Question: Implement the RK5 in the next code and re-write it. In [1]: from pylab import * #Recuerda que pylab importa numpy como np y pyplot
Implement the RK5 in the next code and re-write it.
![Implement the RK5 in the next code and re-write it. In [1]:](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3dace3c1db_29366f3dacdb0a31.jpg)
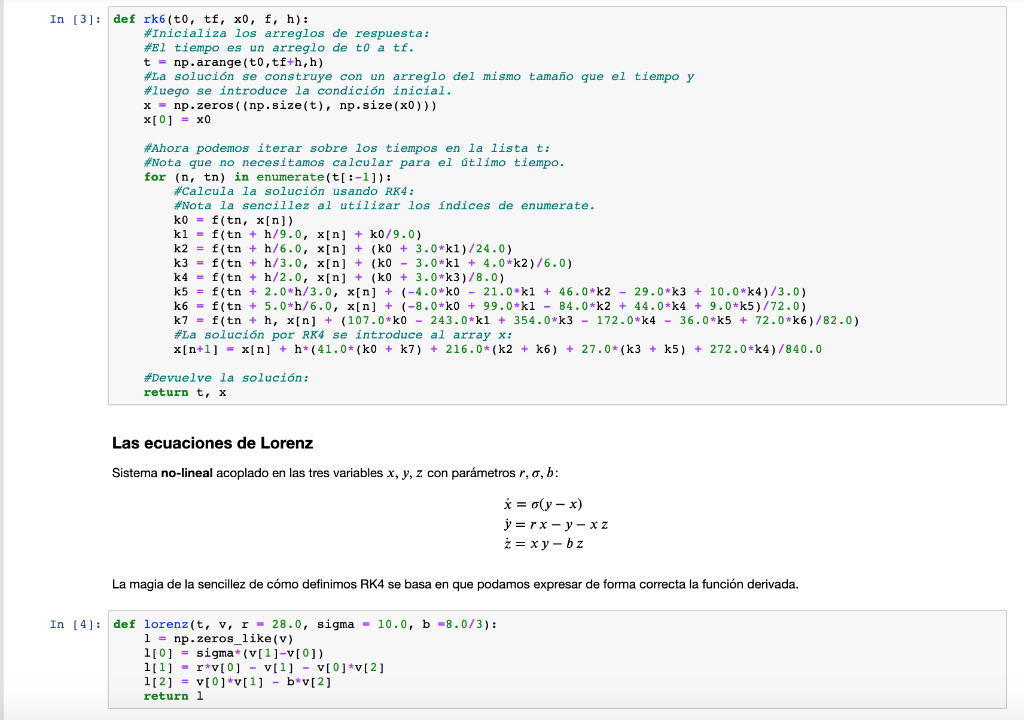
In [1]: from pylab import * #Recuerda que pylab importa numpy como np y pyplot de matplotlib como plt. Smatplotlib inline #Ajustamos algunos parmetros de esttica: from matplotlib import rc plt.rc('font', size=22) El mtodo de Runge-Kutta de orden cuarto: RK4 ste es el famoso mtodo de Runge-Kutta escrito en 11 lneas, podramos reducirlo a 6 en realidad (vale como una tarea reducirlo a seis lneas, dos si se reduce a 5): In [2] : def rk4(to, tf, x0, f, h): #Inicializa los arreglos de respuesta: #El tiempo es un arreglo de to a tf. t = np.arange (t0,tf+h, h) #La solucin se construye con un arreglo del mismo tamao que el tiempo y #luego se introduce la condicin inicial. x = np.zeros((np.size(t), np.size(x0))) x[0] = x0 #Ahora podemos iterar sobre los tiempos en la lista t: #Nota que no necesitamos calcular para el tlimo tiempo. for in, tn) in enumerate(t[:-1]): #calcula la solucin usando RK4: #Nota la sencillez al utilizar los ndices de enumerate. kl = f(tn, x[n]) k2 = f(tn + h/2, x[n] + h*k1/2) k3 = f(tn + h/2, x[n] + h*k2/2) k4 - f(tn h, x[n] + h*k3) #La solucin por RK4 se introduce al array x: x[n+1] - x[n] + h* (kl + 2*k2 + 2*k3 + k4)76 #Devuelve la solucin: return t, X Con base en lo anterior resulta trivial generalizar a un Runge-Kutta de mayor orden buscado en la literatura: In [1]: from pylab import * #Recuerda que pylab importa numpy como np y pyplot de matplotlib como plt. Smatplotlib inline #Ajustamos algunos parmetros de esttica: from matplotlib import rc plt.rc('font', size=22) El mtodo de Runge-Kutta de orden cuarto: RK4 ste es el famoso mtodo de Runge-Kutta escrito en 11 lneas, podramos reducirlo a 6 en realidad (vale como una tarea reducirlo a seis lneas, dos si se reduce a 5): In [2] : def rk4(to, tf, x0, f, h): #Inicializa los arreglos de respuesta: #El tiempo es un arreglo de to a tf. t = np.arange (t0,tf+h, h) #La solucin se construye con un arreglo del mismo tamao que el tiempo y #luego se introduce la condicin inicial. x = np.zeros((np.size(t), np.size(x0))) x[0] = x0 #Ahora podemos iterar sobre los tiempos en la lista t: #Nota que no necesitamos calcular para el tlimo tiempo. for in, tn) in enumerate(t[:-1]): #calcula la solucin usando RK4: #Nota la sencillez al utilizar los ndices de enumerate. kl = f(tn, x[n]) k2 = f(tn + h/2, x[n] + h*k1/2) k3 = f(tn + h/2, x[n] + h*k2/2) k4 - f(tn h, x[n] + h*k3) #La solucin por RK4 se introduce al array x: x[n+1] - x[n] + h* (kl + 2*k2 + 2*k3 + k4)76 #Devuelve la solucin: return t, X Con base en lo anterior resulta trivial generalizar a un Runge-Kutta de mayor orden buscado en la literatura
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


