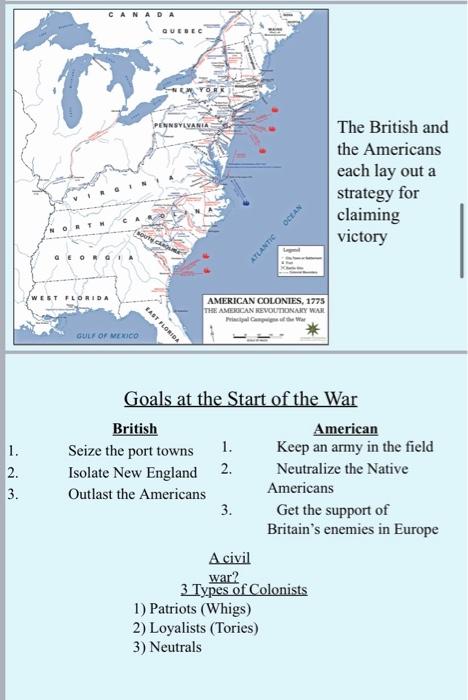
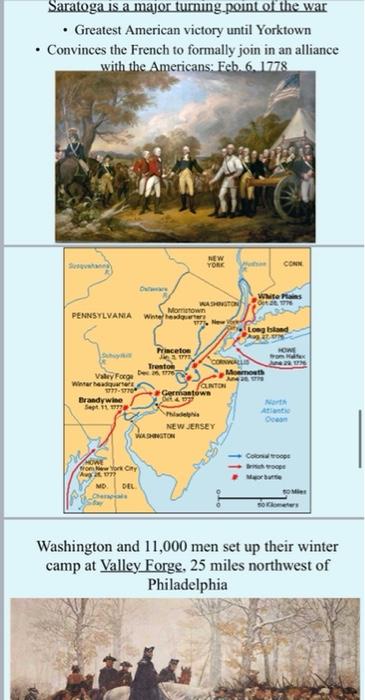
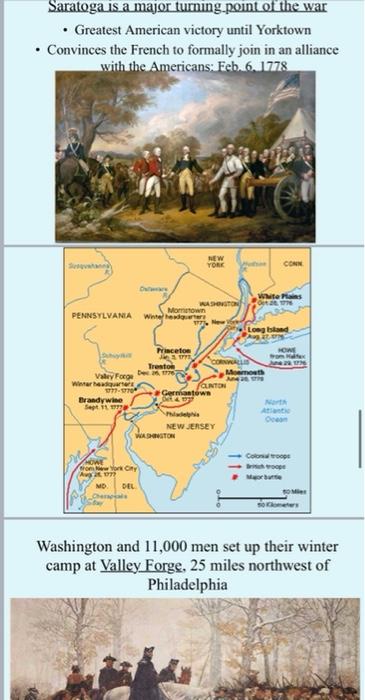
Question: please Answer the all 3 questions 1. Name TWO key events that, in your opinion, were the most important in sharpening the divisions between Great
please Answer the all 3 questions
1. Name TWO key events that, in your opinion, were the most important in sharpening the divisions between Great Britain and the colonists in the late 1760s and early 1770s?
2. What were some of the key issues that unified the colonists at the time of the Revolution? What were some issues that divided them?
3. What was the most important part of the Declaration of Independence at the time it was written? What became the most important part as time went on, and why?
