Question: If we consider two independent Poisson processes with rates 1 and 2 and merge them by recording an arrival whenever an arrival occurs in either
If we consider two independent Poisson processes with rates 1 and 2 and "merge" them by recording an arrival whenever an arrival occurs in either process, then:
The merged process is also Poisson with rate 1 + 2.
Any particular arrival in the merged process has probability 1/(1 + 2) of originating from the first (and 2/(1+2) from the second) process independent of all other arrivals and their origins.
Now consider the following situation: Transmitters A and B independently send messages to a single receiver according to a Poisson process with respective rates A and B. All messages occupy single points in time. The number of words in a message, regardless of the source, is a random variable W independent from everything else:
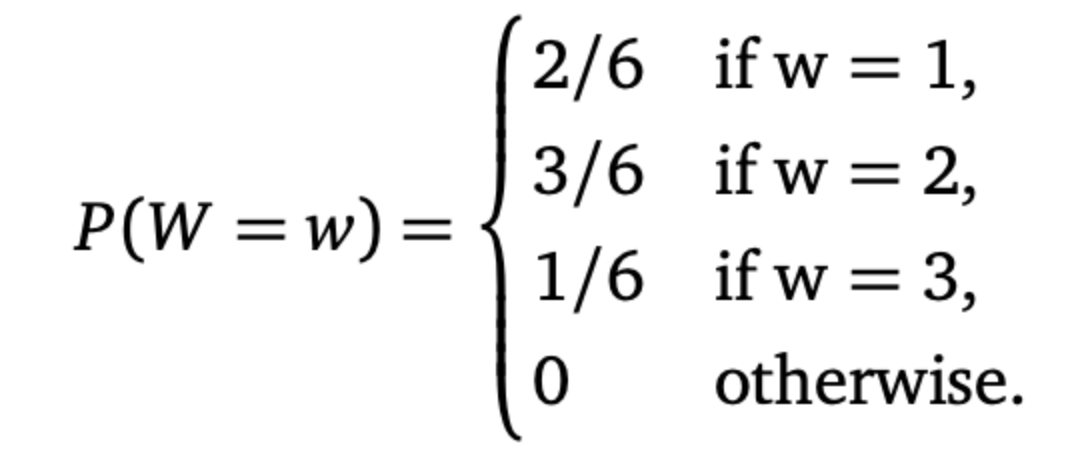
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


