Question: Linear Trend Conceptual Overview: Explore how a linear trend across time provides a forecast for future data points. For two or more time series points,

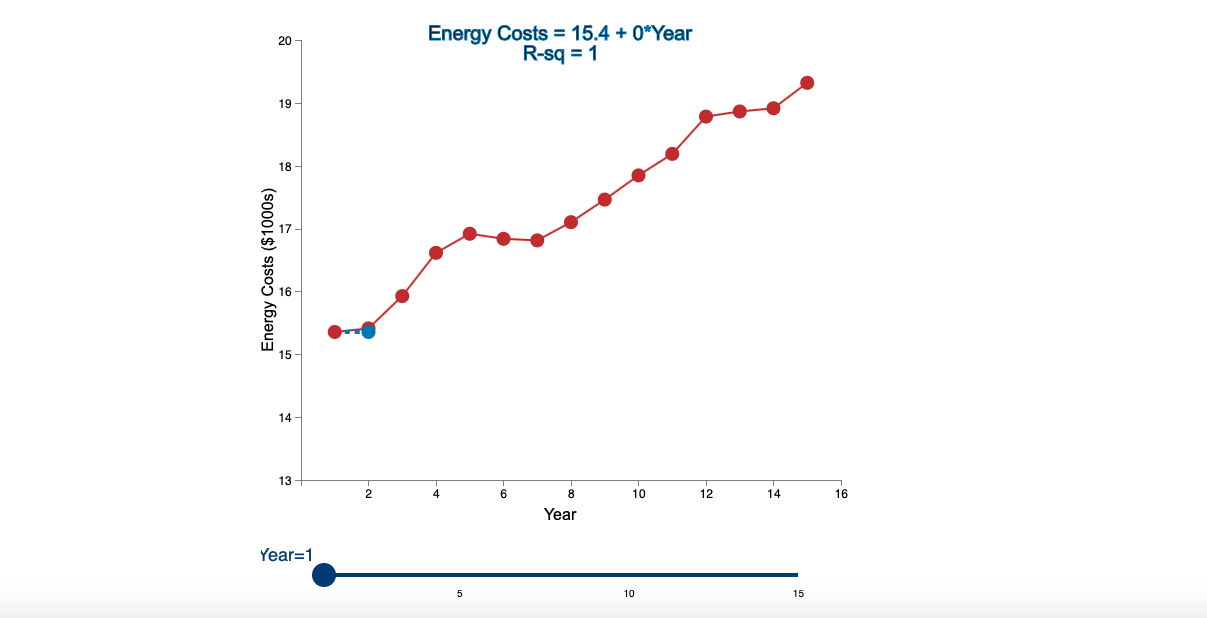
