Question: M An a An = Gu a An a An Ho M Ho 42 Bp Pe * Mi|+ Su|+ Int FO EH EH O 22
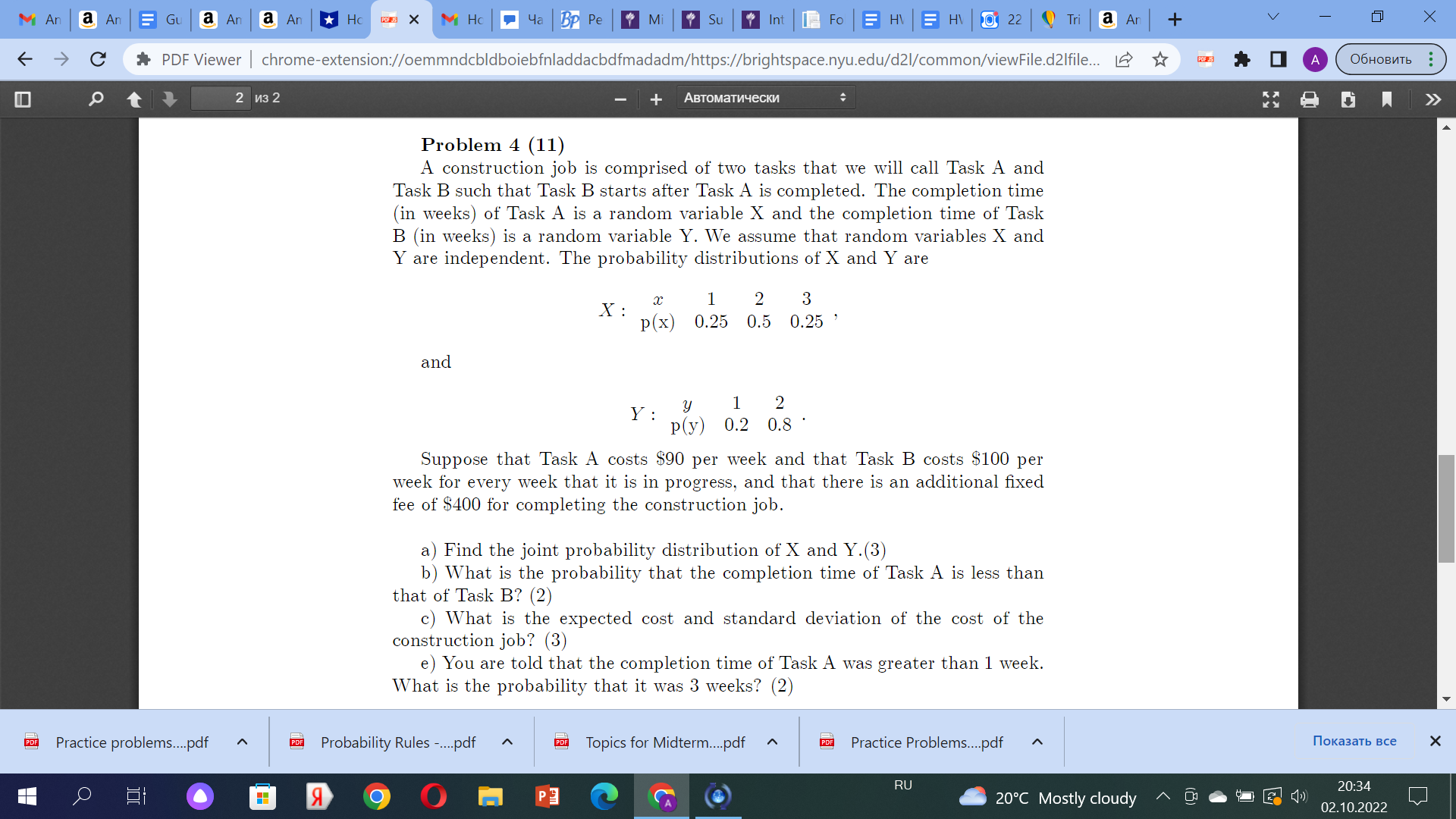

M An a An = Gu a An a An Ho M Ho 42 Bp Pe * Mi|+ Su|+ Int FO EH EH O 22 Q Tri a An + V X C PDF Viewer | chrome-extension://oemmndcbudboiebfnladdacdfmadadm/https://brightspace.nyu.edu/d21/common/viewFile.d2lfile... A 06HOBUTb t 1 N3 2 + ABTOMaTN4ecKN Problem 1 (6) Consider an alarm system for detecting intruders. It there is an intruder, the detection system sounds an alarm with probability 0.95. If there is no intruder, the detection system sounds an alarm with probability 0.1. Assume that the probability of an intruder is 0.4. If the detection system sounds an alarm, what is the probability that an intruder is detected? Problem 2 Nondestructive Evaluation (6) MBS Ex 3.90, page 177. Problem 3 (7) Here is the data set X: 103, 98, 102, 101, 102.5, 110, 101.5.100, 108, 98. The mean and standard deviation of this dataset are = 102.4 S = 3.9. a) Suppose we construct another data set, Y, by multiplying every observa- tion in X by 5. That is yi = 5xi. What is the mean and standard deviation of dataset Y? (1) b) Sunnose we construct another data set. I by adding 2 to every observa- PDF Practice problems...pdf PDF Probability Rules -...pdf PDF Topics for Midterm...pdf ~ PDF Practice Problems..pdf nokasatb Bce X RU LO B O 20:32 P3 20 C Mostly cloudy 02. 10.2022M An a An = Gu a An a An Ho M Ho 42 Bp Pe|+ Mi Su|+ Int FO EH EH 0 22 Q Tri a An + V X C PDF Viewer | chrome-extension://oemmndcbudboiebfnladdacdfmadadm/https://brightspace.nyu.edu/d21/common/viewFile.d2lfile... A 06HOBUTb t 1 N3 2 + ABTOMaTN4ecKN What is the mean and standard deviation of dataset Y? (1) b) Suppose we construct another data set, U, by adding 2 to every observa- tion in X. That is wi = xi + 2 What is the mean and standard deviation of dataset U? (1) c) Suppose we construct yet another dataset, W, by first multiplying every observation in X by 5 and then adding 2. That is, wi = 5x; + 2. What is the mean and standard deviation of dataset W? (2) d) We obtain the final data set, Z, by subtracting from every observation in X, the mean a and dividing the result by s. That is, = = = (xi - x) = Exi-1x. What is the mean and standard deviation of dataset Z? (3) PDF Practice problems...pdf PDF Probability Rules -....pdf PDF Topics for Midterm...pdf PDF Practice Problems...pdf nokasatb Bce X RU LO B O Ed CA 20:33 20C Mostly cloudy 02. 