Question: Problem 9-21 Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you
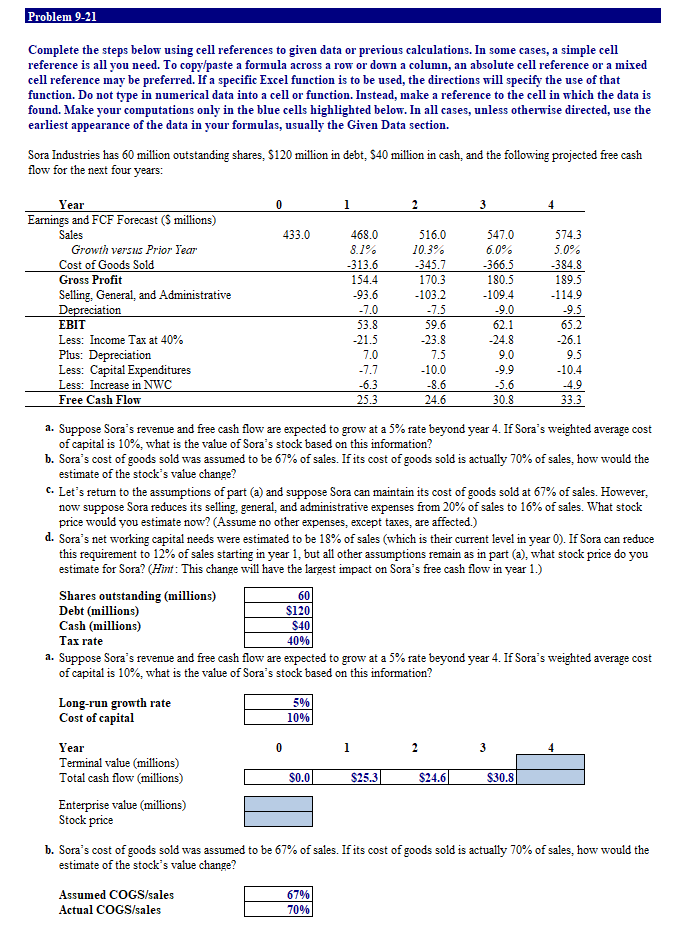
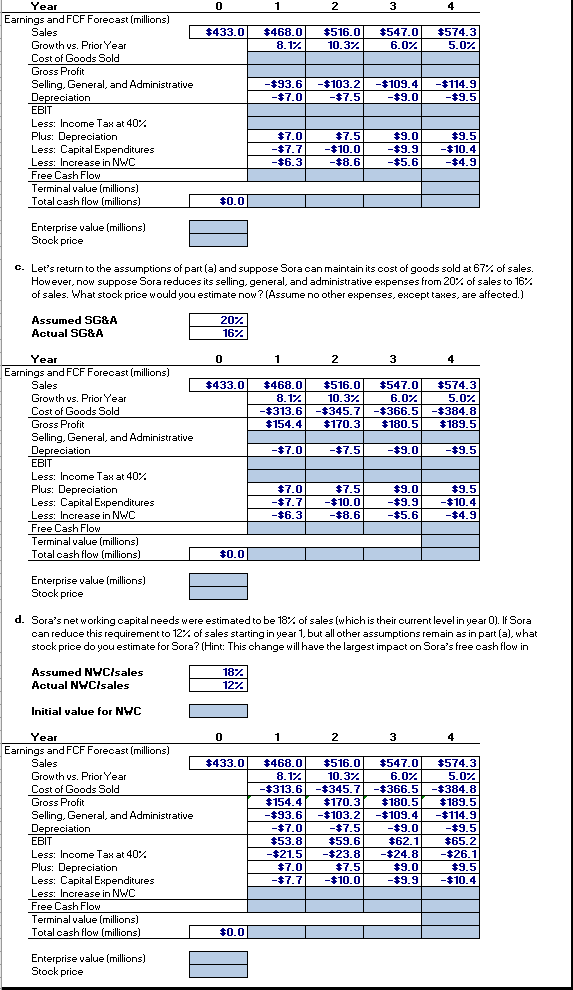
Problem 9-21 Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. Sora Industries has 60 million outstanding shares, $120 million in debt, $40 million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next four years: 433.0 547.0 6.0% -366.5 180.5 -109.4 Year Earnings and FCF Forecast (5 millions) Sales Growth versus Prior Tear Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow 468.0 8.1% -313.6 154.4 -93.6 -7.0 53.8 -21.5 7.0 -7.7 -6.3 25.3 516.0 10.3% -345.7 170.3 -103.2 -7.5 59.6 -23.8 7.5 -10.0 -8.6 24.6 -9.0 574.3 5.0% -384.8 189.5 -114.9 -9.5 65.2 -26.1 9.5 -10.4 -4.9 3 3.3 62.1 -24.8 9.0 -9.9 -5.6 8 30. a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5% rate beyond year 4. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 10%, what is the value of Sora's stock based on this information? b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? c. Let's return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, now suppose Sora reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (which is their current level in year 0). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions remain as in part (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) Shares outstanding (millions) Debt (millions) $120 Cash (millions) $40 Tax rate 40% a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5% rate beyond year 4. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 10%, what is the value of Sora's stock based on this information? Long-run growth rate Cost of capital 5% 10% Year Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) $0.0 $25.3 $24.6 $30.8 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? Assumed COGS/sales Actual COGS/sales Year 2 3 $433.0 $468.0 8.17 $516.0 10.37 $547.0 6 .07 $574.3 5.02 -$93.6 - $7.0 $103.2 -$7.5 -$109.4 $9.0 $114.9 -$9.5 Earnings and FCF Forecast (millions) Sales Growth vs. Prior Year Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) $7.0 -$7.71 $6 31 $7.5 $10.01 -48 $9.0 $9.91 -$5 $9.5 $10.4 -44 9 $0.0 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price o. Let's return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, now suppose Sora reduces its selling general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) Assumed SG&A Actual SG&A 207 16% 1 2 3 $433.0 $468.0 8.12 - $313.6 $154.4 $516.0 10.37 - $345.7 $170.3 $547.0 $574.3 6 .07 5.02 - $366.51 - $384.8 $180.5| $189.5 -$7 n -$75 $9n -$95 Year Earnings and FCF Forecast (millions) Sales Growth vs. Prior Year Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) $7.01 -$7 7 $6 31 $7.51 -$10 - $9.00 $99 -$5 6 $95 -$10.4 -$4.9 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price d. Sora's networking capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (which is their current level in year 0). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions remain as in part (a), what stook price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in 18% Assumed NWC/sales Actual NWC/sales 127 Initial value for NWC 3 $433.0 Year Earnings and FCF Forecast (millions) Sales Growth us. Prior Year Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) D $468.0 8.17 -$313.60 $154 4 $93.6 - $7.01 $53 R -$21.5 $7.0 -$7.7 $516.0 10.32 $345.71 $170 31 $103.21 $7.5 $596 -$23.81 $7.5 -$10.0 $547.0 $574.3 6.07 5.07 $366.51 - $384.8 $180 5 $1895 $109.41 $114.9 $9.0 - $9.5 $62 1 $65 ? $24 8 -$26.1 $9.01 $95 -$9.91 $10.4 $0. 