Question: Note: in all of these problems, start with the value of your underlying asset, and build your binomial trees as we always have before: U=
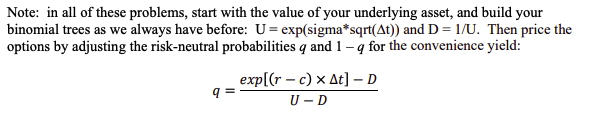

Note: in all of these problems, start with the value of your underlying asset, and build your binomial trees as we always have before: U= exp(sigma*sqrt(At)) and D=1/U. Then price the options by adjusting the risk-neutral probabilities q and 1 q for the convenience yield: exp[(r - c) At] - D q= U-D The spot price of cocoa is $2,194/ton, and the forward curve currently displays a net convenience yield of 8%. In a 12-step binomial tree, calculate the value of a one-year American call option on 1 ton of Cocoa with a strike price equal to $3,000. Assume that the risk-free rate of return is 1.5% per year, and that the volatility of returns on cocoa is 40%. Make sure to highlight the states of nature when early-exercise occurs. (Note: build your tree of underlyings and present your option value tree using whole numbers). Redo problem 2, this time assuming that the net convenience yield is 35% per year. What happened? Redo problem 2 one more time, this time setting the convenience yield on cocoa equal to 2%. What happened this time?. Note: in all of these problems, start with the value of your underlying asset, and build your binomial trees as we always have before: U= exp(sigma*sqrt(At)) and D=1/U. Then price the options by adjusting the risk-neutral probabilities q and 1 q for the convenience yield: exp[(r - c) At] - D q= U-D The spot price of cocoa is $2,194/ton, and the forward curve currently displays a net convenience yield of 8%. In a 12-step binomial tree, calculate the value of a one-year American call option on 1 ton of Cocoa with a strike price equal to $3,000. Assume that the risk-free rate of return is 1.5% per year, and that the volatility of returns on cocoa is 40%. Make sure to highlight the states of nature when early-exercise occurs. (Note: build your tree of underlyings and present your option value tree using whole numbers). Redo problem 2, this time assuming that the net convenience yield is 35% per year. What happened? Redo problem 2 one more time, this time setting the convenience yield on cocoa equal to 2%. What happened this time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


