Question: Need help with this java code to print the same output shown below public class PrintAdjacencyMatrix { public static void main(String[] args) { // adjacency
Need help with this java code to print the same output shown below
public class PrintAdjacencyMatrix { public static void main(String[] args) { // adjacency matrix int [][] distance = {{-1,-1,18,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,-1,-1,-1,5,-1}, //0 {-1,-1,-1,-1,22,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,16,-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,5,13,-1,16,-1}, {18,-1,-1,7,5,7,-1,6,19,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,16,-1,-1}, {16,-1,7,-1,6,-1,-1,4,-1,15,-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,14,11}, {-1,22,5,6,-1,5,-1,-1,25,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,9,-1,-1,-1,-1,10,-1,11,-1}, {-1,-1,7,-1,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,7,-1,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1}, {-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,16,5,18,-1,-1,-1}, {-1,-1,6,4,-1,-1,-1,-1,22,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,15,-1,11}, {-1,-1,19,-1,25,-1,-1,22,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,19,-1,-1},//8 {-1,-1,-1,15,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,3,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,8},//9 {-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,2,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,10,-1,-1,-1},//10 {6,-1,-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,3,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,9},//11 {-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,2,-1,-1,-1,-1,5,-1,6,-1,-1,8,-1,-1,-1},//12 {-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,7,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,-1,8,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},//13 {-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,8,-1,-1,-1,-1},//14 {-1,-1,-1,-1,9,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,5,6,-1,-1,-1,10,-1,-1,9,-1,10,-1},//15 {-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,-1,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,5},//16 {-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,8,-1,10,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},//17 {6,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,8,-1,-1,-1,-1,12,6,-1,8,-1},//18 {-1,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,12,-1,15,-1,-1,-1},//19 {-1,13,-1,-1,10,-1,18,-1,-1,-1,10,-1,8,-1,-1,9,-1,-1,6,15,-1,-1,6,-1},//20 {-1,-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,15,19,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},//21 {5,16,-1,14,11,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,10,-1,-1,8,-1,6,-1,-1,-1},//22 {-1,-1,-1,11,-1,-1,-1,11,-1,8,-1,9,-1,-1,-1,-1,5,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1}}; //23 //Printing the header System.out.println("============================== "+ " ADJACENCY MATRIX OF SINGAPORE "+ "=============================="); // Printing the location index numbers for(int i=0;i
Dijkstra:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Dijkstra { public void computePath(Vertex sourceVertex) { sourceVertex.setMinDistance(0); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(); priorityQueue.add(sourceVertex);
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { Vertex vertex = priorityQueue.poll();
for (Edge edge : vertex.getEdges()) { Vertex v = edge.getTargetVertex(); double weight = edge.getWeight(); double minDistance = vertex.getMinDistance() + weight;
if (minDistance
public List getShortestPathTo(Vertex targetVerte) { List path = new ArrayList();
for (Vertex vertex = targetVerte; vertex != null; vertex = vertex.getPreviosVertex()) { path.add(vertex); }
Collections.reverse(path); return path; } }
App:
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { Vertex v1 = new Vertex("A"); Vertex v2 = new Vertex("B"); Vertex v3 = new Vertex("C");
v1.Add_neighbour(new Edge(1, v1, v2)); v1.Add_neighbour(new Edge(10, v1, v2));
v2.Add_neighbour(new Edge(1, v2, v3));
Dijkstra dijkstra = new Dijkstra(); dijkstra.computePath(v1);
System.out.println(dijkstra.getShortestPathTo(v3)); } }
Edge:
public class Edge { private double weight; private Vertex startVertex; private Vertex targetVertex;
public Edge(double weight, Vertex startVertex, Vertex targetVertex) { this.weight = weight; this.startVertex = startVertex; this.targetVertex = targetVertex; }
public double getWeight() { return weight; } public Vertex getStartVertex() { return startVertex; }
public Vertex getTargetVertex() { return targetVertex; }
public void setWeight(double weight) { this.weight = weight; }
public void setStartVertex(Vertex startVertex) { this.startVertex = startVertex; }
public void setTargetVertex(Vertex targetVertex) { this.targetVertex = targetVertex; } }
Vertex:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;
public class Vertex implements Comparable { private String name; private List edges; private boolean visited; private Vertex previosVertex; private double minDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
public Vertex(String name) { this.name = name; this.edges = new ArrayList(); }
public void Add_neighbour(Edge edge) { this.edges.add(edge); }
public List getEdges() { return edges; }
public void setEdges(List edges) { this.edges = edges; }
public boolean isVisited() { return visited; }
public void setVisited(boolean visited) { this.visited = visited; }
public void setPreviosVertex(Vertex previosVertex) { this.previosVertex = previosVertex; }
public void setMinDistance(double minDistance) { this.minDistance = minDistance; } public Vertex getPreviosVertex() { return previosVertex; }
public double getMinDistance() { return minDistance; }
@Override public String toString() { return name; }
@Override public int compareTo(Vertex otherVertex) { return Double.compare(this.minDistance, otherVertex.minDistance); } }
Java code output has to appear something like this, showing the start from, To, path, and total distance after entering the integer starting point and integer end point.