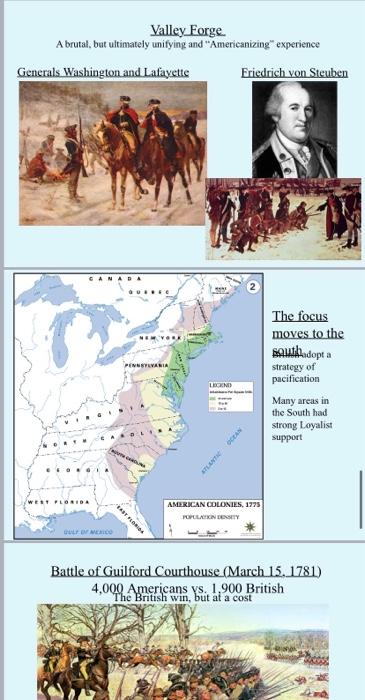
New British Policies following 1763 The new imperial Indian policy Revised Navigation Acts A standing army in America The war put the British govt. deeply in debt, and they wanted the colonists to help pay These new British policies angered the Americans Salutary neglect: avoiding strict enforcement of parliamentary laws, meant to keep the American colonies obedient to England. Americans saw themselves as loyal British subjects Good government depended on the virtue of the people to carry out their civic duty Prime Minister George Grenville and the Sugar Act (1764) Duty on imported sugar Stricter registration for ships Set up admiralty courts in Halifax, Nova Scotia No presumption of innocence and no trial by jury The Stamp Act (1765). . . . . A specially embossed paper on all: newspapers, legal documents, licenses, insurance policies, ship's papers, dice and playing cards An "Internal Tax" "No Taxation without Representation" . . . . Leaders of the protest movement emerge Patrick Henry (VA) Samuel Adams (MA) Merchants, lawyers, and craftsmen sought to moderate the resistance movement by controlling it. They did not want mobs. of the STAMP. An Emilem of the Effects Deco or the firal STAN Groups like the Sons of Liberty form. Encouraged moderate forms of protest; crowd action as a last resort. Sc-p! t! Noi Titoday Morning, December 17, 1765. THE True-born Sons of Li- berty, are delised to meet under LIBERTY- TREE, at XII o 'Clock, THIS DAY, to hear the the public Refignation, under Oath, of ANDREW OLIVER, Ely: Diftributor of Scamps for the Province of the Maflachuetts Bay. A Religgation ? YES The Stamp Act Congress (1765). . 9 colonies: MA, CT, RI, NY, NJ, PA, DE, MD, SC Deny Parliament's right to tax the colonists without representation Stop all imports until the measure is repealed However, due subordination" was owed to measures that fell within Parliament's legitimate authority The Declaratory Act (1766). The colonists win: Parliament repeals the Stamp Act and lowers the Sugar Act duties BUT, Parliament affirmed its full authority to make laws binding the colonies "in all cases whatsoever" The Townshend Duties (1767) . . PM Charles Townshend 5 laws in total Import duties on lead, glass, paint, paper, and tea Designed to set a precedent that the British Parliament had the right to tax the colonies Public protests erupt across the colonies. Organized widespread boycotts, protests, and even mobs. Mob violence could lead to tarring and feathering at times The Association": Members of the VA House of Burgesses convened at the Raleigh Tavern in Williamsburg after the royal governor dissolved the assembly for passing a resolution stating Parliament had no right to tax Virginians without their consent. UTLU Americans boycott British goods Jan. 1. 1769: Boston merchants organize the first boycott (non-importation) agreement Soon spreads to other colonies . Not as effective as it was hoped British exports decline by 38%, but not every American supports the boycott 1771: boycott ends Tensions were high throughout the colonies, especially in Boston, MA 1768: British send more troops to the city Troops and townsmen competed for local jobs March 1770: rioting breaks out between Bostonians and British troops The Boston Massacre (March 5, 1770): A crowd gathered outside the Customs House taunts British soldiers, throwing freksand shexy.hellie into crowd: 5 are killed, 6 are Crispus Attucks: 1st martyr of the American Revolution British and colonial authorities commit to a fair trial for the 8 soldiers When no Loyalist attorney will defend the soldiers, Patriot John Adams takes the case Adams opposed British overreach, but he was committed to the rule of law Volm Adamd Adams wins his case: 6 of the soldiers are acquitted, and 2 are convicted of manslaughter, not murder. Patrick