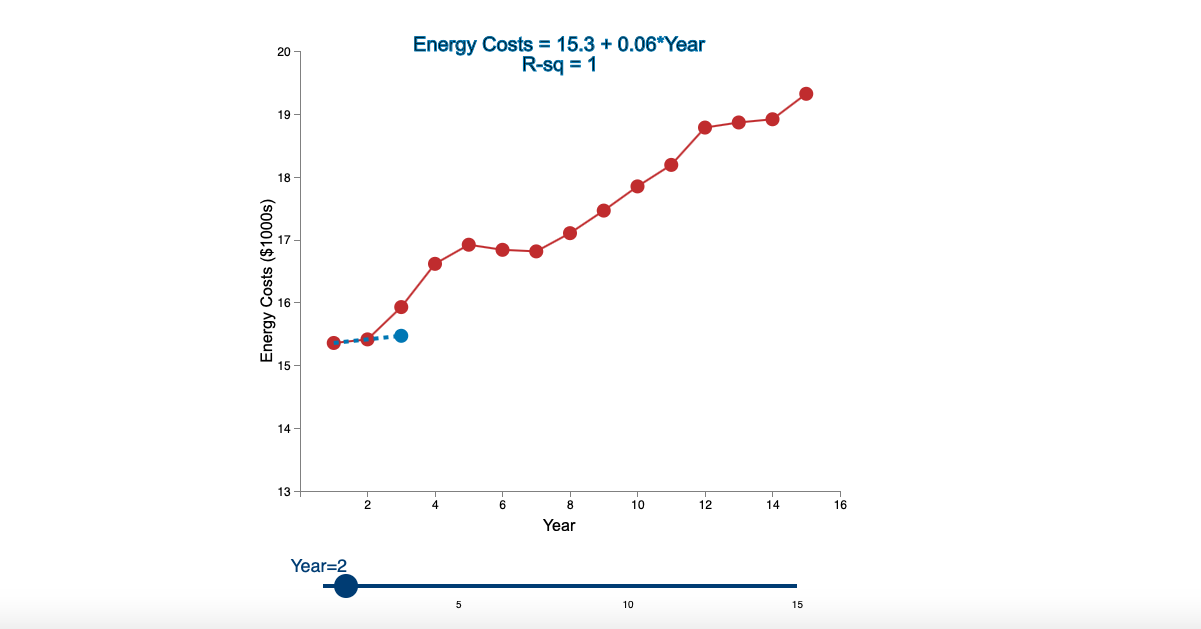
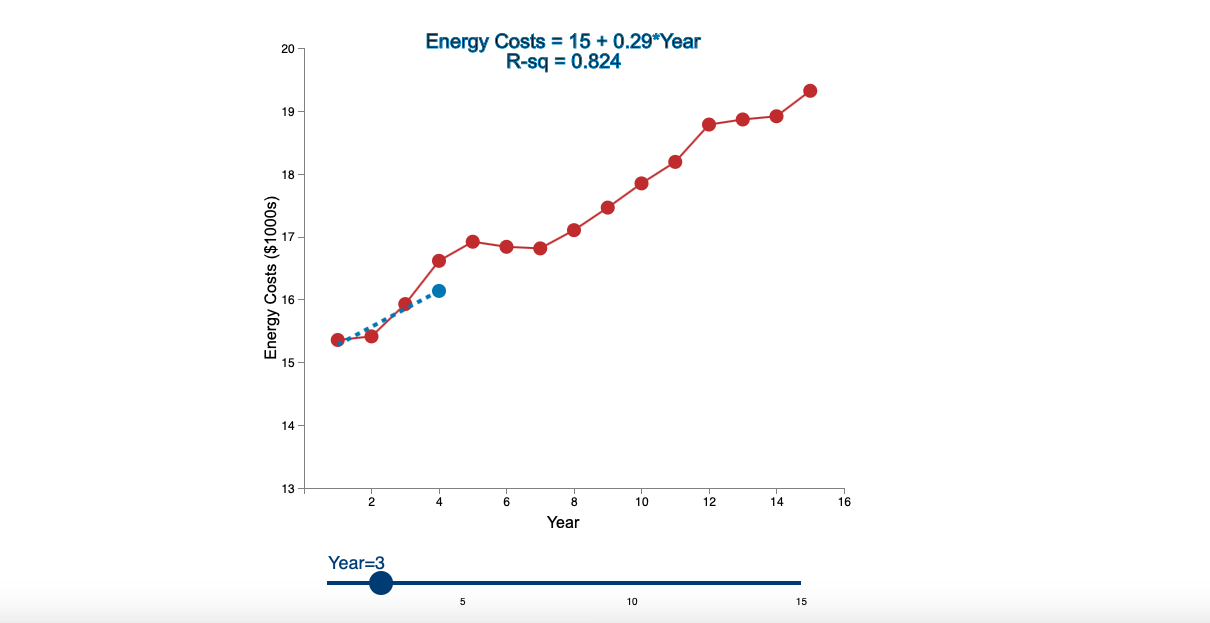
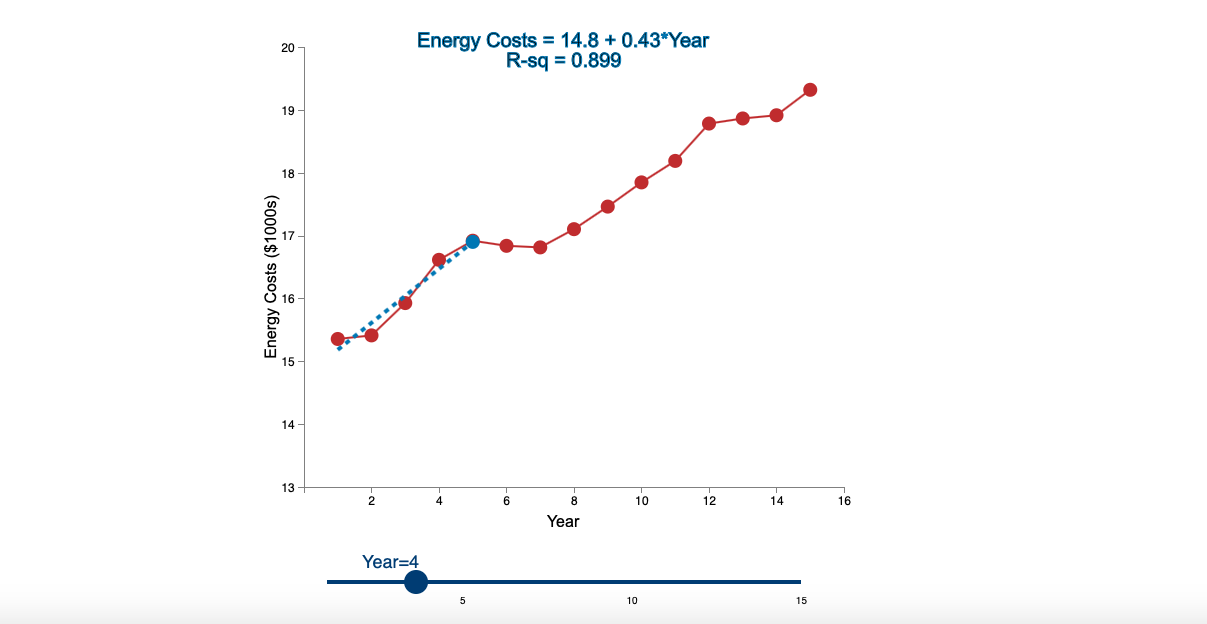
