Question: Let A be an integer array and n is the number of elements in the array. Letj, k and m are arbitrary indexes of
![BUILD-TREE (A, n) for i = FLOOR[n/2] downto 1 do FIX-TREE (A, i, n) FIX-TREE(A, i, n) j = LEFT(i) k =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/questions/2023/11/655a3f0ba426f_1700503181018.jpg)
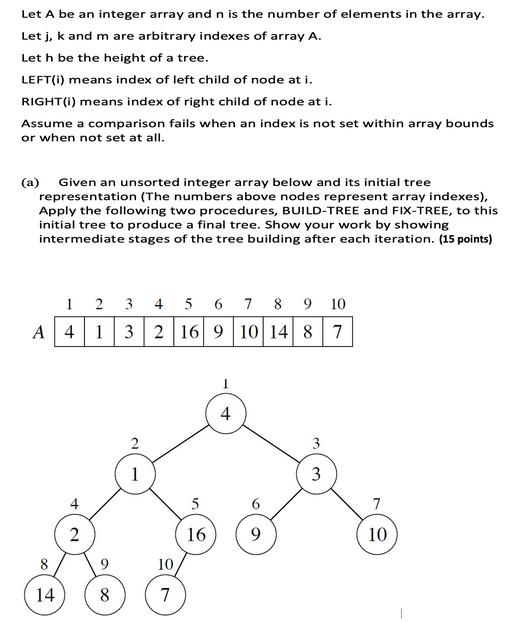
Let A be an integer array and n is the number of elements in the array. Letj, k and m are arbitrary indexes of array A. Let h be the height of a tree. LEFT(i) means index of left child of node at i. RIGHT (i) means index of right child of node at i. Assume a comparison fails when an index is not set within array bounds or when not set at all. (a) Given an unsorted integer array below and its initial tree representation (The numbers above nodes represent array indexes), Apply the following two procedures, BUILD-TREE and FIX-TREE, to this initial tree to produce a final tree. Show your work by showing intermediate stages of the tree building after each iteration. (15 points) A 14 1 4 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 3 2 16 9 10 14 8 7 8 1 10 7 5 16 I 4 9 3 7 10 BUILD-TREE (A, n) for i = FLOOR[n/2] downto 1 do FIX-TREE (A, i, n) FIX-TREE(A, i, n) j=LEFT(i) k = RIGHT(i) if j n and A[j] > A[i] then m = j else m = i if k n and A[k] > A[m] then m = k if m != i then SWAP (A[i], A[m]) FIX-TREE(A, m, n) (b) What is the time comlexity of BUILD-TREE method? (2 points) (c) What is the time comlexity of FIX-TREE method? (3 points)
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Initial tree representation 1 2 3 4 5 16 6 9 7 10 8 14 After apply... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


