Question: In the Molecular Dynamics program as the below by Python, replace the velocity Verlet algo- rithm by the so-called Euler algorithm in which the positions
In the Molecular Dynamics program as the below by Python, replace the velocity Verlet algo- rithm by the so-called Euler algorithm in which the positions and velocities are updated according to the following rule:
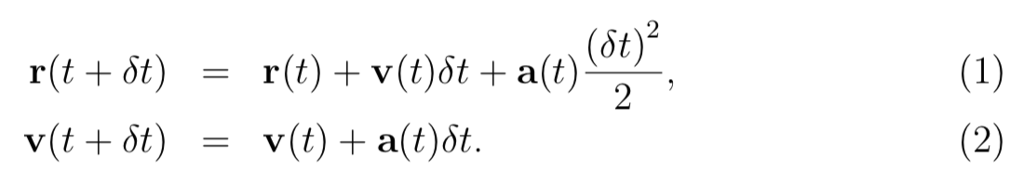
Note that the difference between these algorithms seems quite small. Then, run two simulations, one using the original program and the other using the Euler algorithm program. Compare the dependence of the systemss total energy on time, as calculated by these two programs. Which algorithm would you rather use in your reserach?
For each simulation you should plot the dependence of the kinetic, potential and total energy (all per particle) on time. You should also turn in the relevant portion of the code, i.e. the main loop that updates the positions, velocities and forces.
import numpy as np import math
def ff(dx, dy, i): d2 = dx**2 + dy**2 if d2 > cut2: return 0. else: di6 = 1./d2**3 fff = 4.*(12.*di6**2/d2-6.*di6/d2) if i == 0: return fff*dx if i == 1: return fff*dy def distance(i,j,k): if k == 0: distancex = position[i,0]-position[j,0] distancex -= boxL*round(distancex/boxL) return distancex if k == 1: distancey = position[i,1]-position[j,1] distancey -= boxL*round(distancey/boxL) return distancey def potential(d2): if d2 > cut2: return 0. else: di6 = 1./d2**3 return 4.*(di6**2-di6)-shift def distancesq(i,j): distancex = position[i,0]-position[j,0] distancex -= boxL*round(distancex/boxL) distancey = position[i,1]-position[j,1] distancey -= boxL*round(distancey/boxL) return distancex**2+distancey**2
def gr(hist): for i in range(N): for j in range(i): bin = round(math.sqrt(distancesq(i,j))/dr) if( bin
cut = 2.5 cut2 = cut**2 shift = 4.*(1./cut2**6-1./cut2**3)
dr = 0.05 maxbin = int(boxL/(2.*dr))
delta = 0.001 delta2 = delta/2. deltasq2 = delta**2/2.
# sqrt(N) needs to be an integer! sN = int(math.sqrt(N)) boxL1 = boxL/sN
position = np.zeros((N,2),dtype=float) velocity = np.zeros((N,2),dtype=float) force = np.zeros((N,2),dtype=float) nforce = np.zeros((N,2),dtype=float) hist = np.zeros(maxbin,dtype=float)
for i in range(N): position[i,0] = float(i%sN)*boxL1 position[i,1] = float(i//sN)*boxL1 velocity[i,0] = np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=math.sqrt(T)) velocity[i,1] = np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=math.sqrt(T))
energy = 0. energyk = 0.0 for i in range(N): energyk += (velocity[i,0]**2+velocity[i,1]**2)/2. for j in range(i): energy += potential(distancesq(i,j))
energy=energyk+energy
for i in range(N): for j in range(i): dx = distance(i,j,0) dy = distance(i,j,1) force[i,0] += ff(dx,dy,0) force[j,0] -= ff(dx,dy,0) force[i,1] += ff(dx,dy,1) force[j,1] -= ff(dx,dy,1) energykave = 0. energyave = 0.
nIter=2000 log = open('lj_md_log.dat','w')
for itt in range(0,nIter):
for i in range(N): position[i,0] += velocity[i,0]*delta + force[i,0]*deltasq2 position[i,1] += velocity[i,1]*delta + force[i,1]*deltasq2
for i in range(N): nforce[i,0] = 0. nforce[i,1] = 0.
for i in range(N): for j in range(i): dx = distance(i,j,0) dy = distance(i,j,1) nforce[i,0] += ff(dx,dy,0) nforce[j,0] -= ff(dx,dy,0) nforce[i,1] += ff(dx,dy,1) nforce[j,1] -= ff(dx,dy,1)
for i in range(N): velocity[i,0] += (force[i,0]+nforce[i,0])*delta2 velocity[i,1] += (force[i,1]+nforce[i,1])*delta2 force[i,0] = nforce[i,0] force[i,1] = nforce[i,1] energyk = 0. energy = 0. for i in range(N): energyk += (velocity[i,0]**2+velocity[i,1]**2)/2. for j in range(i): energy += potential(distancesq(i,j)) energykave += energyk energy = energyk+energy energyave += energy if itt%2 == 0: log.write("%10.5f %10.5f %10.5f %10.5f %10.5f " % (float(itt)*delta, energyk/float(N),energykave/float(N*(itt+1)),energy/float(N),energyave/float(N*(itt+1)))) gr(hist) log.close() xy = open('lj_md_xy.dat','w') for i in range(N): x = position[i,0] y = position[i,1] xb = x - boxL*round(x/boxL) yb = y - boxL*round(y/boxL) xy.write("%10d %10.5f %10.5f %10.5f %10.5f " % (i,x,y,xb,yb)) xy.close() grout = open('lj_md_gr.dat','w') const = (dr**2*math.pi*float(N**2)/boxL**2)*float(nIter)/2. for i in range(maxbin): rr = (float(i+1)+.5)**2-(float(i+1)-.5)**2 g = hist[i]/(rr*const) grout.write("%10.5f %10.5f " % (float(i+1)*dr,g)) grout.close()
(5t)2 y(t + ) v(t) + a(t)St. = (5t)2 y(t + ) v(t) + a(t)St. =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


