Question: Please help finish/debug code SERVER.PY CLIENT.py Deliverables (each worth 5 points) 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 2.
Please help finish/debug code
SERVER.PY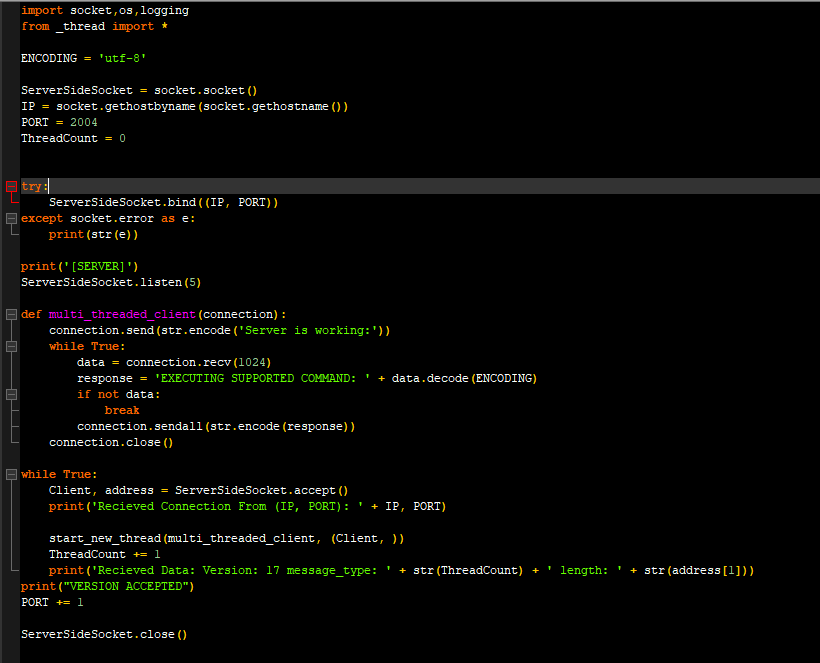
CLIENT.py
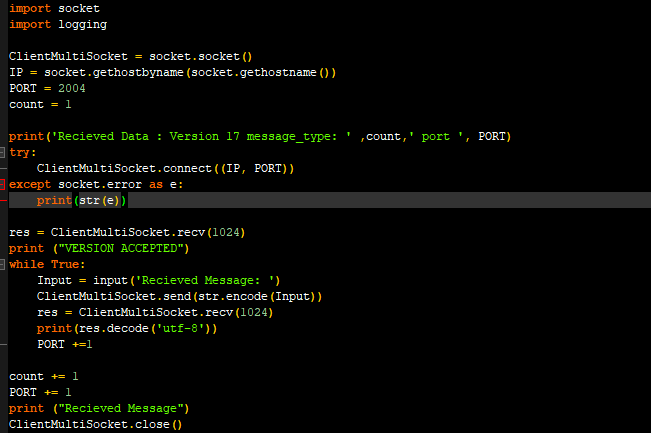

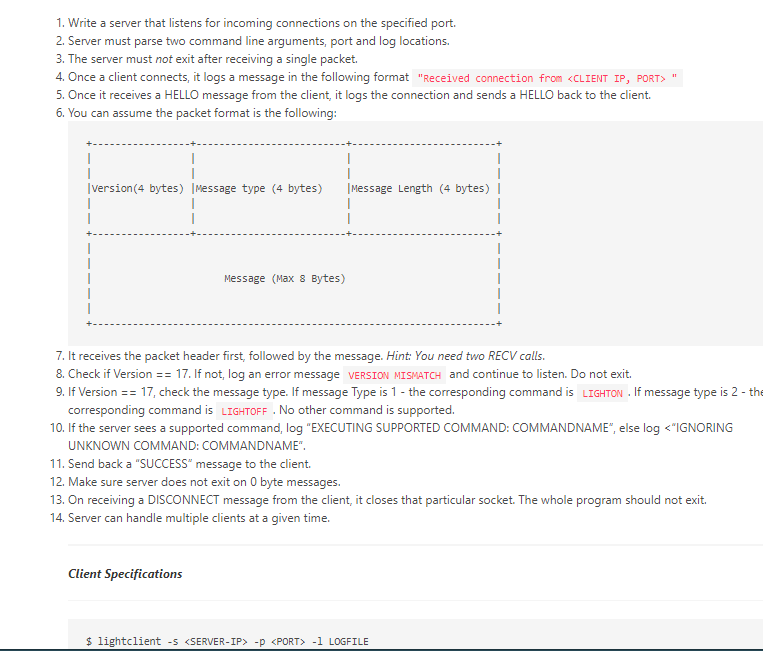
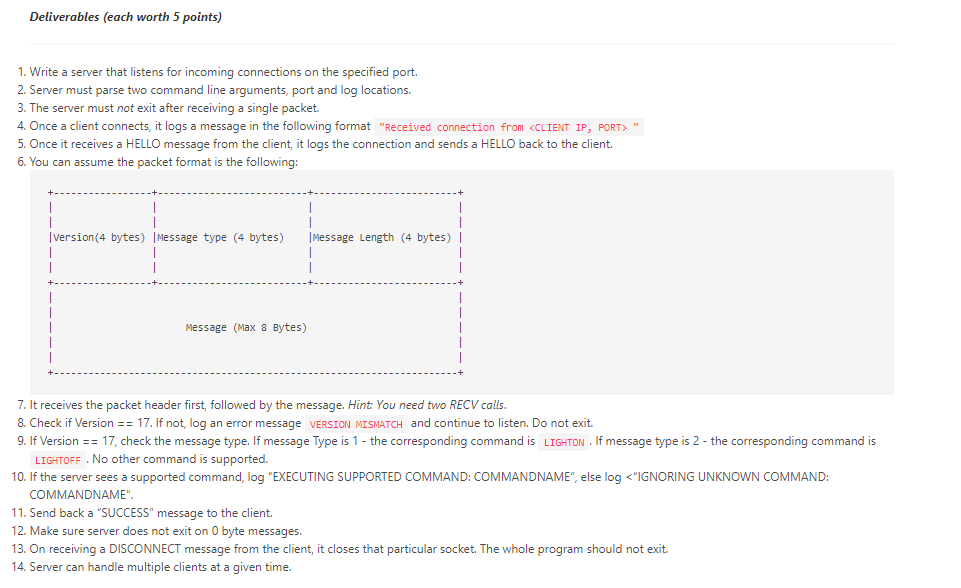
Deliverables (each worth 5 points) 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 2. Server must parse two command line arguments, port and log locations 3. The server must not exit after receiving a single packet. 4. Once a client connects, it logs a message in the following format "Received connection from " 5. Once it receives a HELLO message from the client, it logs the connection and sends a HELLO back to the client. 6. You can assume the packet format is the following: | Version (4 bytes) Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) Message (Max 8 Bytes) 7. It receives the packet header first, followed by the message. Hint: You need two RECV calls. 8. Check if Version == 17. If not, log an error message VERSION MISMATCH and continue to listen. Do not exit. 9. If Version == 17, check the message type. If message Type is 1- the corresponding command is LIGHTON . If message type is 2 - the corresponding command is LIGHTOFF. No other command is supported. 10. If the server sees a supported command, log "EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: COMMANDNAME", else log -1 1. PORT - The port server listens on. 2. Log file location - Where you will keep a record of actions. For example: $ lightserver -p 30000 -1 /tmp/logfile Deliverables (each worth 5 points) 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 2. Server must parse two command line arguments port and log locations. 3. The server must not exit after receiving a single packet. 4. Once a client connects it logs a message in the following format "Received connection from 5. Once it receives a HELLO message from the client, it logs the connection and sends a HELLO back to the client. 6. You can assume the packet format is the following: version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | 1 1 Message (Max 8 Bytes) 7. It receives the packet header first, followed by the message. Hint: You need two RECV calls. 8. Check if Version == 17. If not, log an error message VERSION MISMATCH and continue to listen. Do not exit. 9. If Version == 17, check the message type. If message Type is 1- the corresponding command is LIGHTON. If message type is 2 - the corresponding command is LIGHTOFF . No other command is supported. 