Question: Major Elements of a C++ Variable Watch the video Major Elements of a C++ Variable (3:28) and complete the following statements: 1. When you declare

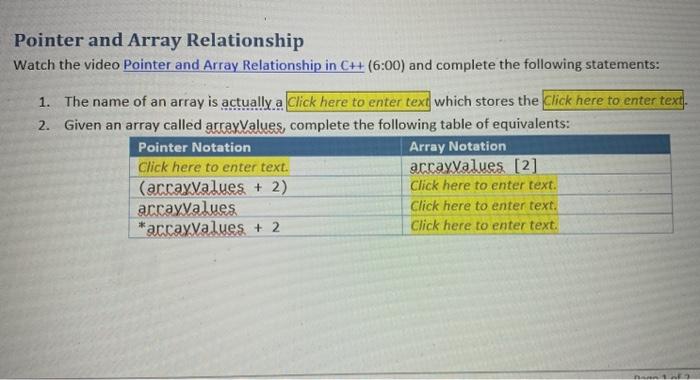
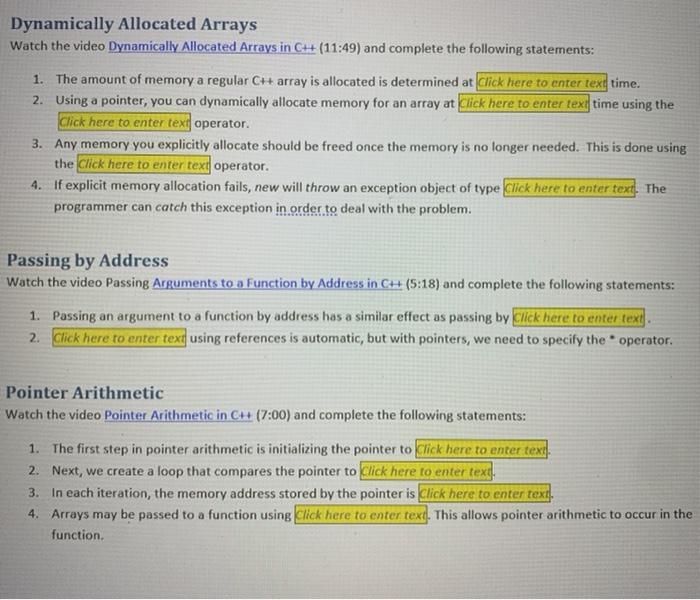
Major Elements of a C++ Variable Watch the video Major Elements of a C++ Variable (3:28) and complete the following statements: 1. When you declare a variable, it reserves a specific amount of memory as determined by the variable's Click here to enter text 2. The memory address of a variable is the address of Click here to enter text of the block of memory reserved for the variable. 3. To determine the amount of memory used by a variable, use the Click here to enter text operator. 4. To determine the memory address of variable, use the click here to enter text operator. Pointer Basics Watch the videos, Basic Pointers in C++ (5:10) and Pointer Variables in C++ (2:44) and complete the following statements: 1. A pointer is a variable which stores Click here to enter text. 2. To declare a pointer, use the type followed by click here to enter text. 3. The process of accessing the value stored at the memory address a pointer points to is called Click here to enter texe. 4. Using an uninitialized pointer will often cause unexpected problems, like click here to enter text for example. S. You can change the address the pointer stores: TRUE or FALSE: Click here to enter tex!? Pointer and Array Relationship Watch the video Pointer and Array Relationship in C++ (6:00) and complete the following statements: 1. The name of an array is actually a click here to enter text which stores the Click here to enter text. 2. Given an array called arrayValues, complete the following table of equivalents: Pointer and Array Relationship Watch the video Pointer and Array Relationship in CH (6:00) and complete the following statements: 1. The name of an array is actually a Click here to enter text which stores the Click here to enter text. 2. Given an array called arrayValues, complete the following table of equivalents: Pointer Notation Array Notation Click here to enter text. arcayvalues. [2] (arcaxvalues + 2) Click here to enter text. arcayvalues Click here to enter text. *arcayvalues. + 2 Click here to enter text. Dynamically Allocated Arrays Watch the video Dynamically Allocated Arrays in CH (11:49) and complete the following statements: 1. The amount of memory a regular C++ array is allocated is determined at Click here to enter textime. 2. Using a pointer, you can dynamically allocate memory for an array at Click here to enter text time using the Click here to enter text operator. 3. Any memory you explicitly allocate should be freed once the memory is no longer needed. This is done using the click here to enter text operator. 4. If explicit memory allocation fails, new will throw an exception object of type Click here to enter text. The programmer can catch this exception in order to deal with the problem. Passing by Address Watch the video Passing Arguments to a Function by Address in CH (5:18) and complete the following statements: 1. Passing an argument to a function by address has a similar effect as passing by click here to enter text. 2. Click here to enter text using references is automatic, but with pointers, we need to specify the operator. Pointer Arithmetic Watch the video Pointer Arithmetic in C++ (7:00) and complete the following statements: 1. The first step in pointer arithmetic is initializing the pointer to Click here to enter texn 2. Next, we create a loop that compares the pointer to Click here to enter text! 3. In each iteration, the memory address stored by the pointer is Click here to enter text. 4. Arrays may be passed to a function using Click here to enter text. This allows pointer arithmetic to occur in the function
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