10.2022M An a An = Gu a An a An Ho M Ho 42 Bp Pe| Mi| Su| Int FO EH EH 22 Q Tri a An + V X C PDF Viewer | chrome-extension://oemmndcbudboiebfnladdacdfmadadm/https://brightspace.nyu.edu/d21/common/viewFile.d2lfile... A 06HOBUTb t 2 3 2 + ABTOMaTN4ecKN Problem 4 (11) A construction job is comprised of two tasks that we will call Task A and Task B such that Task B starts after Task A is completed. The completion time (in weeks) of Task A is a random variable X and the completion time of Task B (in weeks) is a random variable Y. We assume that random variables X and Y are independent. The probability distributions of X and Y are X : 1 2 3 p(x) 0.25 0.5 0.25 ' and Y : y 1 2 p(y) 0.2 0.8 Suppose that Task A costs $90 per week and that Task B costs $100 per week for every week that it is in progress, and that there is an additional fixed fee of $400 for completing the construction job. a) Find the joint probability distribution of X and Y.(3) b) What is the probability that the completion time of Task A is less than that of Task B? (2) c) What is the expected cost and standard deviation of the cost of the construction job? (3) e) You are told that the completion time of Task A was greater than 1 week. What is the probability that it was 3 weeks? (2) PDF Practice problems...pdf PDF Probability Rules -...pdf PDF Topics for Midterm..pdf PDF Practice Problems..pdf nokasatb Bce X RU 20:34 LO B O Ed CA 20 C Mostly cloudy 02. 10.2022depth of the rock quarry. Should this area be mined? 3.90 NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION. Nondestructive evaluation (NDE) describes methods that quantitatively characterize materials, tissues, and structures by noninvasive means, such as X-ray computed tomography, ultrasonics, and acoustic emission. Recently, NDE was used to detect defects in steel castings (JOM, May 2005). Assume that the probability that NDE detects a "hit" (i.e., predicts a defect in a steel casting) when, in fact, a defect exists is .97. (This is often called the probability of detection. ) Also assume that the probability that NDE detects a hit when, in fact, no defect exists is .005. (This is called the probability of a false call.) Past experience has shown a defect occurs once in every 100 steel castings. If NDE detects a hit for a particular steel casting, what is the probability that an actual defect exists
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


