Question: Please answer ALL parts using C language: Here is the code I have so far: #include #include typedef struct TreeNode TreeNode; void visit(TreeNode* node); struct
Please answer ALL parts using C language:
Here is the code I have so far:
#include
typedef struct TreeNode TreeNode; void visit(TreeNode* node); struct TreeNode { char* name; TreeNode* pChild1; TreeNode* pChild2; TreeNode* pChild3; TreeNode* pChild4; }; TreeNode* createNewTreeNode(char name[]) { TreeNode* newTreeNode = (TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); newTreeNode->name = name; newTreeNode->pChild1 = NULL; newTreeNode->pChild2 = NULL; newTreeNode->pChild3 = NULL; newTreeNode->pChild4 = NULL; return newTreeNode; }
void freeingTreeNode(TreeNode* deletedTreeNode) { free(deletedTreeNode); } int main() { TreeNode* Root = createNewTreeNode("Root"); TreeNode* USR = createNewTreeNode("USR"); TreeNode* BIN = createNewTreeNode("BIN"); TreeNode* HOME = createNewTreeNode("HOME"); TreeNode* Exams = createNewTreeNode("Exams"); TreeNode* HWs = createNewTreeNode("HWs"); TreeNode* Projects = createNewTreeNode("Projects"); TreeNode* Grades = createNewTreeNode("Grades"); TreeNode* Drives = createNewTreeNode("Drives"); TreeNode* Docs = createNewTreeNode("Docs"); TreeNode* Main = createNewTreeNode("Main"); TreeNode* Dropbox = createNewTreeNode("Dropbox"); TreeNode* OneDrive = createNewTreeNode("OneDrive");
Root->pChild1 = USR; Root->pChild2 = BIN; Root->pChild3 = HOME; USR->pChild1 = Exams; USR->pChild2 = HWs; USR->pChild3 = Projects; USR->pChild4 = Grades; BIN->pChild1 = Drives; HOME->pChild1 = Docs; HOME->pChild2 = Main; Drives->pChild1 = Dropbox; Drives->pChild2 = OneDrive; visit(Root); }
// Pre-order traversal void visit(TreeNode* node) { printf("%s ", node->name); if (node->pChild1 != NULL) visit(node->pChild1); if (node->pChild2 != NULL) visit(node->pChild2); if (node->pChild3 != NULL) visit(node->pChild3); if (node->pChild4 != NULL) visit(node->pChild4);
}
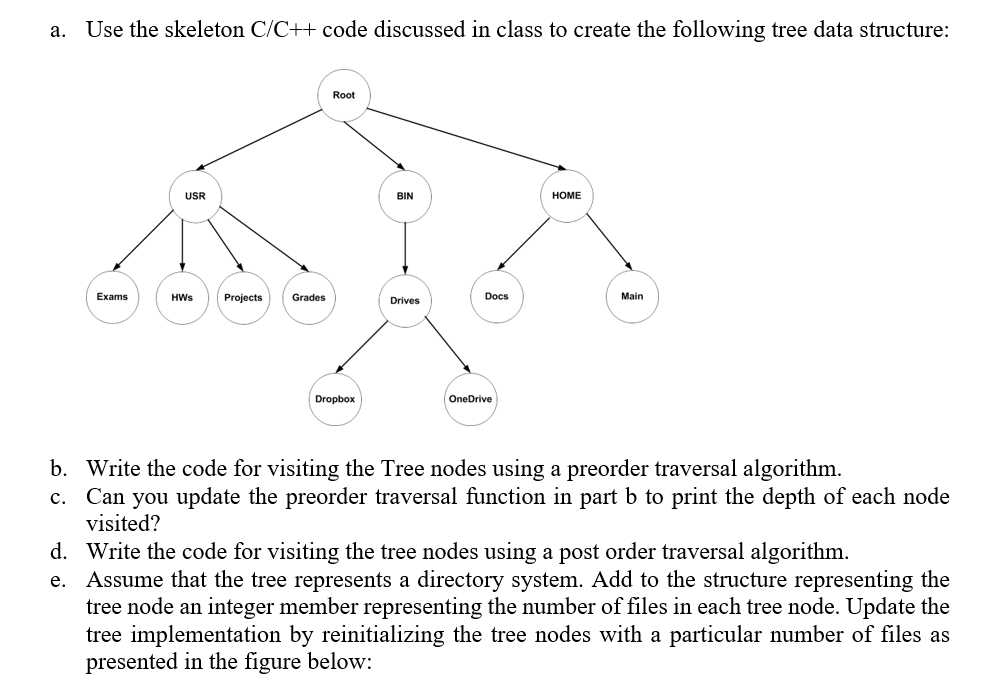
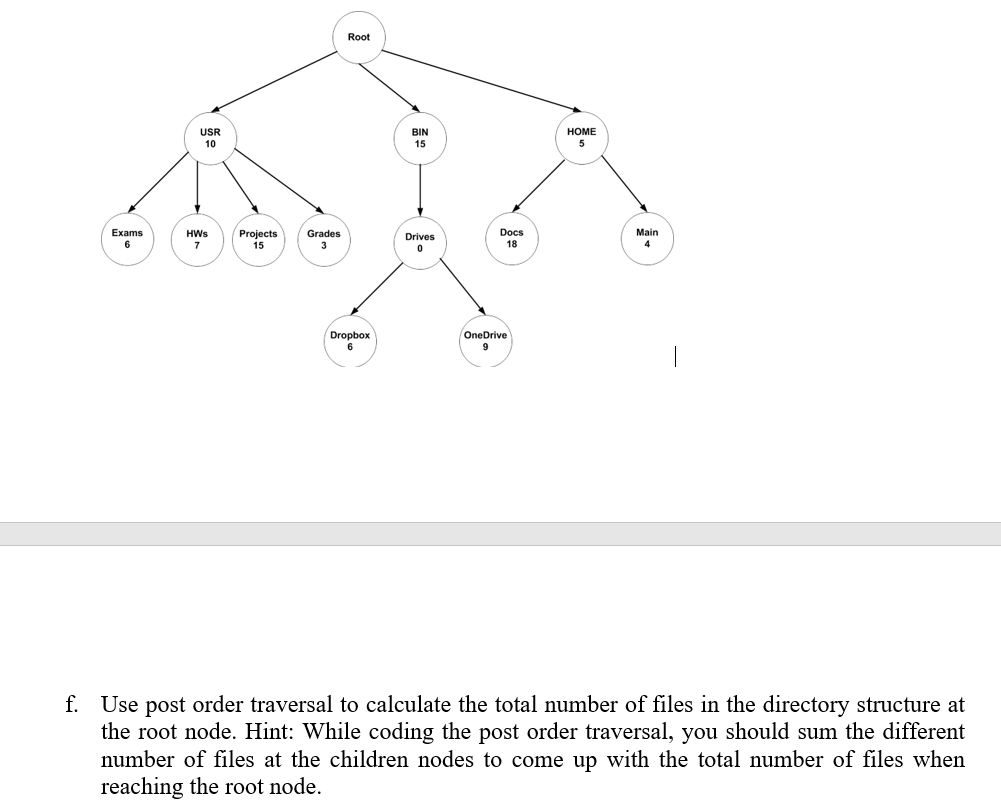
