Question: Please help me code the following in: JAVA Please use many COMMENTS and read the task THOROUGHLY Full points will be awarded, thanks in advance!
Please help me code the following in: JAVA
Please use many COMMENTS and read the task THOROUGHLY
Full points will be awarded, thanks in advance!



 Notes:
Notes:
-Note that the List class in this assignment is more like an ArrayList than the list prototype ADT
-Also, note that you have to build Stack and Queue so that they inherit from List. Thus, for instance, do not just use the linked data structure implementation of a stack
-In the section "Stack & Queue Methods to Override" of the assignment description, some may be confused why it is called "overriding" if you are using insert/remove to create your push/pop/enqueue/dequeue methods in Stack and Queue. What's going on is that you use the parent class (List) version of insert/remove to create push/pop/enqueue/dequeue but then in your child classes (Stack and Queue) you have to override the inherited "copies" of insert/remove with versions that call your child class push/pop/enqueue/dequeue methods because Stack and Queue do not have any methods called insert/remove, etc.
-Note that List needs to include both append and delete methods (delete is the same as remove but just has another name; this happens all the time in coding, where you have two methods of different names that do the same thing).
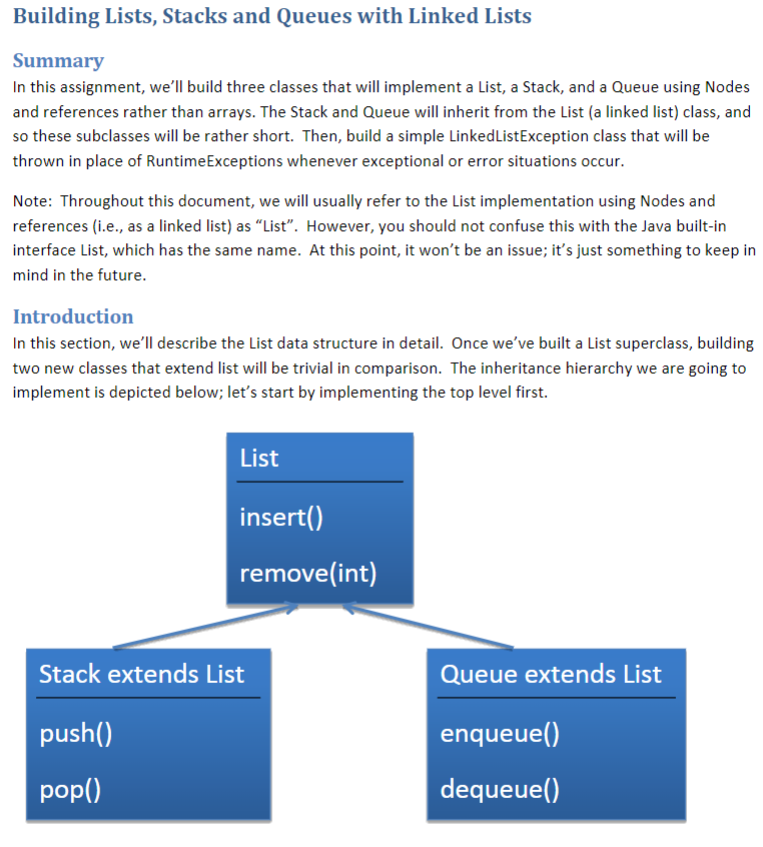
Building Lists, Stacks and Queues with Linked Lists Summary In this assignment, we'll build three classes that will implement a List, a Stack, and a Queue using Nodes and references rather than arrays. The Stack and Queue will inherit from the List (a linked list) class, and so these subclasses will be rather short. Then, build a simple LinkedListException class that will be thrown in place of RuntimeExceptions whenever exceptional or error situations occur. Note: Throughout this document, we will usually refer to the List implementation using Nodes and references (i.e., as a linked list) as "List". However, you should not confuse this with the Java built-in interface List, which has the same name. At this point, it won't be an issue; it's just something to keep in mind in the future. Introduction In this section, we'll describe the List data structure in detail. Once we've built a List superclass, building two new classes that extend list will be trivial in comparison. The inheritance hierarchy we are going to implement is depicted below; let's start by implementing the top level first. List insert() remove(int) Stack extends List push() pop() Queue extends List enqueue() dequeue()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