Carr's obituary. His deathbed testimony was used by Adams in the soldiers defense La Wednesday Night died. Parrick Carr, an Inhabitant of this Town of the Wound he received in King Sueet on the bloody and exeuable Night of the sth Inita Hebad just before lebis Home, and opon his coming into the Street received the fatal Ball in his Hip which polled out at the oppoite Side ; this is the filth Life that has been facrificed by the Rage of the Soldiery, but it is feared it will not be the latt, as everal otletes are dangerously isoguilling of their Wounds. His Remains were at- tended on Saturday lat from Faneuil-Hall by a numerous and repectable Train of Mourners, to the fame Grave, in which thoe who fell by the ame Hands of Violence were intered the latt Weck. . PM Lord Frederick North Repealed the Townshend Duties, EXCEPT for the one on tea This was done as a symbolic act . The Gaspe Affair . 1772: British Lt. William Dudingston sailed the Gaspe to Narragansett Bay in RI to patrol for smugglers Dudingston is hated by local RI citizens June 9, 1772: the Gaspe chases the Hannah The Gaspe runs aoround Local members of the Providence Sons of Liberty board the ship and set it on fire, destroying it . Committees of Correspondence Rallied opposition against the British 7,000 to 8,000 colonials served on these Argued that colonial rights are natural rights, not based on the English constitution Committees spread throughout the colonies, coordinating activities March 1773-May 1774: all the colonies join in a inter-colonial committee of correspondence From Resistance to Rebellion MA Governor Thomas Hutchinson became synonymous with the hated measures of the British The Hutchinson-Oliver Letters, 1773 Benjamin Franklin discovers a series of letters from Hutchinson Hutchinson recommended that popular government be taken from the people "by degrees" There should be an abridgment of what are called English liberties" MA demands that he be . The situation deteriorates in Boston Parliament passed the Tea Act in 1773 Designed to save the British East India Company Boston once again is the flashpoint of protests Nov. 27, 1773: The Dartmouth arrives in Boston, full of tea Brethren, and Fellow Citizens ! , that and deter- table Tools to Miniltry and Governor, the TEA CONSISTES, (thole Traitons to their Country, Bunchers, who have done, and are de Ing cvety Thing to Murder and detroy all that shall and in the Way of their private intereft) are determined to come and relidegsin in the Town of Bolton I therefore give you this early Notice that you may hold yourelves in Readines, on the thortelt Notice, to give them focha Reception, fuch vile Ingrates defense JOYCE, jun (Chairman of the Committee for Tarring Erabering If any peron fhould be fo harly as to Tarthlu down, they may capett my loved centment The Boston Tea Party: Sam Adams and 30 to 130 Boston men board the ship and dump 342 chests of tea in Boston Harbor (No. 16 1772) The British response is swift May 1774: General Thomas Gage arrives The new military governor of Massachusetts Authorized to implement the Coercive Acts aka The Intolerable Acts The Coercive (Intolerable) Acts, 1774 Parliament closes Boston Harbor Removes the charter for MA Bay and dissolves the colonial legislature General Gage installed as military governor Legalized the housing (quartering) of troops at the public expense in any available building, even in private homes Colonial governors had their powers strengthened throughout the colonies Heste The able Dvetom. or. Amenn seatewing the Bitter Draught. The First Continental Congress, September 1. 1774: Agree to boycotts and to stop all exports; set-up Committees of Observation and Safety organized n sses Creation of the "Minutemen Oct. 15, 1774: the MA Committee of Safety creates special units, the "minutemen" April 18. 