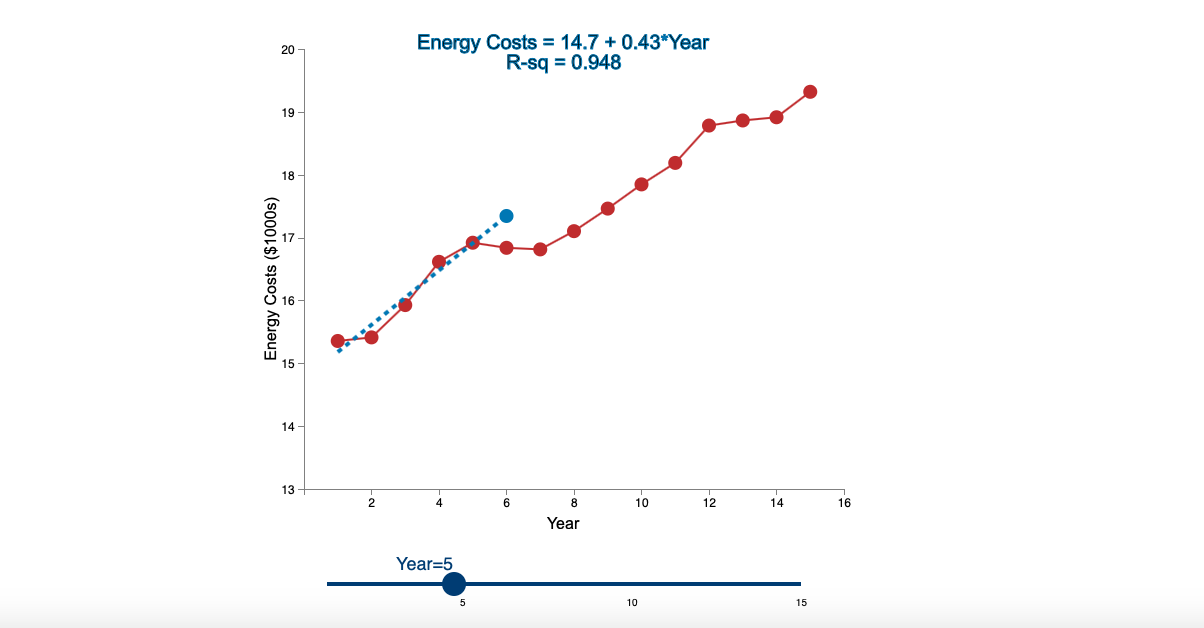
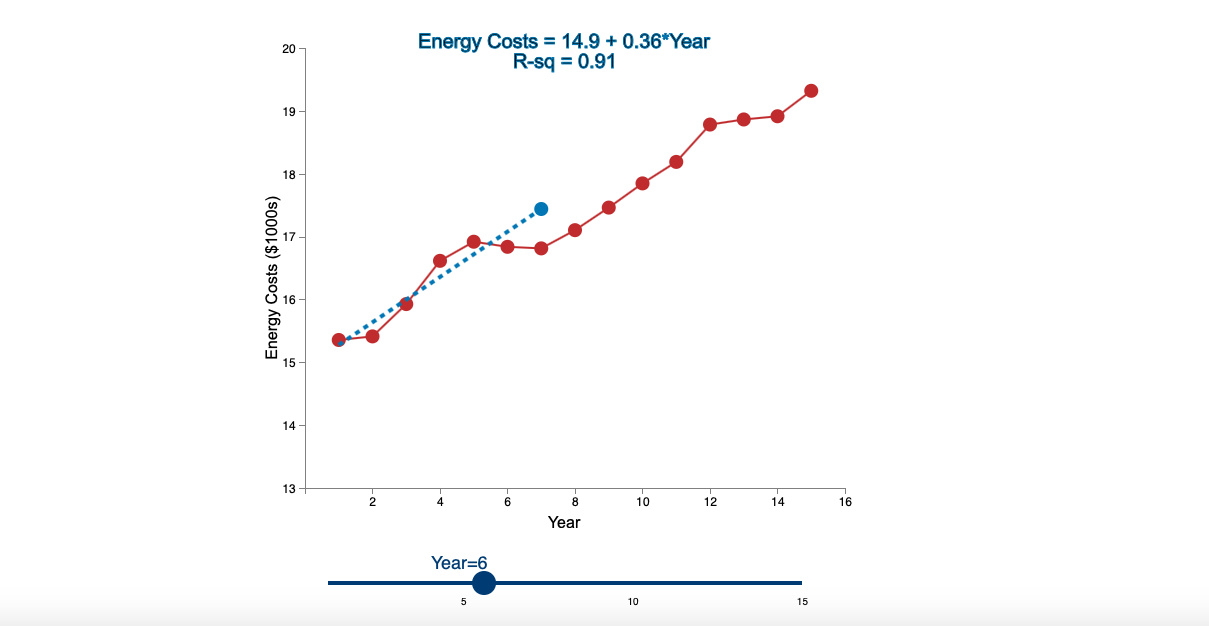