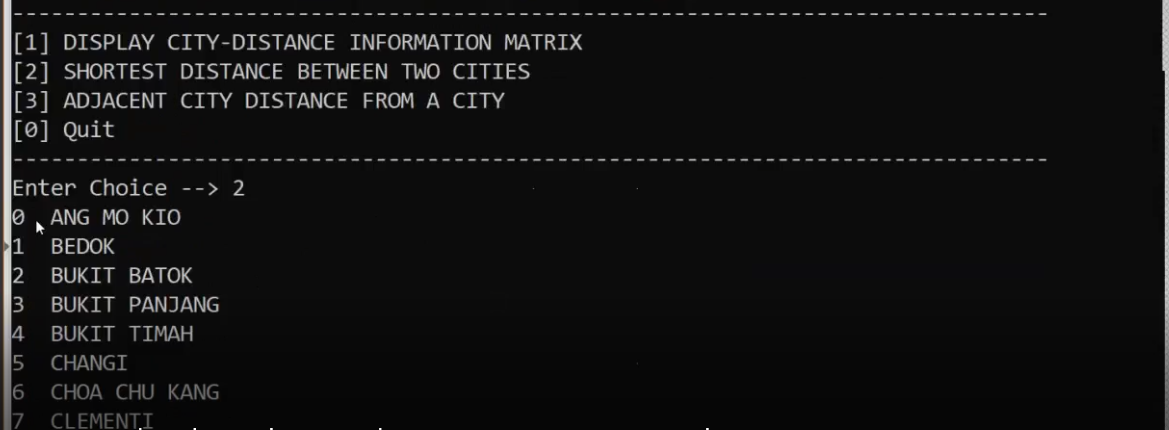
![below public class PrintAdjacencyMatrix { public static void main(String[] args) { //](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66ef6d09bab7f_04866ef6d08ab338.jpg)
Here is the requirements needed for the question (need help with requirement 2,3, and 4)
![adjacency matrix int [][] distance = {{-1,-1,18,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,6,-1,-1,-1,5,-1}, //0 {-1,-1,-1,-1,22,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,16,-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,5,13,-1,16,-1}, {18,-1,-1,7,5,7,-1,6,19,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,16,-1,-1}, {16,-1,7,-1,6,-1,-1,4,-1,15,-1,16,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,14,11}, {-1,22,5,6,-1,5,-1,-1,25,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,9,-1,-1,-1,-1,10,-1,11,-1},](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66ef6d0aa4bb1_05066ef6d0a0abb8.jpg)

Picture of adjacency matrix for viewing of distance (Do download to zoom)
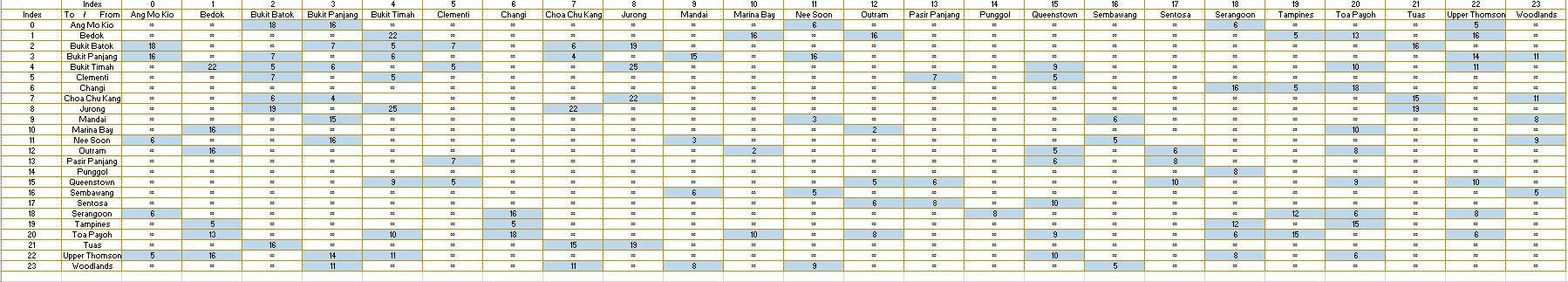
[1] DISPLAY CITY-DISTANCE INFORMATION MATRIX [2] SHORTEST DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO CITIES [3] ADJACENT CITY DISTANCE FROM A CITY [0] Quit Enter Choice --> 2 0 ANG MO KIO 1 BEDOK 2 BUKIT BATOK 3 BUKIT PANJANG 4 BUKIT TIMAH 5 CHANGI 6 CHOA CHU KANG CLEMENTI 18 SERANGOON 19 TAMPINES 20 TOA PAYOH 21 TUAS 22 UPPER THOMSON 23 WOODLANDS Select a integer starting point: 0 Select a integer end point: 9 Start from: ANG MO KIO To: MANDAI Path: ANG MO KIO -> NEE SOON -> MANDAI Total Distance: 9km Requirement 1 - Representation of the map in Figure 1 Represent the city-distance information shown in the map in Figure 1 with a weighted graph using adjacency matrix or link-list. Sembawang Woodlands 5 6 19 9 GO 5 Choa Chu Kang 5/ 14 15 22 Bukit 6 18 Mandal 3 Punggol Nee Soon 11/15 16 6 Sakit 16 Ang Mo Kio 8 6 16 Changi Ranjang 7 6 18 8 Serangoon 12 5 ypper 6 11 Thomson 16 Tampines Batak 15 Bukit 16 19/ 22 Simah 5 10 10 Noa Payoh 16 9 Bedok 5 Clement 8l VO Marina Bay Queenstown 6 16 Pasir 5 Panjang Outram 10 8 16 Fuas 257 59 19 Jurong 5 OD Soniusa Figure 1 Requirement 2 - Implementation Write an interactive program that given the start and destination cities, will determine the shortest route between them and its total distance. It is all right to have 0 distance; i.e., start and end at the same city. You can assume that the roads are all bi-direction; i.e., vehicle can travel in both directions. The output of