a. Use the skeleton C/C++ code discussed in class to create the following tree data structure: Root USR BIN HOME Exams HWS Projects Grades Drives Docs Main Dropbox OneDrive b. Write the code for visiting the Tree nodes using a preorder traversal algorithm. c. Can you update the preorder traversal function in part b to print the depth of each node visited? d. Write the code for visiting the tree nodes using a post order traversal algorithm. Assume that the tree represents a directory system. Add to the structure representing the tree node an integer member representing the number of files in each tree node. Update the tree implementation by reinitializing the tree nodes with a particular number of files as presented in the figure below: e. Root HOME USR 10 BIN 15 Exams HWS 7 Projects 15 Grades 3 Drives 0 Docs 18 Main 4 6 Dropbox OneDrive 9 6 | f. Use post order traversal to calculate the total number of files in the directory structure at the root node. Hint: While coding the post order traversal, you should sum the different number of files at the children nodes to come up with the total number of files when reaching the root node. a. Use the skeleton C/C++ code discussed in class to create the following tree data structure: Root USR BIN HOME Exams HWS Projects Grades Drives Docs Main Dropbox OneDrive b. Write the code for visiting the Tree nodes using a preorder traversal algorithm. c. Can you update the preorder traversal function in part b to print the depth of each node visited? d. Write the code for visiting the tree nodes using a post order traversal algorithm. Assume that the tree represents a directory system. Add to the structure representing the tree node an integer member representing the number of files in each tree node. Update the tree implementation by reinitializing the tree nodes with a particular number of files as presented in the figure below: e. Root HOME USR 10 BIN 15 Exams HWS 7 Projects 15 Grades 3 Drives 0 Docs 18 Main 4 6 Dropbox OneDrive 9 6 | f. Use post order traversal to calculate the total number of files in the directory structure at the root node. Hint: While coding the post order traversal, you should sum the different number of files at the children nodes to come up with the total number of files when reaching the root node
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