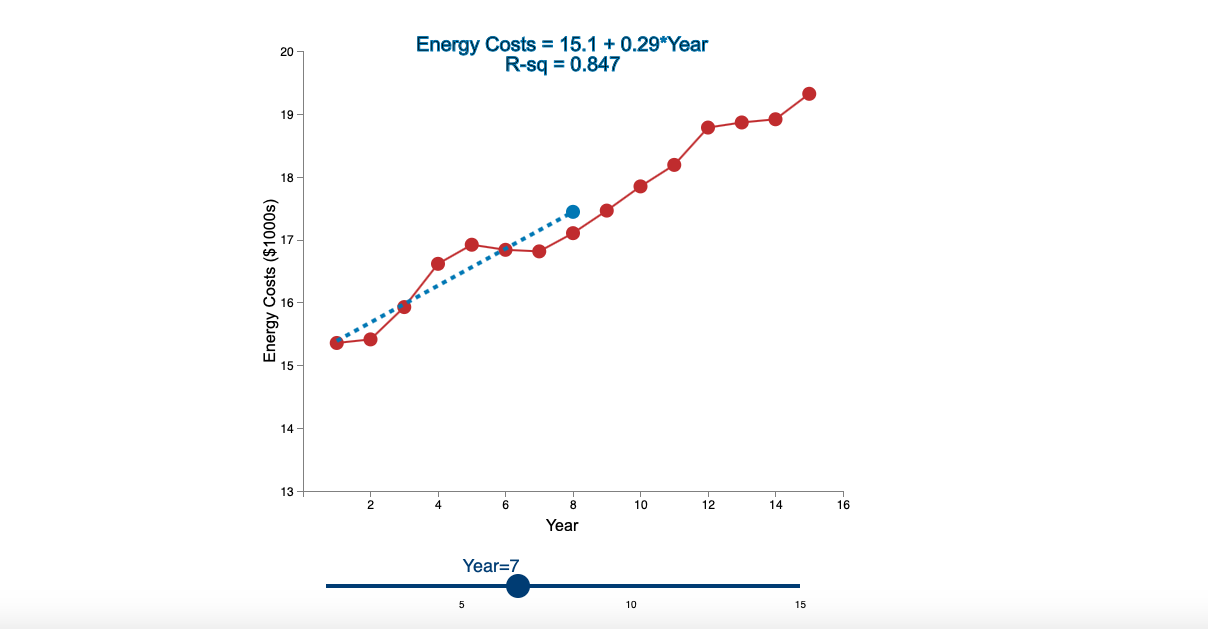
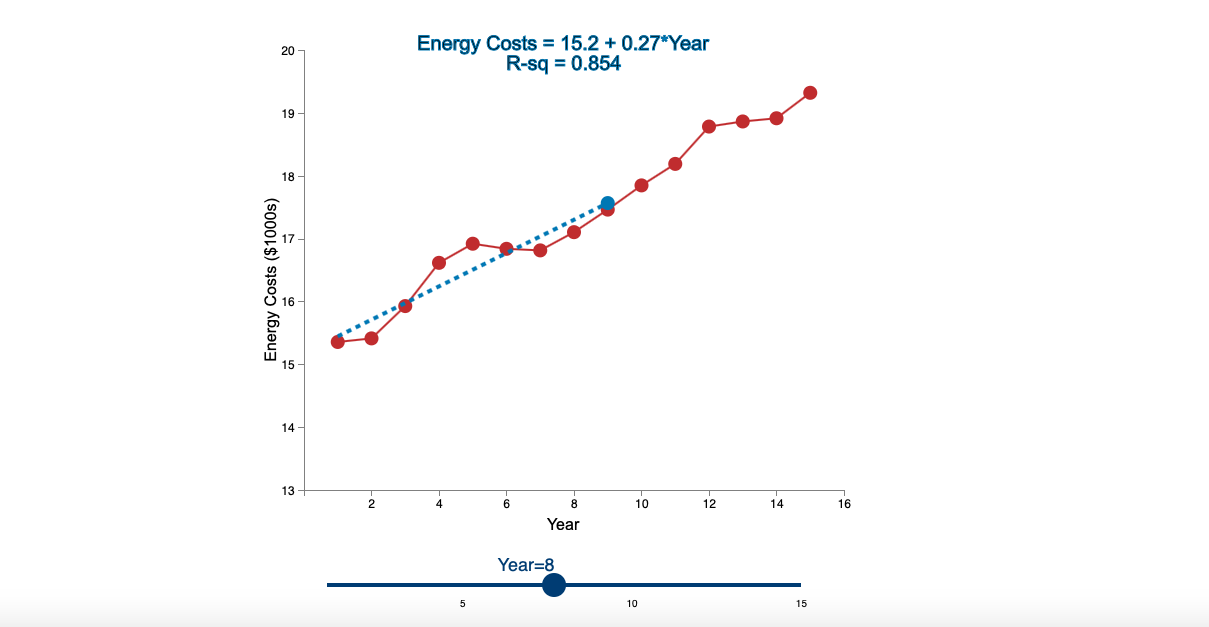
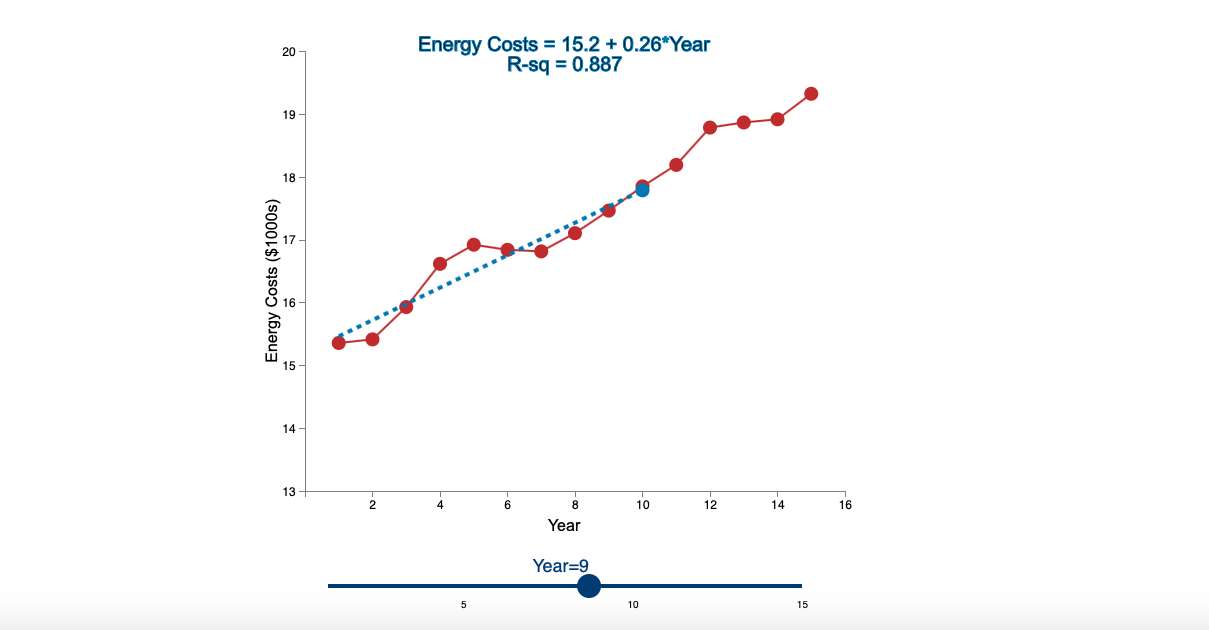