1775: Gage orders 700 troops to march from Boston to Concord to seize the town's munitions Lexington and Concord: "Shot Heard "Round the World" British: 73 dead and 202 wounded Americans: 49 dead, 39 wounded, and 4 missing American British Concord Am Lasington ATS Bench The American Revolution: How revolutionary was it? The 2nd Continental Congress: the colonial governing body during the Revolution The Siege of Boston: April 19. 1775 to March 17. 1776 Amon Concord ATS The Siege of Boston: April 19. 1775 to March 17. 1776 American Lasing Concorde AITH Berish advance British Victories American victories British troop movements American troop movements The Battle of Bunker Hill (1775): A pyrrhic victory for the British The Siege of Boston: April 19, 1775 to March 17. 1776 Thomas Paine, Common Sense (January 1776): Lays out the case for independence and rejecting the king COMMON SENSE; IXHABITANTS AMERICA, #T CANADA QUEBEC WE EW YORK PENNSYLVANIA The British and the Americans each lay out a strategy for claiming CANADA QUEBEC HUYORK PENNSYLVANIA The British and the Americans each lay out a strategy for claiming victory OCEAN ATLANTIC GEORG WEST FLORIDA AMERICAN COLONIES, 1775 THE AMERICAN REVOUTIONARY WAR GULF OF MEXICO KABT FLORIDA 1. 2. 3. Goals at the Start of the War British American Seize the port towns 1. Keep an army in the field Isolate New England 2. Neutralize the Native Outlast the Americans Americans 3. Get the support of Britain's enemies in Europe A civil war? 3 Types of Colonists 1) Patriots (Whigs) 2) Loyalists (Tories) 3) Neutrals 100-200,000 men served in the Continental Army Washington = Commander-in-Chief 4,000 to 15,000 served at any given time British forces: 50,000 British troops + 30,000 Hessians Nearly 50.000 thousand Loyalists fought for the king Fred u17586274 fotosearch.com The American Revolution was a civil war in Indian Country Attempt to stay neutral Pulled into the conflict . Most sided with the British, but not all The Iroquois were split: 4 Iroquois nations sided with the 2 sided with the Americans British; The Declaration of Independence. 1776: Articulating values of independence 1. Themes present in the Declaration Attacking the King, not Parliament. Why? - Draws on Thomas Paine - Monarchy as a symbol of tyranny Rights are based on natural law. What are they? - John Locke: Life, liberty, and property - Life. liberty, and the pursuit of happiness 2. -John Locke: Life, liberty, and property - Life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness Legacy: What is the most important part of the document? 3. The Declaration of Independence. 1776: Articulating values of independence NEW YORK Wudson CONN De White Plains WASHINGTON Oct 1776 Morristown PENNSYLVANIA Winter heaters 17. New York Oity Long Island A 27.776 Princeton HOWE Doku. 1778 from CORNWALLI Trenton Valley Forge De 10 Monmouth Winnerheter CLINTON 1777-177 Germantown Brandywine Oct Sept. in Nort Philadelphia Atlantic Ocean NEW JERSEY WASHINGTON Map of the wala, te Battles of 1776 and early 1777 HOME Colonie British troops from New York GRY Aug 1777 MO DEL Che Se 50 Miles someters 1776: Victories and Losses Ideological high points: Paine's Common Sense and The Declaration of Independence Losses: Washington is driven out of NYC The Battles of Long Island (8/27/1776) and White Plains (10/28/1776) Victories: Morale builders into the new year Battles of Trenton (12/25 and 12/26) and Princeton (1/3/1777) Washington crossing the Delaware: Iconic image. Historically accurate? The Battle of Saratoga (Sept.-Oct. 18. 1777): Gen. Horatio Gates (American) vs. Gen. Burgoyne (British) SUROTRE BUMOVE es ADIRONDACK MOUNTAINS Saratoga is a major turning point of the war Greatest American victory until Yorktown . Convinces the French to formally join in an alliance with the Americans: Feb 6. 