Question: Question: 16a.In the previous section of this problem set, explain why the calculated YTM of a bond could b... 16a.In the previous section of this
Question: 16a.In the previous section of this problem set, explain why the calculated YTM of a bond could b...

16a.In the previous section of this problem set, explain why the calculated YTM of a bond could be a bad characterization (inaccurate) of the rate of return of a bond investment.
| Hint [1]: how was YTM calculated from the cash flows of the bond? Hint [3]: see lecture notes on the concept of "yield illusion". | |||||
| Hint [2]: what assumptions were made on this TVM-based calculation? | |||||
b.If YTM is a potentially bad method of calculation of a bond's rate of return, what other method of calculation is more appropriate? And why is this method always correct (accurate)?
| Hint [1]: how was YTM calculated from the cash flows of the bond? Hint [3]: see lecture notes on the concept of "yield illusion". | |||||
| Hint [2]: what assumptions were made on this TVM-based calculation? | |||||
c.,Are there any bad assumptions made in the calculation of the YTM of zero-coupon bonds?
| Hint [1]: any incorrect TVM assumptions made on it's bond's cash flows? Hint [2]: any "yield illusion" problems? |
17a.3 years ago, you acquired a 10-year 0% coupon, $1,000 face value bond at a YTM of 6%. Today, you sold this bond at a YTM of 3%. Calculate your annualized Horizon Yield [HY].
a.Assuming annual compounding, show your work below:
b.Assuming sem-annual compounding, show your work below:
18.Bonds of RCY Corporation with a face value of $1,000 sells for $975, mature in 5 years, and have a 5% coupon rate paid semiannually. Calculate the investor's RCY by assuming the following:
| - Bond sold to yield at 5% and the end of the 3-year holding period. |
| - Reinvestment rate 4% APR during this holding period. |
| - PS: state what assumption(s) you need to make in calculating this RCY. |
a. Show your calculations in the space below:
b.Briefly explain in the space below why there are potentially two answers to the RCY calculation?
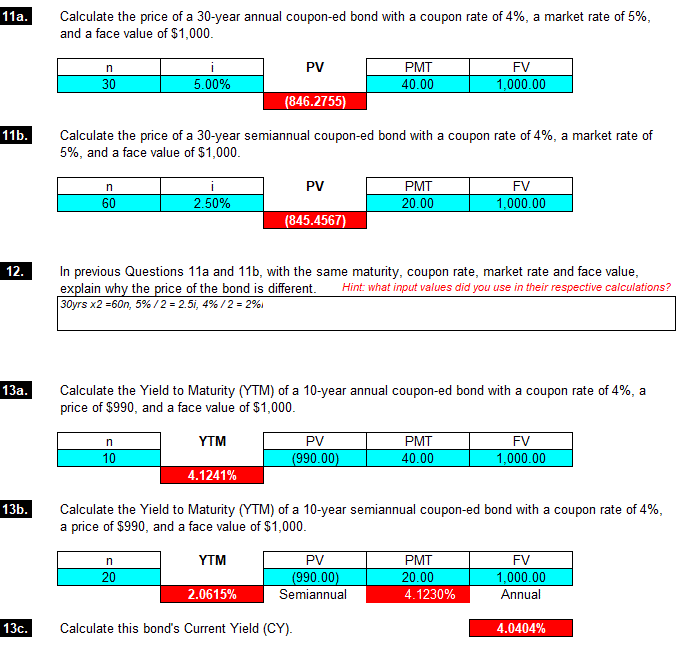
11a. Calculate the price of a 30-year annual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a market rate of 5%, and a face value of $1,000. PV n 30 5.00% PMT 40.00 FV 1,000.00 (846.2755) 11b. Calculate the price of a 30-year semiannual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a market rate of 5%, and a face value of $1,000. PV n 60 PMT 20.00 FV 1,000.00 2.50% (845.4567) 12. In previous Questions 11a and 11b, with the same maturity, coupon rate, market rate and face value, explain why the price of the bond is different. Hint what input values did you use in their respective calculations? 30yrs x2 =60n, 5%/2 = 2.5i, 4% /2 = 2% 13a. Calculate the Yield to Maturity (YTM) of a 10-year annual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a price of $990, and a face value of $1,000. n YTM PV (990.00) PMT 40.00 FV 1,000.00 10 4.1241% 13b. Calculate the Yield to Maturity (YTM) of a 10-year semiannual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a price of $990, and a face value of $1,000. n YTM PV FV 20 (990.00) Semiannual PMT 20.00 4.1230% 1,000.00 Annual 2.0615% 13c. Calculate this bond's Current Yield (CY). 4.0404% 14. In previous Questions 13a and 13b, with the same maturity, coupon rate, market rate and face value, explain why the YTM of the bond is different. Hint what input values did you use in their respective calculations? 