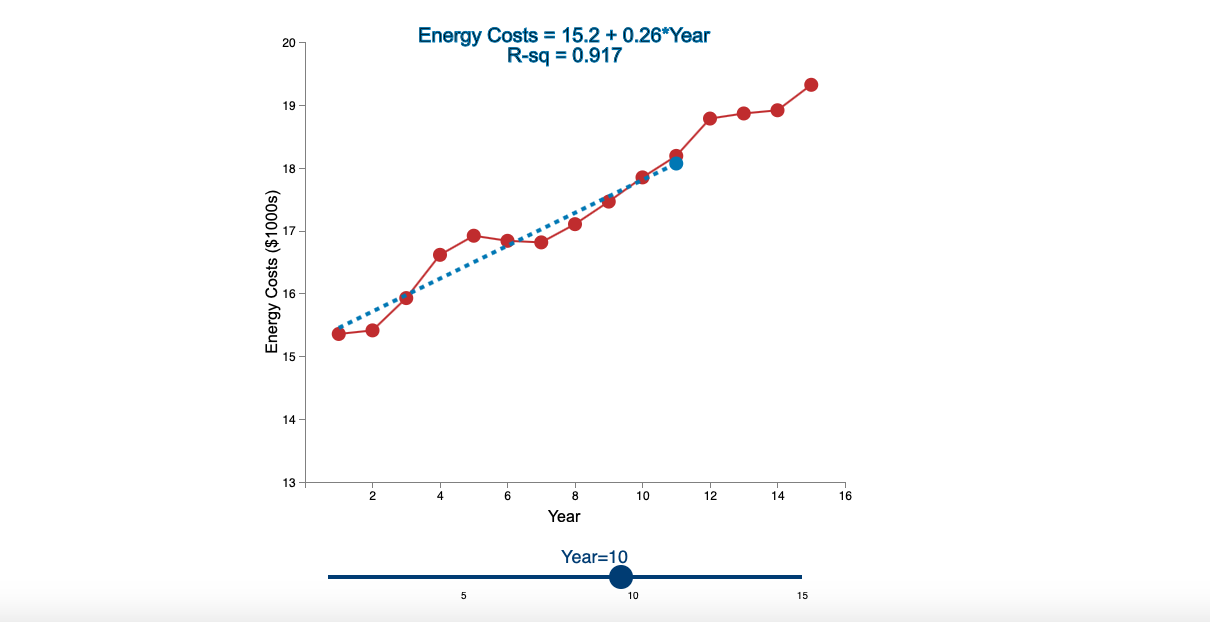
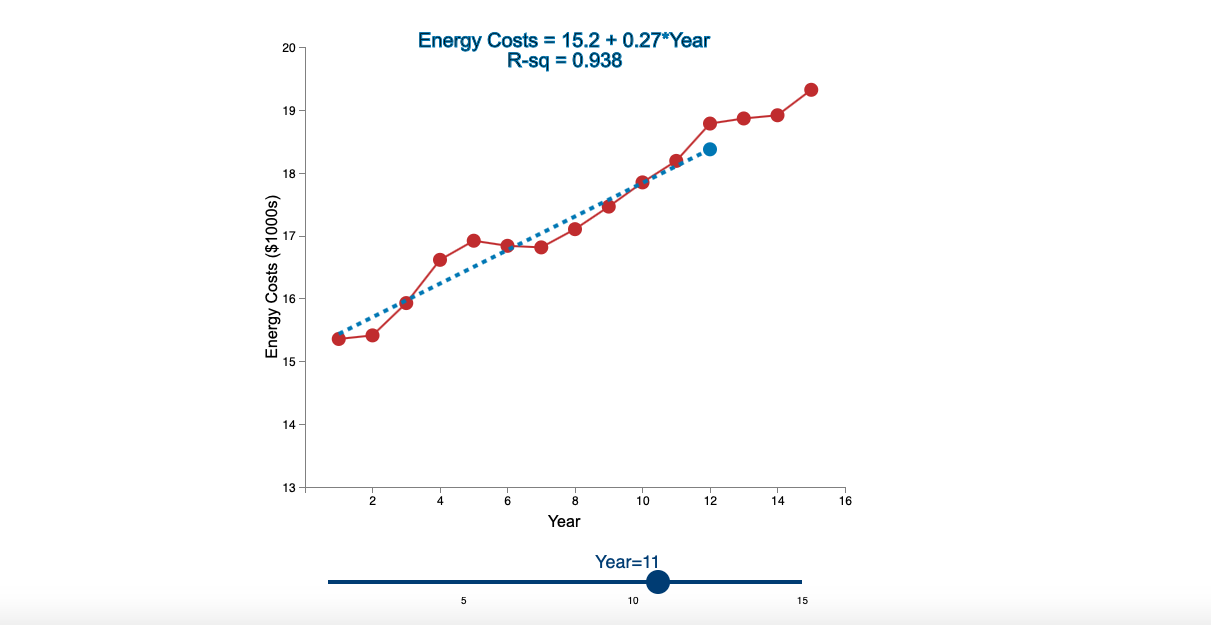
