Question: If possible, please be thorough and simple with the explanation. The Arrhenius Equation 5 1 point The Arrhenius Equation describes the trend exhibited by reaction
If possible, please be thorough and simple with the explanation. 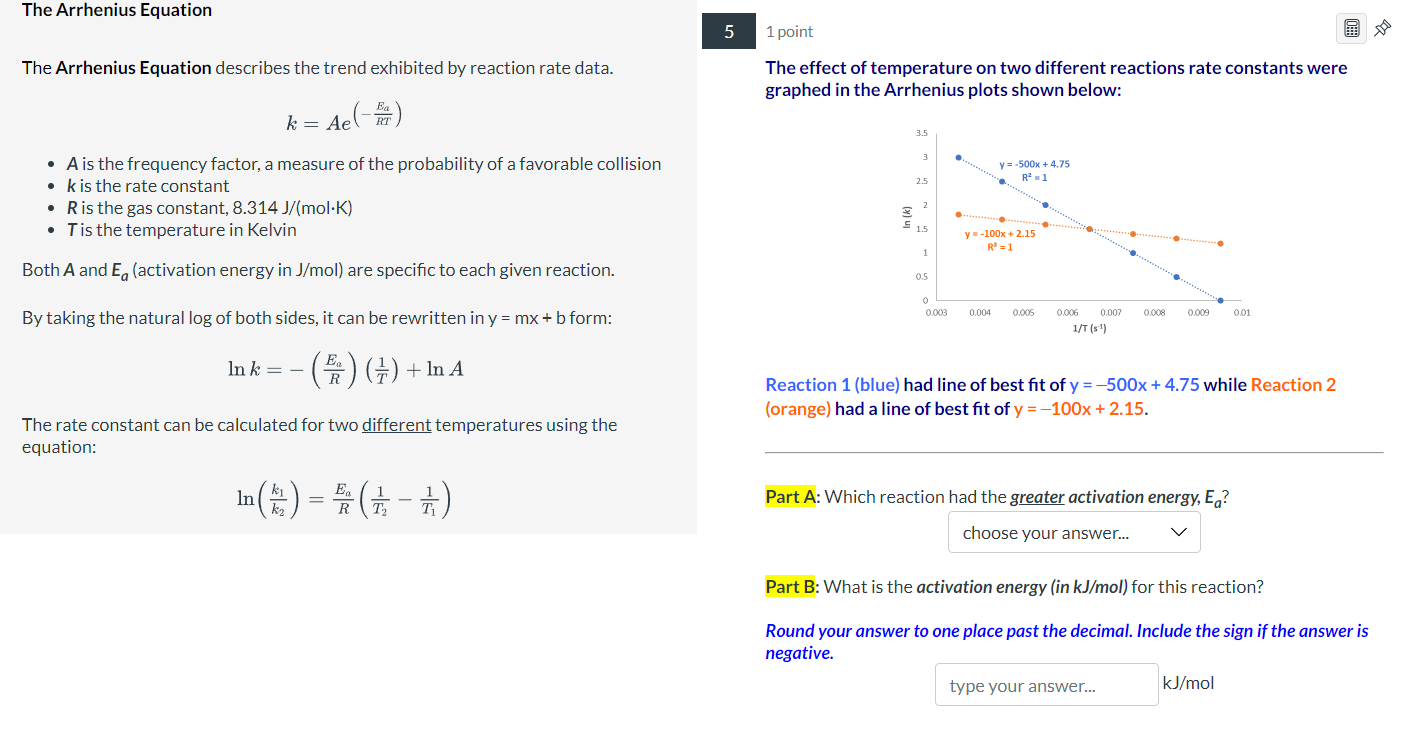
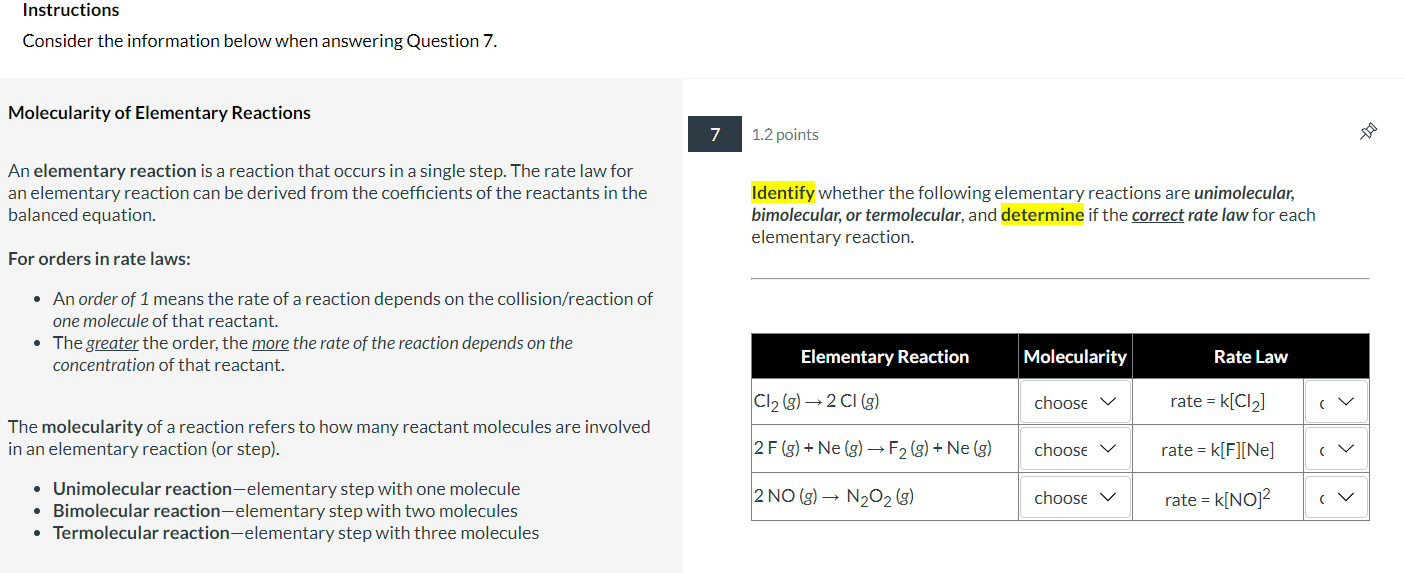
The Arrhenius Equation 5 1 point The Arrhenius Equation describes the trend exhibited by reaction rate data. The effect of temperature on two different reactions rate constants were k=Ae(RTEa) graphed in the Arrhenius plots shown below: - A is the frequency factor, a measure of the probability of a favorable collision - k is the rate constant - R is the gas constant, 8.314J/(molK) - T is the temperature in Kelvin Both A and Ea (activation energy in J/mol ) are specific to each given reaction. By taking the natural log of both sides, it can be rewritten in y=mx+b form: lnk=(REa)(T1)+lnA Reaction 1 (blue) had line of best fit of y=500x+4.75 while Reaction 2 The rate constant can be calculated for two different temperatures using the (orange) had a line of best fit of y=100x+2.15. equation: ln(k2k1)=REa(T21T11) Part A: Which reaction had the greater activation energy, Ea ? Part B: What is the activation energy (in kJ/mol ) for this reaction? Round your answer to one place past the decimal. Include the sign if the answer is negative. kJ/mol Instructions Consider the information below when answering Question 7. Molecularity of Elementary Reactions 7 1.2 points An elementary reaction is a reaction that occurs in a single step. The rate law for an elementary reaction can be derived from the coefficients of the reactants in the Identify whether the following elementary reactions are unimolecular, balanced equation. bimolecular, or termolecular, and determine if the correct rate law for each elementary reaction. For orders in rate laws: - An order of 1 means the rate of a reaction depends on the collision/reaction of one molecule of that reactant. - The greater the order, the more the rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of that reactant. The molecularity of a reaction refers to how many reactant molecules are involved in an elementary reaction (or step). - Unimolecular reaction-elementary step with one molecule - Bimolecular reaction-elementary step with two molecules - Termolecular reaction-elementary step with three molecules
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


