Question: Provide solutions for attached questions below. 2. At this point, we can analyze (stability, steady-state gain, sinusoidal steady-state gains, time-constant, etc.) of first-order, linear dynamical
Provide solutions for attached questions below.

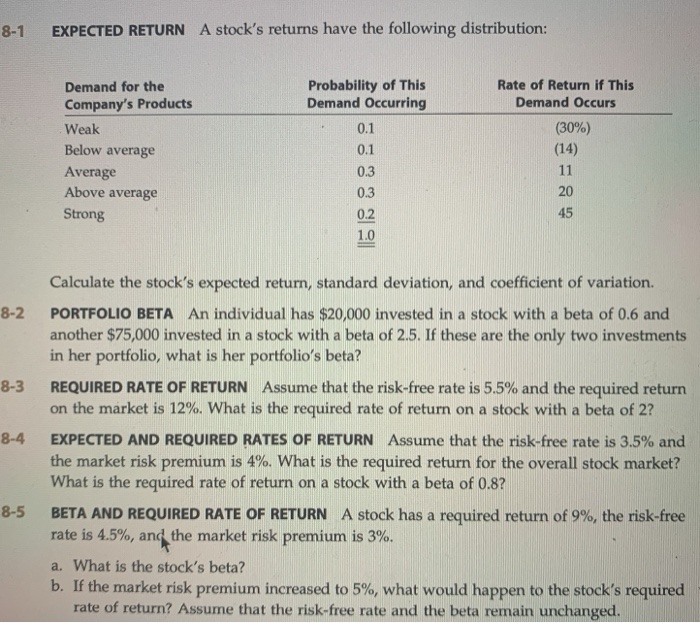


2. At this point, we can analyze (stability, steady-state gain, sinusoidal steady-state gains, time-constant, etc.) of first-order, linear dynamical systems. We previously analyzed a Ist-order process model, and a proportional-control strategy. In this problem, we try a different situation, where the process is simply proportional, but the controller is a Ist-order, linear dynamical system. Specifically, suppose the process model is non-dynamic ("static" ) simply y(t) = cu(t) + Bd(t) where o and B are constants. The control strategy is dynamic i (t) = ar(t) + bir(t) + bzym(t) u(t) = cr(t) + dir(t) where ym(t) = y(t) + n(t) and the various "gains" (a, bi, . .., di) constitute the design choices in the control strategy. Be careful, notation-wise, since (for example) d, is a constant parameter, and d(t) is a signal (the disturbance). (a) Eliminate u and ym from the equations to obtain a differential equation for r of the form r(t) = Ar(t) + Bir(t) + Bad(t) + Ban(t) which governs the closed-loop behavior of r. Note that A, B1, B2, By are functions of the parameters a, b1, ... in the control strategy, as well as the process parameters o and B. (b) What relations on (a, b1. .... dj, or, B) are equivalent to closed-loop system stability? (c) As usual, we are interested in the effect (with feedback in place) of (r, d, n) on (y, u), the regulated variable, and the control variable, respectively. Find the coefficients (in terms of (a, bi, . . ., d1, 0, B)) so that y(t) = Cix(t) + Dur(t) + Died(t) + Dian(t) u(t) = Car(t) + Dar(t) + Dad(t) + Dzan(t) (d) Suppose that T. > 0 is a desired closed-loop time constant. Write down the constraints on the a, b1, b2, c and di (i.e., the parameters of the controller to be design) such that the following conditions hold: . closed-loop is stable . closed-loop time constant is To . steady-state gain from d -> y is 0 . steady-state gain from r - y is 12. At this point, we can analyze (stability, steady-state gain, sinusoidal steady-state gains, time-constant, etc.) of first-order, linear dynamical systems. We previously analyzed a Ist-order process model, and a proportional-control strategy. In this problem, we try a different situation, where the process is simply proportional, but the controller is a Ist-order, linear dynamical system. Specifically, suppose the process model is non-dynamic ("static" ) simply y(t) = cu(t) + Bd(t) where o and B are constants. The control strategy is dynamic i (t) = ar(t) + bir(t) + bzym(t) u(t) = cr(t) + dir(t) where ym(t) = y(t) + n(t) and the various "gains" (a, bi, . .., di) constitute the design choices in the control strategy. Be careful, notation-wise, since (for example) d, is a constant parameter, and d(t) is a signal (the disturbance). (a) Eliminate u and ym from the equations to obtain a differential equation for r of the form r(t) = Ar(t) + Bir(t) + Bad(t) + Ban(t) which governs the closed-loop behavior of r. Note that A, B1, B2, By are functions of the parameters a, b1, ... in the control strategy, as well as the process parameters o and B. (b) What relations on (a, b1. .... dj, or, B) are