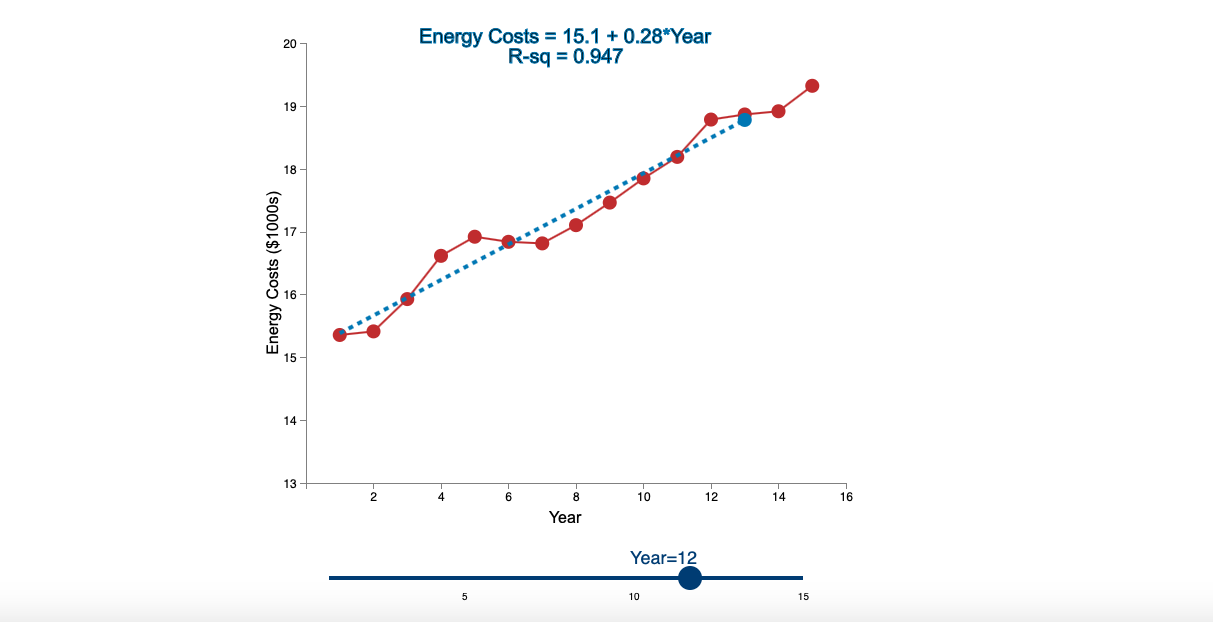
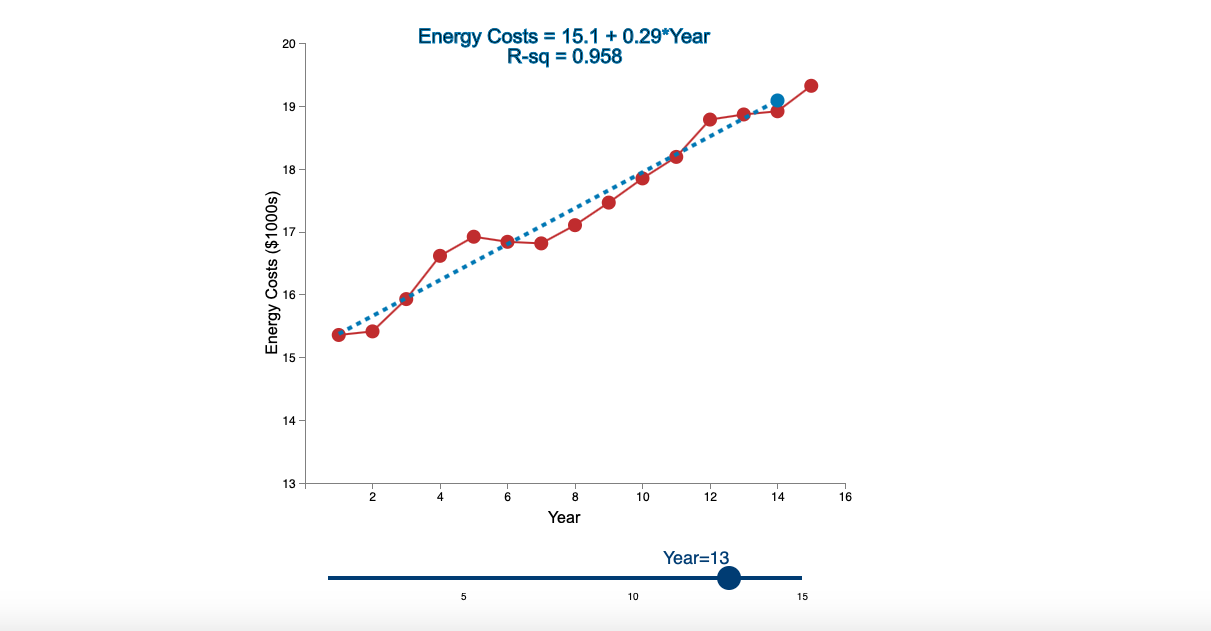
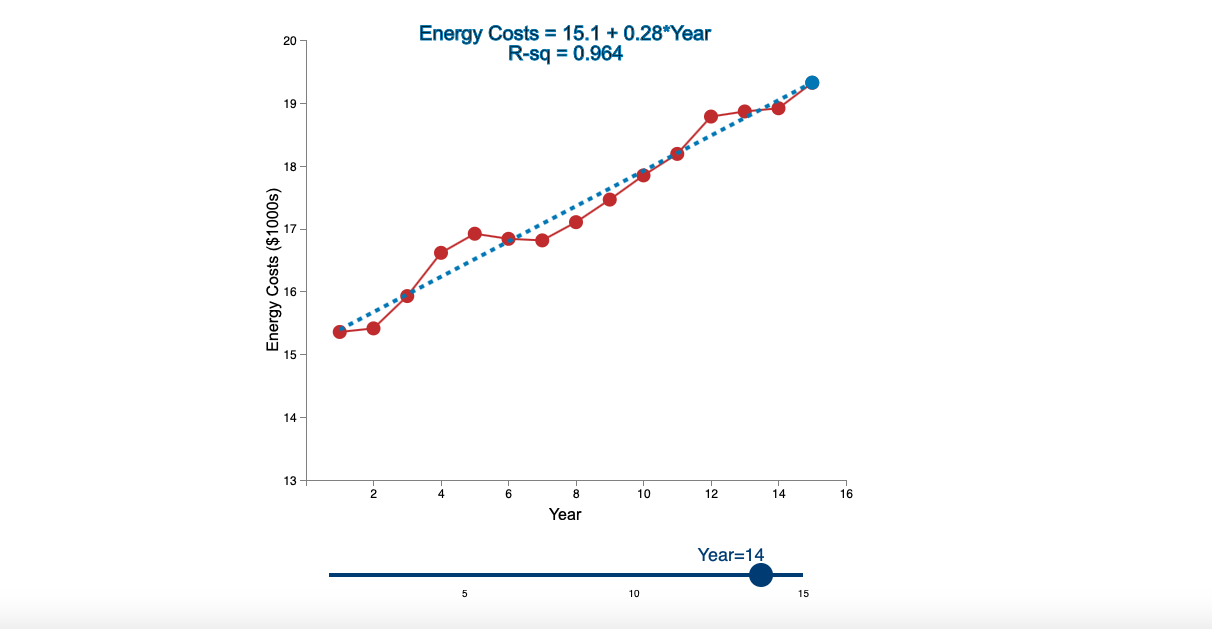
