Question: Problem 5. In a multiprogramming environment, several concurrent com- putational processes compete for the use of resources (e.g., disk, scanner, CD-rom). A resource is assigned
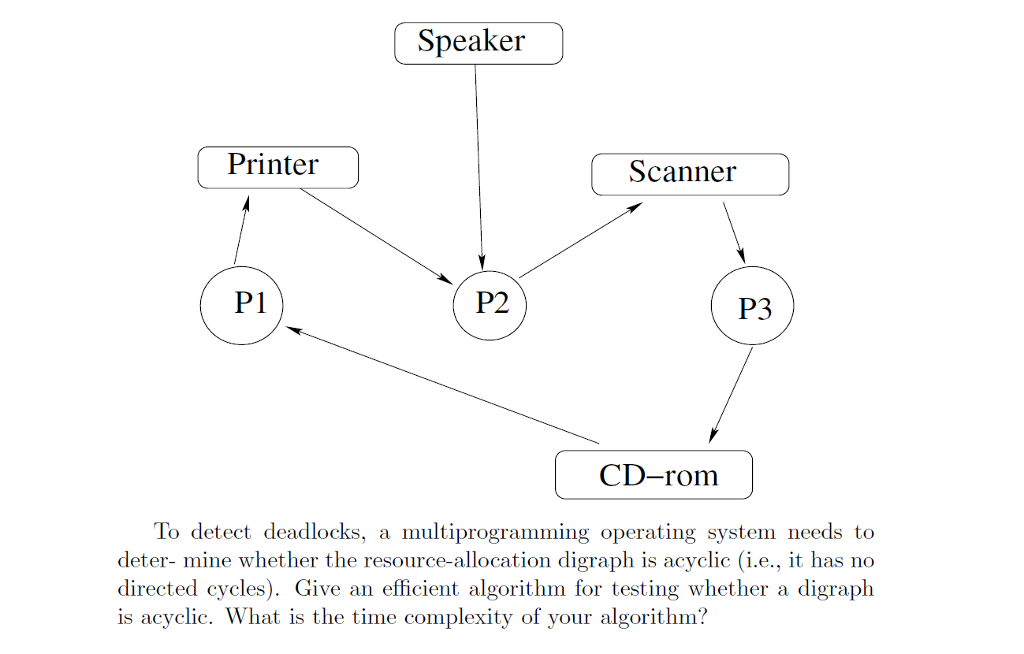
Problem 5. In a multiprogramming environment, several concurrent com- putational processes compete for the use of resources (e.g., disk, scanner, CD-rom). A resource is assigned to at most one process, while the other processes who have requested that resource are waiting until the resource is released and made available. A deadlock occurs when processes end up waiting forever because resources are never freed. This happens when the resource-allocation digraph contains a directed cycle. Indeed, if such a cycle exists, say po; ro; pi; T1; p2; r2; po, we have that processor po is waiting for resource ro, which is assigned to processor pi. At the same time, processon p? is waiting for resource ri, which is assigned to processor p2, and processor p2 is waiting for resource r2, which is assigned to processor po. Hence, po, P1 and p2 keep on waiting indefinitely for resources. The example below shows a deadlock caused by a directed cycle in the resource- allocation digraph Problem 5. In a multiprogramming environment, several concurrent com- putational processes compete for the use of resources (e.g., disk, scanner, CD-rom). A resource is assigned to at most one process, while the other processes who have requested that resource are waiting until the resource is released and made available. A deadlock occurs when processes end up waiting forever because resources are never freed. This happens when the resource-allocation digraph contains a directed cycle. Indeed, if such a cycle exists, say po; ro; pi; T1; p2; r2; po, we have that processor po is waiting for resource ro, which is assigned to processor pi. At the same time, processon p? is waiting for resource ri, which is assigned to processor p2, and processor p2 is waiting for resource r2, which is assigned to processor po. Hence, po, P1 and p2 keep on waiting indefinitely for resources. The example below shows a deadlock caused by a directed cycle in the resource- allocation digraph
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


