Question: (i) (5p) For a binary European call option which pays $1 if ST > K and nothing else, draw on three separate figures (2p)



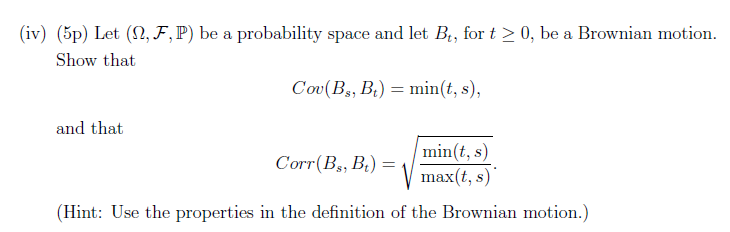
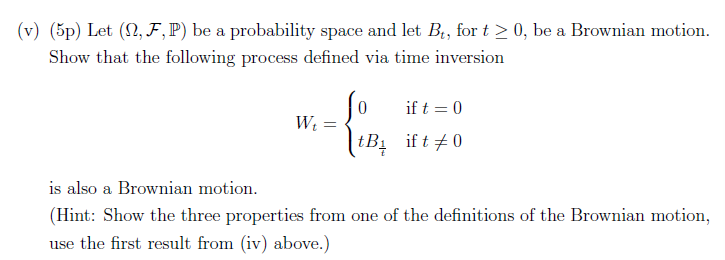
(i) (5p) For a binary European call option which pays $1 if ST > K and nothing else, draw on three separate figures (2p) the pay-off function of the option as a function of ST (3p) the graph of the "delta" of the option as a function of current stock price St for some arbitrary t> 0 less than T. (3p) the graph of the delta of the option as a function of current stock price ST8t for a small t > 0. Explain what happens with the "delta" of the option when St 0. (ii) (5p) At time t the stock price is trading at S = $40. An option on that stock has a delta A = 0.4127 and gamma I' = 0.1134. Using this information, find (an approx- imate) new value of delta, At+st, if St+st = $42.75 at time t + St, for a small St > 0. (iii) (5p) What is riskier: a call option or the underlying? Provide all the necessary derivations. (Assume Black-Scholes model and consider a one-day time horizon and compute which has bigger Delta as a fraction of value.) (iv) (5p) Let (, F, P) be a probability space and let Bt, for t 0, be a Brownian motion. Show that Cov(Bs, B) = min(t, s), and that min(t, s) Corr (Bs, Bt) = max(t, s) (Hint: Use the properties in the definition of the Brownian motion.) (v) (5p) Let (2, F,P) be a probability space and let Bt, for t 0, be a Brownian motion. Show that the following process defined via time inversion 0 if t = 0 W = tB ift 0 is also a Brownian motion. (Hint: Show the three properties from one of the definitions of the Brownian motion, use the first result from (iv) above.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