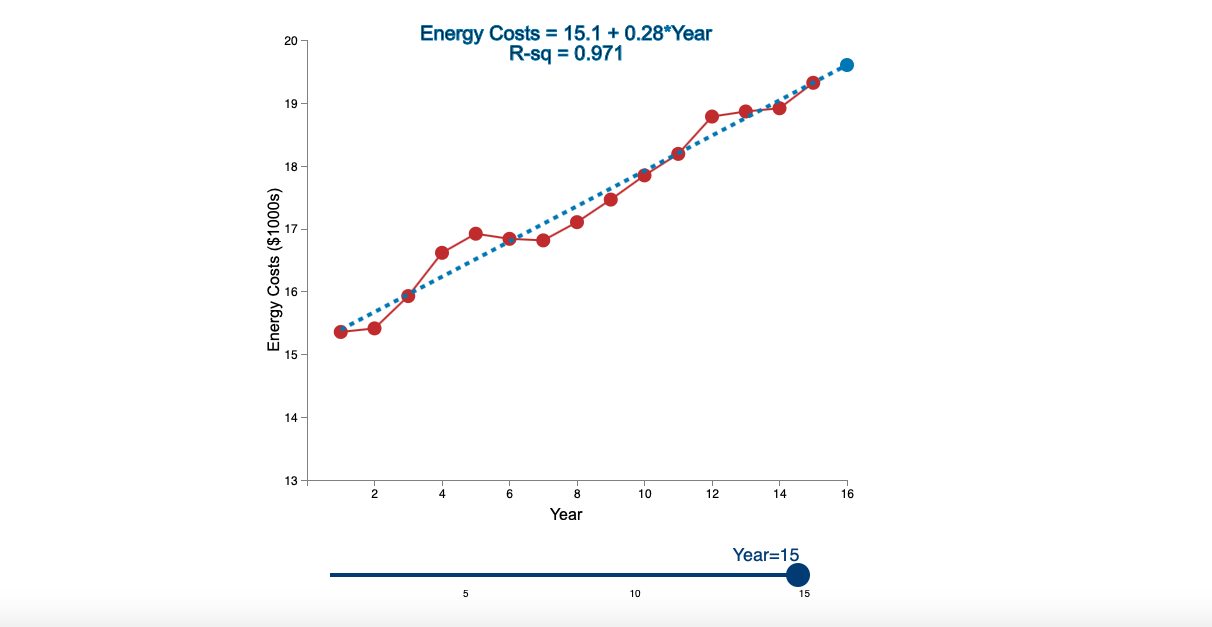

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