your program may look something similar as follow: Start from: Changi To: Choa Chu Kang Path: Changi -> Toa Payoh -> Bukit Timah -> Bukit Batok -> Choa Chu Kang Total distance: 39 Km. Requirement 3 - Test run Test your program by determining the following routes: Changi to Choa Chu Kang Bedok to Bukit Batok Marina Bay to Woodlands Sembawang to Bukit Timah Upper Thomson to Outram Bukit Batok to Tampines Requirement 4 - Program Complexity Derive the program running time complexity of your algorithm using Big-O notation. State clearly how you arrive at the Big-O notation. Partial marks will be awarded only for stating without showing the work in arriving at your conclusion. 21 2 Bukit Batok 18 3 Bukit Panjang 16 5 Clementi Bukit Timah Bedok 6 Changi Cho Chu Karig 8 Jurong 9 Mandai 12 Outram 11 Nee Soon 6 13 Pasir Panjang 10 Marina Bay . 16 14 Punggol 15 Queenstown 17 Sentosa 16 Sembawang 18 Serangoon 6 19 Tampines 20 Toa Payoh Tuas 22 23 Upper Thomson Woodlands 5 16 . = 16 = = = 5 13 7 22 5 6 7 19 Index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 16 6 4 4 = 15 90 16 = = = 11 7. 5 7 6 5 se 22 19 25 10 9 5 14 11 = 5 7 16 5 18 - 4 = 22 = 6 19 11 15 19 25 22 . 15 2 3 = . 8 16 . 2 2 6 . 5 10 Index 0 To | From Ang Mo Kio Ang Mo Kio Bedok Bukit Batok 18 Bukit Panjang 16 Bukit Timah Clementi = Changi ChaChu Karig Jurong Mandai Marina Bay Nee Soon 6 6 Outram Pasir Panjang = Punggol Queenstown Sembawang Sentosa Serangoon 6 Tampines Toa Payoh Tuas = Upper Thomson 5 Woodlands = 16 = = 3 = = = -- . 9 16 2 8 8 5 6 = 6 8 7 = = = 8 = 9 9 5 19 5 6 = -- 10 9 9 = 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 10 6 5 . . 5 - = 6 8 10 e = . 8 8 12 = 16 5 18 = 6 15 19 = 5 13 = - 8 = 6 = 10 10 8 9 12 6 . 8 . = 15 16 15 19 = 16 11 10 6 14 11 11 8 9 5 = [1] DISPLAY CITY-DISTANCE INFORMATION MATRIX [2] SHORTEST DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO CITIES [3] ADJACENT CITY DISTANCE FROM A CITY [0] Quit Enter Choice --> 2 0 ANG MO KIO 1 BEDOK 2 BUKIT BATOK 3 BUKIT PANJANG 4 BUKIT TIMAH 5 CHANGI 6 CHOA CHU KANG CLEMENTI 18 SERANGOON 19 TAMPINES 20 TOA PAYOH 21 TUAS 22 UPPER THOMSON 23 WOODLANDS Select a integer starting point: 0 Select a integer end point: 9 Start from: ANG MO KIO To: MANDAI Path: ANG MO KIO -> NEE SOON -> MANDAI Total Distance: 9km Requirement 1 - Representation of the map in Figure 1 Represent the city-distance information shown in the map in Figure 1 with a weighted graph using adjacency matrix or link-list. Sembawang Woodlands 5 6 19 9 GO 5 Choa Chu Kang 