10yrs x 2 = 20N, 4% x 1000/2 = $20PMT 15. a) Calculate the Yield to Call (YTC) of a 20-year semiannual coupon-ed par bond with a coupon rate of 4% and a face value of $1,000. This bond was recalled 5 years into the life of the bond at a call price of $1,025. YTC PV PMT FV 10 (1,000.00) 20.00 1,025.00 2.2260% Semiannual 4.4519% Annual n b) Why can the YTM of this bond be determined without calculation? Put your response in the space below: Hint check the values of the coupon rate and the market rate. Sicne the bond is a par bond, YTM and coupon rate of the bond will be equal 4%. c) Give two reasons why this bond's YTC is greater than its YTM. Put your response in the space below: Hint compare the respective CFs between YTM and YTC calculations. 1) bc the price to call was higher than the par value of the bond. This make YTC of the bond higher than YTM of the bond. 2) YTC is greater since it was calle Reinvestment Risk and Interest-Rate Risk 11a. Calculate the price of a 30-year annual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a market rate of 5%, and a face value of $1,000. PV n 30 5.00% PMT 40.00 FV 1,000.00 (846.2755) 11b. Calculate the price of a 30-year semiannual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a market rate of 5%, and a face value of $1,000. PV n 60 PMT 20.00 FV 1,000.00 2.50% (845.4567) 12. In previous Questions 11a and 11b, with the same maturity, coupon rate, market rate and face value, explain why the price of the bond is different. Hint what input values did you use in their respective calculations? 30yrs x2 =60n, 5%/2 = 2.5i, 4% /2 = 2% 13a. Calculate the Yield to Maturity (YTM) of a 10-year annual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a price of $990, and a face value of $1,000. n YTM PV (990.00) PMT 40.00 FV 1,000.00 10 4.1241% 13b. Calculate the Yield to Maturity (YTM) of a 10-year semiannual coupon-ed bond with a coupon rate of 4%, a price of $990, and a face value of $1,000. n YTM PV FV 20 (990.00) Semiannual PMT 20.00 4.1230% 1,000.00 Annual 2.0615% 13c. Calculate this bond's Current Yield (CY). 4.0404% 14. In previous Questions 13a and 13b, with the same maturity, coupon rate, market rate and face value, explain why the YTM of the bond is different. Hint what input values did you use in their respective calculations? 10yrs x 2 = 20N, 4% x 1000/2 = $20PMT 15. a) Calculate the Yield to Call (YTC) of a 20-year semiannual coupon-ed par bond with a coupon rate of 4% and a face value of $1,000. This bond was recalled 5 years into the life of the bond at a call price of $1,025. YTC PV PMT FV 10 (1,000.00) 20.00 1,025.00 2.2260% Semiannual 4.4519% Annual n b) Why can the YTM of this bond be determined without calculation? Put your response in the space below: Hint check the values of the coupon rate and the market rate. Sicne the bond is a par bond, YTM and coupon rate of the bond will be equal 4%. c) Give two reasons why this bond's YTC is greater than its YTM. Put your response in the space below: Hint compare the respective CFs between YTM and YTC calculations. 1) bc the price to call was higher than the par value of the bond. This make YTC of the bond higher than YTM of the bond. 2) YTC is greater since it was calle Reinvestment Risk and Interest-Rate Risk
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