0 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price Problem 9-21 Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. Sora Industries has 60 million outstanding shares, $120 million in debt, $40 million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next four years: 433.0 547.0 6.0% -366.5 180.5 -109.4 Year Earnings and FCF Forecast (5 millions) Sales Growth versus Prior Tear Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow 468.0 8.1% -313.6 154.4 -93.6 -7.0 53.8 -21.5 7.0 -7.7 -6.3 25.3 516.0 10.3% -345.7 170.3 -103.2 -7.5 59.6 -23.8 7.5 -10.0 -8.6 24.6 -9.0 574.3 5.0% -384.8 189.5 -114.9 -9.5 65.2 -26.1 9.5 -10.4 -4.9 3 3.3 62.1 -24.8 9.0 -9.9 -5.6 8 30. a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5% rate beyond year 4. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 10%, what is the value of Sora's stock based on this information? b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? c. Let's return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, now suppose Sora reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (which is their current level in year 0). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions remain as in part (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) Shares outstanding (millions) Debt (millions) $120 Cash (millions) $40 Tax rate 40% a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5% rate beyond year 4. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 10%, what is the value of Sora's stock based on this information? Long-run growth rate Cost of capital 5% 10% Year Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) $0.0 $25.3 $24.6 $30.8 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? Assumed COGS/sales Actual COGS/sales Year 2 3 $433.0 $468.0 8.17 $516.0 10.37 $547.0 6 .07 $574.3 5.02 -$93.6 - $7.0 $103.2 -$7.5 -$109.4 $9.0 $114.9 -$9.5 Earnings and FCF Forecast (millions) Sales Growth vs. Prior Year Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) $7.0 -$7.71 $6 31 $7.5 $10.01 -48 $9.0 $9.91 -$5 $9.5 $10.4 -44 9 $0.0 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price o. Let's return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, now suppose Sora reduces its selling general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) Assumed SG&A Actual SG&A 207 16% 1 2 3 $433.0 $468.0 8.12 - $313.6 $154.4 $516.0 10.37 - $345.7 $170.3 $547.0 $574.3 6 .07 5.02 - $366.51 - $384.8 $180.5| $189.5 -$7 n -$75 $9n -$95 Year Earnings and FCF Forecast (millions) Sales Growth vs. Prior Year Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) $7.01 -$7 7 $6 31 $7.51 -$10 - $9.00 $99 -$5 6 $95 -$10.4 -$4.9 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price d. Sora's networking capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (which is their current level in year 0). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions remain as in part (a), what stook price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in 18% Assumed NWC/sales Actual NWC/sales 127 Initial value for NWC 3 $433.0 Year Earnings and FCF Forecast (millions) Sales Growth us. Prior Year Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General, and Administrative Depreciation EBIT Less: Income Tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increase in NWC Free Cash Flow Terminal value (millions) Total cash flow (millions) D $468.0 8.17 -$313.60 $154 4 $93.6 - $7.01 $53 R -$21.5 $7.0 -$7.7 $516.0 10.32 $345.71 $170 31 $103.21 $7.5 $596 -$23.81 $7.5 -$10.0 $547.0 $574.3 6.07 5.07 $366.51 - $384.8 $180 5 $1895 $109.41 $114.9 $9.0 - $9.5 $62 1 $65 ? $24 8 -$26.1 $9.01 $95 -$9.91 $10.4 $0. 0 Enterprise value (millions) Stock price
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