1778 NEW YORK CONN We as RASTO Motown PENNSYLVANIA When Longbad Valley Food Wienerbedrer -7704 Erandywine Sept 11 12 Princeton Sex Treston CORNALI 17 Mamos FONTON Germantown NA NEW JERSEY WASTON Co RY Avg MD G DEL Me Soomes Washington and 11,000 men set up their winter camp at Valley Forge, 25 miles northwest of Philadelphia 1776: Victories and Losses Ideological high points: Paine's Common Sense and The Declaration of Independence Losses: Washington is driven out of NYC The Battles of Long Island (8/27/1776) and White Plains (10/28/1776) Victories: Morale builders into the new year Battles of Trenton (12/25 and 12/26) and Princeton (1/3/1777) Washington crossing the Delaware: Iconic image. Historically accurate? The Battle of Saratoga (Sept.-Oct. 18. 1777): Gen. Horatio Gates (American) vs. Gen. Burgoyne (British) SUROTRE BUMOVE es ADIRONDACK MOUNTAINS Saratoga is a major turning point of the war Greatest American victory until Yorktown . Convinces the French to formally join in an alliance with the Americans: Feb 6. 1778 NEW YORK CONN We as RASTO Motown PENNSYLVANIA When Longbad Valley Food Wienerbedrer -7704 Erandywine Sept 11 12 Princeton Sex Treston CORNALI 17 Mamos FONTON Germantown NA NEW JERSEY WASTON Co RY Avg MD G DEL Me Soomes Washington and 11,000 men set up their winter camp at Valley Forge, 25 miles northwest of Philadelphia Valley Forge A brutal, but ultimately unifying and "Americanizing experience Generals Washington and Lafayette Friedrich von Steuben CANADA The focus moves to the southadopt a strategy of pacification Many areas in the South had strong Loyalist support LEGEND STAATEN ESO WEI FLORIDA AMERICAN COLONIES, 1775 OPEAN SY * Battle of Guilford Courthouse (March 15. 1781) 4,000 Americans ys. 1.900 British The British win, but at a cost Battle of Guilford Courthouse (March 15, 1781) 4,000 Americans ys. 1,900 British The British win, but at a cost Greene breaks British control in SC and GA. Cornwallis has to go back to VA to obtain new supplies Gen. Nathaniel Greene Gen. Charles Cornwallis NEW YORK NEW PORT HARTFORD WHITE PLAH PENNSYLVANIA Allied army of Washington & Rochambeau PHILADELPHIA Army arrives from France Cornwallis becomes De Batas with French trapped at Yorktown HEAD. Na Atlantic Ocean VE ARAPOLIS MD The joint American-French forces commanded BISTE PENNSYLVANA Allied army of Washington & Rocharbebu Army arrives from France Comwallis becomes De Bars with French trapped at Yorktown PHILADELPHA sige guns HEAD- Atlanti Ocean ARAPOL ALEXANDRIA MD Lafayette Gloucester Point Yorktop British fleet WILLIAMBEIRO anved 5 Sept Battle of the Capes (5-8 Sept) VIRONA De Grasse French Fleet arrived 30 Aug CAROLINA The joint American-French forces commanded by Washington and Rochambeau close in British surrender at Yorktown: October 19. 1781 SUKKINDER OF LOAD CONWALLIS AT YORKTOW. do Trembes 1797 painting GREAT BRITAIN Treaty of Paris. 1783: John Adams, Ben Franklin, and John Jay present America U.S.. territory and independence MSort UNITED STATES SPAIN Inspiration for the world: the chance to explore Der Ante Ocean Inspiration for the world: the chance to explore republican government on a large scale Gut of Meco SPAIN Treaty of Paris 1783 African Americans served on both sides for the promise of The number of free black predomised after the Revolution 1750: a few thousand; 1800: 200.000+ Roles for women Organized the homefront 1/16 of the war's participants were women Mainly "camp followers Secret Soldiers: Deborah Sampson "Molly Pitcher Mary Hays McCauley "Remember the ladies" Abigail Adams Republican Womanhood American women were to instill virtue in their children and be the vessels from which new citizens were born The war is a disaster for Native Americans Ignored by the Treaty of Paris The only minority group given any sort of legal recognition in the new nation. GREAT BRITAIN UNITED STATES SPAIN Die AB Ocean SPAIN Gure Treaty of Paris 1783