Question: Please answer question 2 and I will upvote if correct! An important parameter in the design of gas absorbers is the ratio of the flow

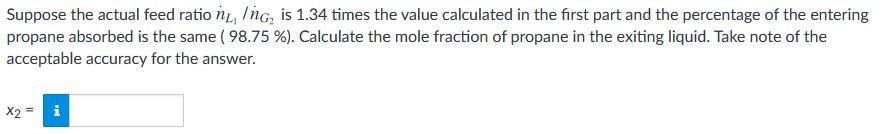
Please answer question 2 and I will upvote if correct!
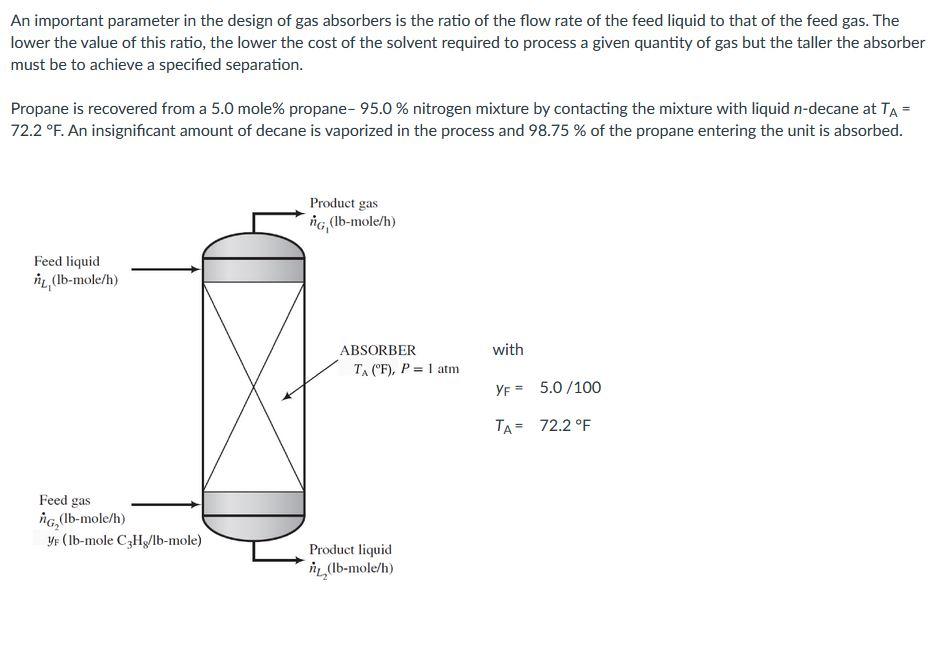
An important parameter in the design of gas absorbers is the ratio of the flow rate of the feed liquid to that of the feed gas. The lower the value of this ratio, the lower the cost of the solvent required to process a given quantity of gas but the taller the absorber must be to achieve a specified separation. Propane is recovered from a 5.0 mole% propane- 95.0 % nitrogen mixture by contacting the mixture with liquid n-decane at TA= 72.2 F. An insignificant amount of decane is vaporized in the process and 98.75 % of the propane entering the unit is absorbed. Product gas ig, (Ib-mole/h) Feed liquid L. (lb-mole/h) with ABSORBER T. ("F), P = 1 atm YF = 5.0 /100 TA= 72.2 F Feed gas ng, (lb-mole/h) yr (Ib-mole CzHg/lb-mole) Product liquid ni L, (Ib-mole/h) The highest possible propane mole fraction in the exiting liquid is that in equilibrium with the propane mole fraction in the feed gas (a condition requiring an infinitely tall column). Using Raoult's law to relate the mole fractions of propane in the feed gas and liquid, calculate the ration, Ing, corresponding to this limiting condition. bar To predict the vapor pressure of propane, you may use the Antoine equation log10 p measured in Kelvin and A = 4.53678, B = 1149.36, C = 24.906. -)) = A- B with T T + C ni, Ing= 8.528 Suppose the actual feed ration, Ing, is 1.34 times the value calculated in the first part and the percentage of the entering propane absorbed is the same ( 98.75 %). Calculate the mole fraction of propane in the exiting liquid. Take note of the acceptable accuracy for the answer. X2 = PO
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


