Question: Problem 10.7 Assume that the phase is defined such that a 7-pulse reverses the accumulated phase of all spins: -. In terms of k-space,

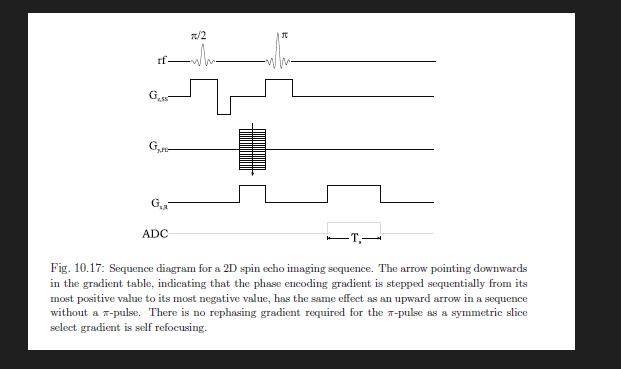
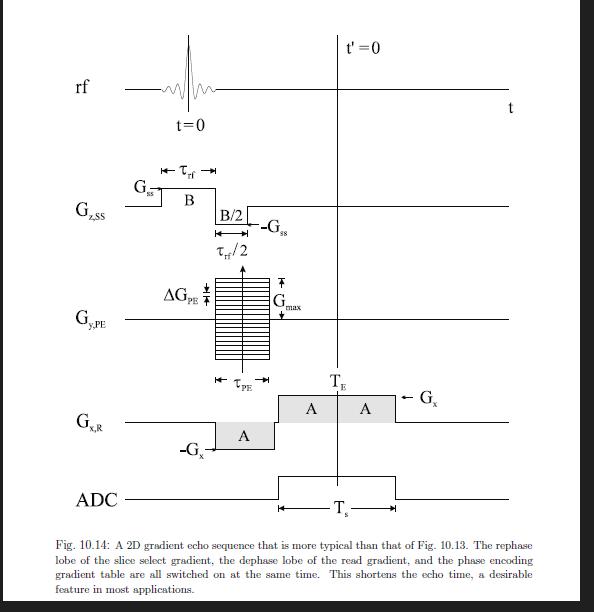
Problem 10.7 Assume that the phase is defined such that a 7-pulse reverses the accumulated phase of all spins: -. In terms of k-space, the x-pulse is equivalent to a reflection through the origin: k-k. a) Show that the k-space diagram for the spin echo experiment shown in Fig. 10.17 is identical to that in Fig. 10.15b which corresponds to the gra- dient echo sequence shown in Fig. 10.14. b) Find the k-space diagram for the spin echo experiment shown in Fig. 10.17 if the phase encoding gradient table is applied after the T-pulse, but before the read gradient. (The dephasing read gradient lobe is unchanged.) rf ADC 7/2 J -T,- Fig. 10.17: Sequence diagram for a 2D spin echo imaging sequence. The arrow pointing downwards in the gradient table, indicating that the phase encoding gradient is stepped sequentially from its most positive value to its most negative value, has the same effect as an upward arrow in a sequence without a z-pulse. There is no rephasing gradient required for the -pulse as a symmetric slice select gradient is self refocusing. rf GLSS y,PE GR x,R ADC G- t=0 B AGTE +44 -G- B/2 + 14 T/2 A G F G max A t' =0 TR E A G -T Fig. 10.14: A 2D gradient echo sequence that is more typical than that of Fig. 10.13. The rephase lobe of the slice select gradient, the dephase lobe of the read gradient, and the phase encoding gradient table are all switched on at the same time. This shortens the echo time, a desirable feature in most applications. Problem 10.7 Assume that the phase is defined such that a 7-pulse reverses the accumulated phase of all spins: -o. In terms of k-space, the x-pulse is equivalent to a reflection through the origin: k-k. a) Show that the k-space diagram for the spin echo experiment shown in Fig.10.17 is identical to that in Fig. 10.15b which corresponds to the gra- dient echo sequence shown in Fig. 10.14. b) Find the k-space diagram for the spin ocho experiment shown in Fig. 10.17 if the phase encoding gradient table is applied after the T-pulse, but before the read gradient. (The dephasing read gradient lobe is unchanged.) rf ADC 7/2 J -T,- Fig. 10.17: Sequence diagram for a 2D spin echo imaging sequence. The arrow pointing downwards in the gradient table, indicating that the phase encoding gradient is stepped sequentially from its most positive value to its most negative value, has the same effect as an upward arrow in a sequence without a T-pulse. There is no rephasing gradient required for the -pulse as a symmetric slice select gradient is self refocusing. rf GLSS y,PE GR x,R ADC G- t=0 B AGTE +44 -G- B/2 + 14 T/2 A G F G max A t' =0 TR E A G -T Fig. 10.14: A 2D gradient echo sequence that is more typical than that of Fig. 10.13. The rephase lobe of the slice select gradient, the dephase lobe of the read gradient, and the phase encoding gradient table are all switched on at the same time. This shortens the echo time, a desirable feature in most applications.
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Here is a hypothetical plot that represents the evolution of MRI signal intensity over tim... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