equivalent to closed-loop system stability? (c) As usual, we are interested in the effect (with feedback in place) of (r, d, n) on (y, u), the regulated variable, and the control variable, respectively. Find the coefficients (in terms of (a, bi, . . ., d1, 0, B)) so that y(t) = Cix(t) + Dur(t) + Died(t) + Dian(t) u(t) = Car(t) + Dar(t) + Dad(t) + Dzan(t) (d) Suppose that T. > 0 is a desired closed-loop time constant. Write down the constraints on the a, b1, b2, c and di (i.e., the parameters of the controller to be design) such that the following conditions hold: . closed-loop is stable . closed-loop time constant is To . steady-state gain from d -> y is 0 . steady-state gain from r - y is 18-1 EXPECTED RETURN A stock's returns have the following distribution: Demand for the Probability of This Rate of Return if This Company's Products Demand Occurring Demand Occurs Weak 0.1 (30%) Below average 0.1 (14) Average 0.3 11 Above average 0.3 20 Strong 45 Calculate the stock's expected return, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation. 8-2 PORTFOLIO BETA An individual has $20,000 invested in a stock with a beta of 0.6 and another $75,000 invested in a stock with a beta of 2.5. If these are the only two investments in her portfolio, what is her portfolio's beta? 8-3 REQUIRED RATE OF RETURN Assume that the risk-free rate is 5.5% and the required return on the market is 12%. What is the required rate of return on a stock with a beta of 2? 8-4 EXPECTED AND REQUIRED RATES OF RETURN Assume that the risk-free rate is 3.5% and the market risk premium is 4%. What is the required return for the overall stock market? What is the required rate of return on a stock with a beta of 0.8? 8-5 BETA AND REQUIRED RATE OF RETURN A stock has a required return of 9%, the risk-free rate is 4.5%, and the market risk premium is 3%. a. What is the stock's beta? b. If the market risk premium increased to 5%, what would happen to the stock's required rate of return? Assume that the risk-free rate and the beta remain unchanged.QUESTION 11 Determining the price of compact discs is a concern of: a. neither macroeconomics nor microeconomics. b. both macroeconomics and microeconomics. c. microeconomics. d. macroeconomics.Question: 1. Suppose the price of x1 is $20 and the price of x2 is $4. If good x1 is on the horizontal axis... 1. Suppose the price of x, is $20 and the price of xz is $4. If good x, is on the horizontal axis, what is the slope of the consumer's budget constraint? a. -0.20 b. -0.25 C -5.0 d. -0.2 e. -4.0 f. -20.0 2. Suppose the price of x1 is $5 and the price of x2 is $1 and Toni's income is $20. Suppose Toni gets a $5 gift card that can only be used for the purchase of x1 and there is no resale value of the gift card. With the gift card, the commodity bundle (1,20) is on Toni's budget constraint. True False 3. Tiffany's utility function is given by the formula U(x1, x2) = min(20x1, 10x2). If x1 = x2, which commodity will have a greater marginal utility? A. Both x1 and x2 have the same marginal utility B. It is not possible to determine which commodity has higher marginal utility C. x2 D. x1 4. For U(X X2) = 6x,1/8 + X2, preferences are a. consistent with diminishing marginal rate of substitution. b. consistent with constant marginal rate of substitution. C consistent with increasing marginal rate of substitution
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