5/ 14 15 22 Bukit 6 18 Mandal 3 Punggol Nee Soon 11/15 16 6 Sakit 16 Ang Mo Kio 8 6 16 Changi Ranjang 7 6 18 8 Serangoon 12 5 ypper 6 11 Thomson 16 Tampines Batak 15 Bukit 16 19/ 22 Simah 5 10 10 Noa Payoh 16 9 Bedok 5 Clement 8l VO Marina Bay Queenstown 6 16 Pasir 5 Panjang Outram 10 8 16 Fuas 257 59 19 Jurong 5 OD Soniusa Figure 1 Requirement 2 - Implementation Write an interactive program that given the start and destination cities, will determine the shortest route between them and its total distance. It is all right to have 0 distance; i.e., start and end at the same city. You can assume that the roads are all bi-direction; i.e., vehicle can travel in both directions. The output of your program may look something similar as follow: Start from: Changi To: Choa Chu Kang Path: Changi -> Toa Payoh -> Bukit Timah -> Bukit Batok -> Choa Chu Kang Total distance: 39 Km. Requirement 3 - Test run Test your program by determining the following routes: Changi to Choa Chu Kang Bedok to Bukit Batok Marina Bay to Woodlands Sembawang to Bukit Timah Upper Thomson to Outram Bukit Batok to Tampines Requirement 4 - Program Complexity Derive the program running time complexity of your algorithm using Big-O notation. State clearly how you arrive at the Big-O notation. Partial marks will be awarded only for stating without showing the work in arriving at your conclusion. 21 2 Bukit Batok 18 3 Bukit Panjang 16 5 Clementi Bukit Timah Bedok 6 Changi Cho Chu Karig 8 Jurong 9 Mandai 12 Outram 11 Nee Soon 6 13 Pasir Panjang 10 Marina Bay . 16 14 Punggol 15 Queenstown 17 Sentosa 16 Sembawang 18 Serangoon 6 19 Tampines 20 Toa Payoh Tuas 22 23 Upper Thomson Woodlands 5 16 . = 16 = = = 5 13 7 22 5 6 7 19 Index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 16 6 4 4 = 15 90 16 = = = 11 7. 5 7 6 5 se 22 19 25 10 9 5 14 11 = 5 7 16 5 18 - 4 = 22 = 6 19 11 15 19 25 22 . 15 2 3 = . 8 16 . 2 2 6 . 5 10 Index 0 To | From Ang Mo Kio Ang Mo Kio Bedok Bukit Batok 18 Bukit Panjang 16 Bukit Timah Clementi = Changi ChaChu Karig Jurong Mandai Marina Bay Nee Soon 6 6 Outram Pasir Panjang = Punggol Queenstown Sembawang Sentosa Serangoon 6 Tampines Toa Payoh Tuas = Upper Thomson 5 Woodlands = 16 = = 3 = = = -- . 9 16 2 8 8 5 6 = 6 8 7 = = = 8 = 9 9 5 19 5 6 = -- 10 9 9 = 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 10 6 5 . . 5 - = 6 8 10 e = . 8 8 12 = 16 5 18 = 6 15 19 = 5 13 = - 8 = 6 = 10 10 8 9 12 6 . 8 . = 15 16 15 19 = 16 11 10 6 14 11 11 8 9 5 =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


