Question: One vegetable processing company acquired by PFC was Eagle Foods (EF), with an acquisition value of $140 million. The acquisition included purchasing EFs wholly owned
One vegetable processing company acquired by PFC was Eagle Foods (EF), with an acquisition value of $140 million. The acquisition included purchasing EFs wholly owned Mexican subsidiary, Eagle Foods Sociedad Anonima (EFSA). In late 2000, the government of Mexico introduced new regulations that were intended to raise tax revenues but, simultaneously, would hurt maquiladoras competitiveness. Specifically, the Mexican government requires that maquiladoras report as a minimum pre-tax income the largest of two computations: (a) 6.5 percent of total operating expenses, or (b) 6.9 percent of operating assets.
During acquisition due diligence, the controller of EF indicated that EFSA was in compliance with the first option of the Safe Harbor provision. Specifically, EFSAs transfer price to EF was at least 6.5 percent of manufacturing conversion costs, an amount that was internally referred to as total cost to the border. Exhibit 1 compares the net income of PFC for broccoli production based on domestic operation (produced by PFC) and the net income of PFC based on combined operations (broccoli production by both PFC and EFSA). 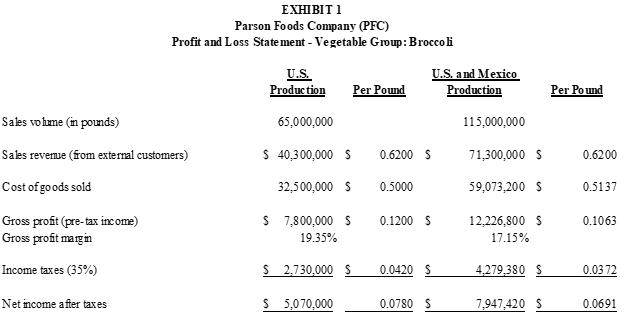
Exhibit 2 shows that EFSAs broccoli manufacturing conversion costs (i.e. direct labor and manufacturing overhead) per pound ($0.0600 and $0.0900 per pound, respectively) are indeed much cheaper than the comparable PFC domestic costs ($0.1500 and $0.2500 per pound, respectively). 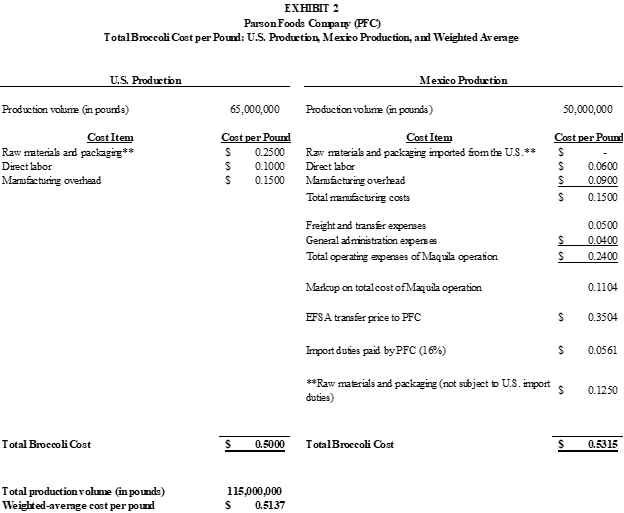
The financial analyst generated an EFSA income statement as presented in Exhibit 3. 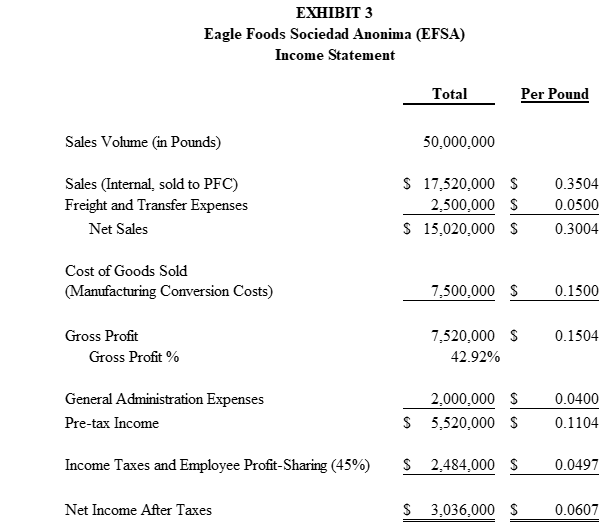
The financial analyst noticed several factors that complicate the analysis of the profitability for EFSA and PFC. First, while the federal income tax rates of EFSA (located in Mexico) and PFC (located in the U.S.) are both 35 percent, EFSAs pre-tax income is subject to another financial burden. Specifically, the Mexican government mandates that all Mexican companies, including maquiladoras, distribute to their employees 10 percent of their pre-tax income in the form of employee profit-sharing. In essence, the effective tax rate of EFSA is 45 percent (35 percent federal income tax and 10 percent mandatory employee profit sharing), resulting in a 10 percent difference in effective tax rates between EFSA (45 percent) and PFC (35 percent). Second, PFC pays an import duty rate of 16 percent. That is, PFC pays $0.1600 for every dollar of pre-tax profit earned by EFSA in Mexico. Third, the financial analyst learned that the exchange rates of the Mexican peso to the U.S. Dollar had been volatile.
Using the current transfer price between EFSA and PFC, the financial analyst summarizes the overall impact of federal income taxes, mandatory profit sharing, and import duties (see Exhibit 4). The analyst also summarizes the total pre-tax income of PFC based on the current transfer price (see Exhibit 5). 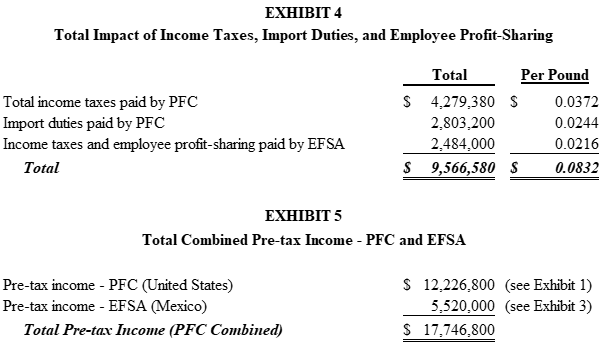
Required:
- What conditions might exist that encourage EFSA management not to charge the minimum allowable transfer price under the Safe Harbor provisions?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