10. If the server sees a supported command, log "EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: COMMANDNAME, else log -D -1 LOGFILE Deliverables (each worth 5 points) 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 2. Server must parse two command line arguments, port and log locations 3. The server must not exit after receiving a single packet. 4. Once a client connects, it logs a message in the following format "Received connection from " 5. Once it receives a HELLO message from the client, it logs the connection and sends a HELLO back to the client. 6. You can assume the packet format is the following: | Version (4 bytes) Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) Message (Max 8 Bytes) 7. It receives the packet header first, followed by the message. Hint: You need two RECV calls. 8. Check if Version == 17. If not, log an error message VERSION MISMATCH and continue to listen. Do not exit. 9. If Version == 17, check the message type. If message Type is 1- the corresponding command is LIGHTON . If message type is 2 - the corresponding command is LIGHTOFF. No other command is supported. 10. If the server sees a supported command, log "EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: COMMANDNAME", else log -1 1. PORT - The port server listens on. 2. Log file location - Where you will keep a record of actions. For example: $ lightserver -p 30000 -1 /tmp/logfile Deliverables (each worth 5 points) 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 2. Server must parse two command line arguments port and log locations. 3. The server must not exit after receiving a single packet. 4. Once a client connects it logs a message in the following format "Received connection from 5. Once it receives a HELLO message from the client, it logs the connection and sends a HELLO back to the client. 6. You can assume the packet format is the following: version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | 1 1 Message (Max 8 Bytes) 7. It receives the packet header first, followed by the message. Hint: You need two RECV calls. 8. Check if Version == 17. If not, log an error message VERSION MISMATCH and continue to listen. Do not exit. 9. If Version == 17, check the message type. If message Type is 1- the corresponding command is LIGHTON. If message type is 2 - the corresponding command is LIGHTOFF . No other command is supported. 10. If the server sees a supported command, log "EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: COMMANDNAME, else log -D -1 LOGFILE








