Question: Please Code in VHDL. Only alu.vhd, dff.vhd, overflow.vhf, and pa1tests20 need to be edited. The template for those are below. I have been trying to
Please Code in VHDL. Only alu.vhd, dff.vhd, overflow.vhf, and pa1tests20 need to be edited. The template for those are below. I have been trying to solve this for the past 8 hours and I haven't made much progress. I am mostly having trouble with the alu.vhd and dff.vhd modules. Any help would be much appreciated
_______________________________________________________________________________________________

pa1.vhd
library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL;
entity pa1 is port(clk, reset, en : in std_logic; sel : in unsigned(2 downto 0); A : in unsigned(31 downto 0); Output : out unsigned(63 downto 0); overflow : out std_logic); end pa1;
architecture Behavioral of pa1 is signal Out_int : unsigned(63 downto 0) := (others => '0'); signal O : unsigned(63 downto 0) := (others => '0'); begin
Output A, sel => sel, B => Out_int(31 downto 0), O => O );
dff : entity work.dff port map ( clk => clk, reset => reset, en => en, D => O, Q => Out_int );
o_flow : entity work.overflow port map ( data => Out_int(63 downto 32), overflow => overflow );
end Behavioral;
dff.vhd
library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL;
entity dff is port (clk, reset, en : in std_logic; D : in unsigned(63 downto 0); Q : out unsigned(63 downto 0)); end dff;
architecture Behavioral of dff is signal Q_int : unsigned(63 downto 0) := (others => '0'); begin
end Behavioral;
alu.vhd
library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL; use ieee.std_logic_misc.all;
entity alu is port ( A, B : in unsigned(31 downto 0); sel : in unsigned(2 downto 0); O : out unsigned(63 downto 0)); end entity alu;
architecture Behavioral of alu is
end Behavioral;
overflow.vhd
library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL; use ieee.std_logic_misc.all;
entity overflow is port (data : in unsigned(31 downto 0); overflow : out std_logic); end overflow;
architecture Behavioral of overflow is
begin
end Behavioral;
pa1tests20.vhd COMPONENT pa1 PORT( clk : IN std_logic; reset : IN std_logic; en : IN std_logic; sel : IN unsigned(2 downto 0); A : IN unsigned(31 downto 0); Output : OUT unsigned(63 downto 0); overflow : OUT std_logic ); END COMPONENT;
-- Clock period definitions constant clk_period : time := 10 ns; --Inputs signal clk, reset, en : std_logic := '0'; signal sel : unsigned(2 downto 0) := (others => '0'); signal A : unsigned(31 downto 0) := (others => '0');
--Outputs signal Output : unsigned(63 downto 0); signal overflow : std_logic; BEGIN -- Instantiate the Unit Under Test (UUT) uut: pa1 PORT MAP ( clk => clk, reset => reset, en => en, sel => sel, A => A, Output => Output, overflow => overflow);
-- Clock process definitions clk_process :process begin clk
-- Stimulus process -- insert stimulus here
wait; end process;
END;
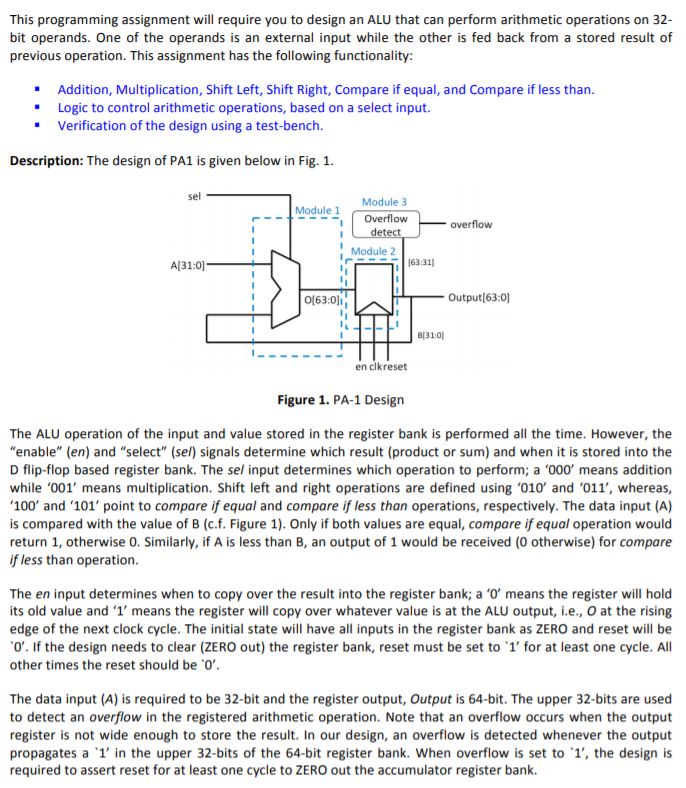
This programming assignment will require you to design an ALU that can perform arithmetic operations on 32- bit operands. One of the operands is an external input while the other is fed back from a stored result of previous operation. This assignment has the following functionality: . Addition, Multiplication, Shift Left, Shift Right, Compare if equal, and Compare if less than. Logic to control arithmetic operations, based on a select input. Verification of the design using a test-bench. Description: The design of PA1 is given below in Fig. 1. sel Module 1 Module 3 Overflow - Overflow detect Module 2 163:31) A[31:0) 0[63:0) Output[63:0) 310 en clkreset Figure 1. PA-1 Design The ALU operation of the input and value stored in the register bank is performed all the time. However, the "enable" (en) and "select" (sel) signals determine which result (product or sum) and when it is stored into the D flip-flop based register bank. The sel input determines which operation to perform; a '000' means addition while '001' means multiplication. Shift left and right operations are defined using '010' and '011', whereas, '100' and '101' point to compare if equal and compare if less than operations, respectively. The data input (A) is compared with the value of B (cf. Figure 1). Only if both values are equal, compare if equal operation would return 1, otherwise 0. Similarly, if A is less than B, an output of 1 would be received (0 otherwise) for compare if less than operation. The en input determines when to copy over the result into the register bank; a 'o' means the register will hold its old value and 'l' means the register will copy over whatever value is at the ALU output, i.e., o at the rising edge of the next clock cycle. The initial state will have all inputs in the register bank as ZERO and reset will be "O'. If the design needs to clear (ZERO out) the register bank, reset must be set to 'l' for at least one cycle. All other times the reset should be 'O'. The data input (A) is required to be 32-bit and the register output, Output is 64-bit. The upper 32-bits are used to detect an overflow in the registered arithmetic operation. Note that an overflow occurs when the output register is not wide enough to store the result. In our design, an overflow is detected whenever the output propagates a '1' in the upper 32-bits of the 64-bit register bank. When overflow is set to '1', the design is required to assert reset for at least one cycle to ZERO out the accumulator register bank. The ALU is expected to perform an unsigned integer add, multiply, shift, and compare operations. We do not require structural VHDL for these operations. You can use behavioral operators and the appropriate IEEE libraries for your design. One design option is to use constrained unsigned to represent the input operand (i.e., A: in unsigned (31 downto 0) for the A operand), and use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL library to perform the + and * numeric operations. Use the library function for the shift operations. For example, when shifting B input left by one bit, then use shift_left (unsigned(B), 1). Comparison operations can be performed via library functions or simple
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


