covariance and numpy.linalg.eig() function to get eigen values.
def eigen(X): pass
# Problem 2 example
eigen_values, eigen_vectors = eigen(X)
print(eigen_vectors) print(eigen_values) plt.plot(X_norm[:,0],X_norm[:,1],"*b") plt.grid() plt.plot([0,eigen_vectors[0,0]],[0,eigen_vectors[1,0]],"r") plt.plot([0,eigen_vectors[0,1]],[0,eigen_vectors[1,1]],"r") plt.axis('square') plt.show()
[[ 0.84500497 -0.53475846] [ 0.53475846 0.84500497]] [2.76215622 0.39785666]
Problem 3
Using the following formulation calculate the transformed values which are coordinates on the new basis as follows
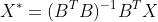
where B consists of eigenvectors corresponds the largest mm eigenvalues.
In the formulation above we assumed that columns corresponds to observations and rows corresponds to variables. So if your input matrix has rows as observations and columns as variables you may want to take the transpose of input matrix X as follows:
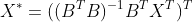
def transform(X, eigen_values, eigen_vectors, m): pass
#Problem 3 example
X_transformed = transform(X_norm, eigen_values, eigen_vectors, 2) print(X_transformed[0])
[-2.18610263 -0.18439728]
Problem 4
Put all the steps together in a function. You will use matrix X and the number of components m as inputs and the transformed matrix as output
def pca(X, m): pass
# Problem 4 example from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
X = load_iris()["data"]
X_transformed = pca(X, 2) print(X_transformed[0])
[-2.26470281 -0.4800266 ]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


