Question: Markov Chain There are 2 cables, A and B, transmitting signals between Sydney and Melbourne. The waiting times until cable A or cable B breaks
Markov Chain
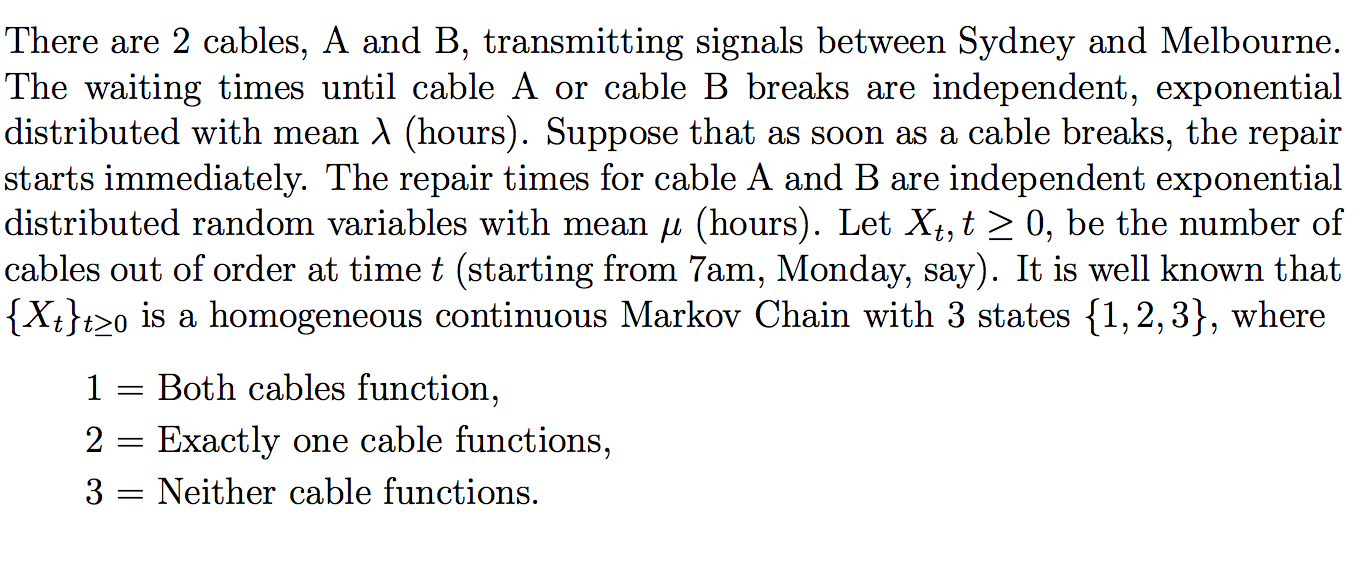
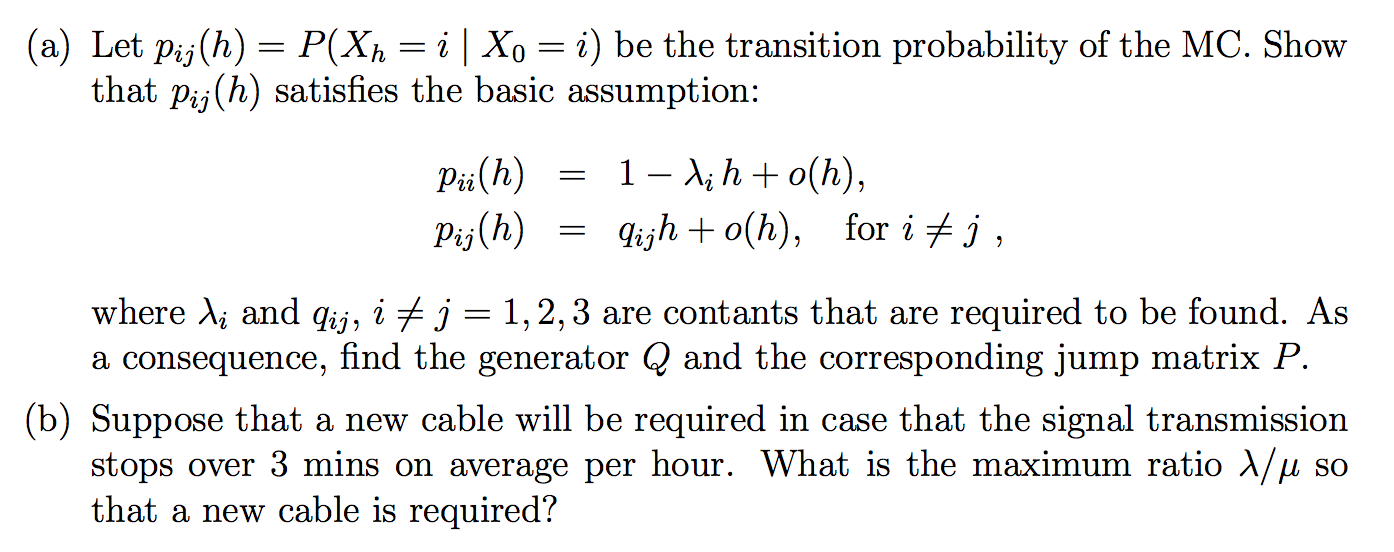
There are 2 cables, A and B, transmitting signals between Sydney and Melbourne. The waiting times until cable A or cable B breaks are independent, exponential distributed with mean A (hours). Suppose that as soon as a cable breaks, the repair starts immediately. The repair times for cable A and B are independent exponential distributed random variables with mean u (hours). Let Xht 2 0, be the number of cables out of order at time 75 (starting from 7am, Monday, say). It is well known that {X t}t20 is a homogeneous continuous Markov Chain with 3 states {1, 2, 3}, where 1 2 Both cables function, 2 = Exactly one cable functions, 3 2 Neither cable functions. (a) Let pij(h) = P(Xh = i | Xo = 2) be the transition probability of the MC. Show that pij(h) satisfies the basic assumption: Pii(h) = 1 - xih + o(h), Pij(h) = qijh to(h), for if j , where li and qij, i * j = 1, 2,3 are contants that are required to be found. As a consequence, find the generator Q and the corresponding jump matrix P. (b) Suppose that a new cable will be required in case that the signal transmission stops over 3 mins on average per hour. What is the maximum ratio 1/M so that a new cable is required
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


