Question: Problem 2 (a) What is the Black-Scholes partial differential equation (PDE) for the price f(t, St) at time t of a European derivative security on
Problem 2
(a) What is the Black-Scholes partial differential equation (PDE) for the price f(t, St) at time t of a European derivative security on a stock with price St? What does each term in the equation mean?
(b) The Black-Scholes PDE does not specify whether the derivative is a call option, a put option, or some other derivative. How do you incorporate the derivative payoff when using Black-Scholes PDE to price a derivative?
(c) (Not graded, optional for those interested) There is an exotic European-style derivative whose price at time t equals ZektS 2 t if the stock price at time t is St , with Z and k two constants. The stock price follows a geometric Brownian motion with volatility equal to 40% per annum. The risk-free rate is 5% per annum continuously compounded. Determine k. The following calculus facts will be useful:
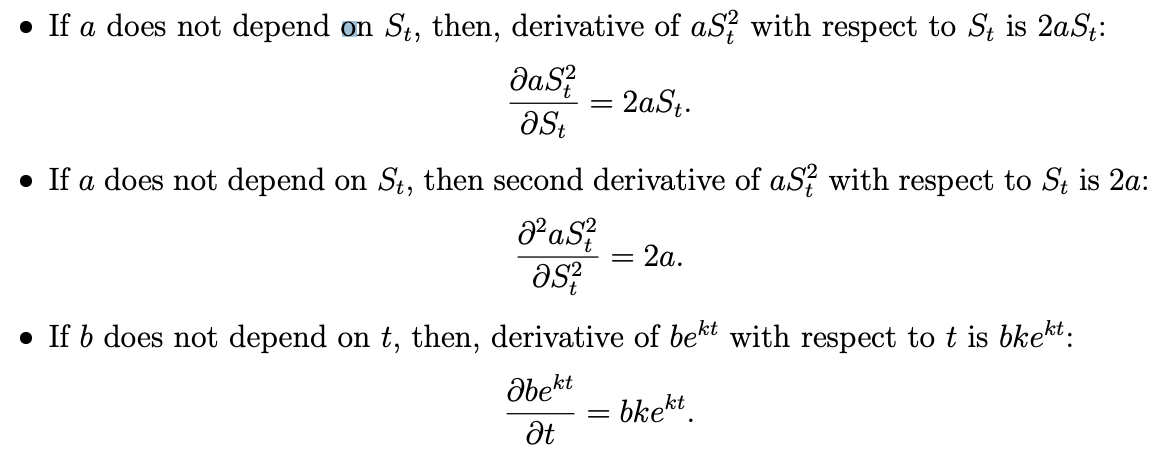
If a does not depend on St, then, derivative of as with respect to St is 2aSt: das 2aSt. ast = If a does not depend on St, then second derivative of aS with respect to St is 2a: das - 2a. as? If b does not depend on t, then, derivative of bekt with respect to t is bkekt. abekt = bkekt. at If a does not depend on St, then, derivative of as with respect to St is 2aSt: das 2aSt. ast = If a does not depend on St, then second derivative of aS with respect to St is 2a: das - 2a. as? If b does not depend on t, then, derivative of bekt with respect to t is bkekt. abekt = bkekt. at
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


