Question: please please help me to write about product any Product [10-15 Refer to the PPTs of Chapter-6 on Product and price. Just Take the topics
please please help me to write about product any Product [10-15 




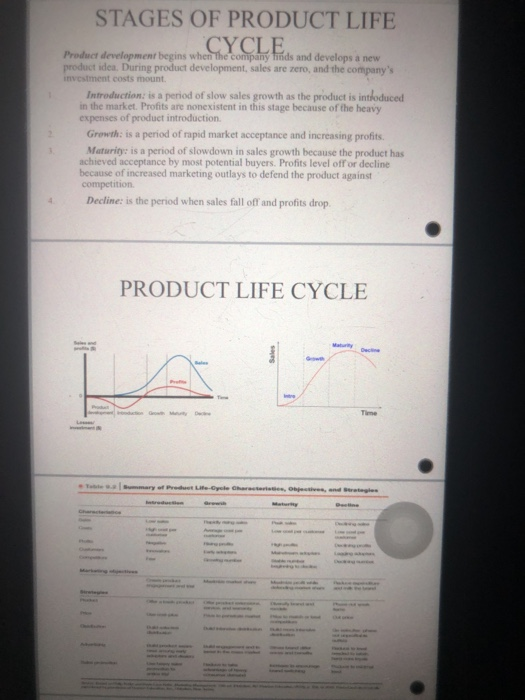

CONTENTS Introduction Product Branding Packaging Labelling New product development Product life cycle Pricing 1- INTRODUCTION Product - Anything that can be offered to a market for attention, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. Includes more than just tangible objects. Service- An activity, benefit or satisfaction offered for sale that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything. Products fall into two broad classes based on the types of consumers who use them Consumer products. These are products and services bought by final consumers for personal consumption Industrial products: These are those products purchased for further processing or for use in conducting a business Type of consumer Product Consideration Shopping Specialty Uneought om powy Wedne convenient the producer Do by both the new L yg such and Red dong re INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS CLASSIFICATION Supplies and Materials & Parts Capital Items services Raw materials, components etc. Mostly sold to other industrial users Price and service key Issues Industrial products used in production or operations E.g. IT systems, buildings infrastructure Operating supplies (e.g. energy) and business services (e.g. maintenance, security) 2- PRODUCT LINE Product Line: A product line is a group of related products all marketed under brand name that is sold by the same company. A group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups are marketed through the same types of outlets, or fall within given price ranges A company can expand its product line in two ways: Line filling: Product line filling involves adding more items within the present range of the line Line stretching: It occurs when a company lengthens its product line beyond its current range. The company can stretch its line downward, upward or both ways PRODUCT LINE DEPTH & BREADTH Product Mix (Product portfolio): It is the set of all products and services or the total range of products offered by a company Product breadth refers to all product lines that company has to offer to its Product depth refers to the number of products in company's specific product line Coca Cola Soft drinks 3- BRANDING -DEFINITION Anme terminsymbol, or design, or combination of these, that identifies the products or services of one seller or group of sellers and differentiates them from those of competitors Branding helps buyers: To identify products Identify product quality and consistency Branding h eller Provides legal protection for unique product features that otherwise might be copied by competitors Branding helps the seller to segment markets Ee rather than offering just one general product to all consumers, Toyota can offer the different Lexus, Toyota, and Scion brands cach with numerous sub-brands wuch as Camry Corolla Yaris and Land Cruiser 4- BRANDING STRATEGIES In building brands, companies need to make decisions about brand positioning, brand name selection, brand sponsorship, and brand development 333 A company also has four choices when it comes to developing brands. It can introduce line extensions, brand extensions, multi-brands, or new brands Product category FIGURE 18.5 Brand Development Strategies e nsion ension M ads New brands 5- PACKAGING Packaging involves designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product . Traditionally, the primary function of the package was to hold and protect the product. Recently increased competition and clutter on retail store shelves means that packages must now perform many sales tacks from attracting buyers to communicating brand positioning to closing the sale . Companies realize the power of good packaging to create immediate consumer recognition of a brand Innovative packaging can give a company an advantage over competitors and boost sales. Distinctive packaging may even become an important part of a brand's identity . Eg: Tiffany's distinctive blue boxes have come to embody the exclusive jewelry retailer's premium legacy and positioning 6- LABELING AND LOGOS Labels and logos range from simple tags attached to products to comples graphics that are part of the packaging The label helps to identify the product or brand . The label might also describe several things about the product Who made it Where it was made When it was made Its contents How it is to be used How to use it safely . Finally, the label might help to promote the brand and engage customers Labels and brand logos can support the band's positioning and add personality 7- NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT A firm can obtain new products in two ways Acquisition New Product Development NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Idea t ion The systematic search for new product des Meer Screening new product ideas to spot good ones and drop poor possible Producer A detailed version of the new product idea stated in meaningful Come Testing new product concept with a group of tarpt consumento find the Concepts have strong consumer appeal Markering d a w. Designing initial marketing strategy for new product based on the product Concept B i asa A review of the les costs and profit projections for a new producto find out whether these factors satisfy the company's objectives Preddwl Developing the product concept into a physical product to m e that the product ideas can be turned into a workable market offering Test make the stage of new product development in which the product and proposed marketing programare tested in realistic market settings Commerc i o Introducing a new product into the market 8- PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE Product life cycle is the progression of an item/product through the various stages of its time on the market. It's a four basic stages through which a product progress Introduction Growth Maturity Decline STAGES OF PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE Product development begins when the company tinds and develops a new product idea. During product development, sales are zero, and the company's investment costs mount Introduction is a period of slow sales growth as the product is intoduced in the market. Profits are nonexistent in this stage because of the heavy expenses of product introduction Growth: is a period of rapid market acceptance and increasing profits. Maturity is a period of slowdown in sales growth because the product has achieved acceptance by most potential buyers. Profits level off or decline because of increased marketing outlays to defend the product against competition Decline is the period when sales fall off and profits drop PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE 9- PRICING CONCEPTS Price- The amount of money charged for a product or service, or the sum of the values that customers exchange for the benefits of having or using the product or service The challenge of pricing is to find the price that will let the company make a fair profit by getting paid for the customer value it creates . Price remains an important element in the marketing mix, it is the only marketing mix element that produces revenue for the company. 10- PRICING STRATEGIES 1) Customer value-based pricing: Setting price based on buyers' perceptions of value rather than on the seller's cost. Types of value-based pricing: Good-value pricing: Offering just the right combination of quality and good service at a fair price. Value-added pricing: Attaching value-added features and services to differentiate a company's offers and charging higher prices 2) Cost-based pricing: Setting prices based on the costs of producing, distributing, and selling the product plus a fair rate of return for effort and risk. Types of Cost: Fixed costs: (overhead) Costs that do not vary with production or sales level. Variable costs: Costs that vary directly with the level of production Total costs: The sum of the fixed and variable costs for any given level of production
Refer to the PPTs of Chapter-6 on Product and price. Just Take the topics of Product from the PPT's of the chapter and then write a chapter using the topics as per the guidelines. Use online sources and books for the purpose.
Chapter 6







Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


