Question: Reaction Rate: Faster or Slower Part I - Predicting the Reaction Rates Directions: Assume that the substances below are the reactants for different reactions. Indicate
Reaction Rate: Faster or Slower
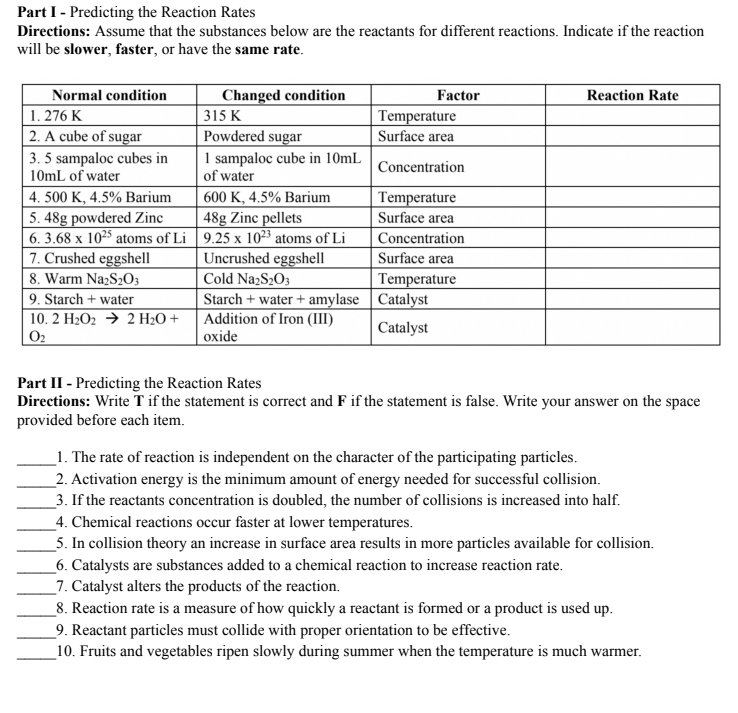
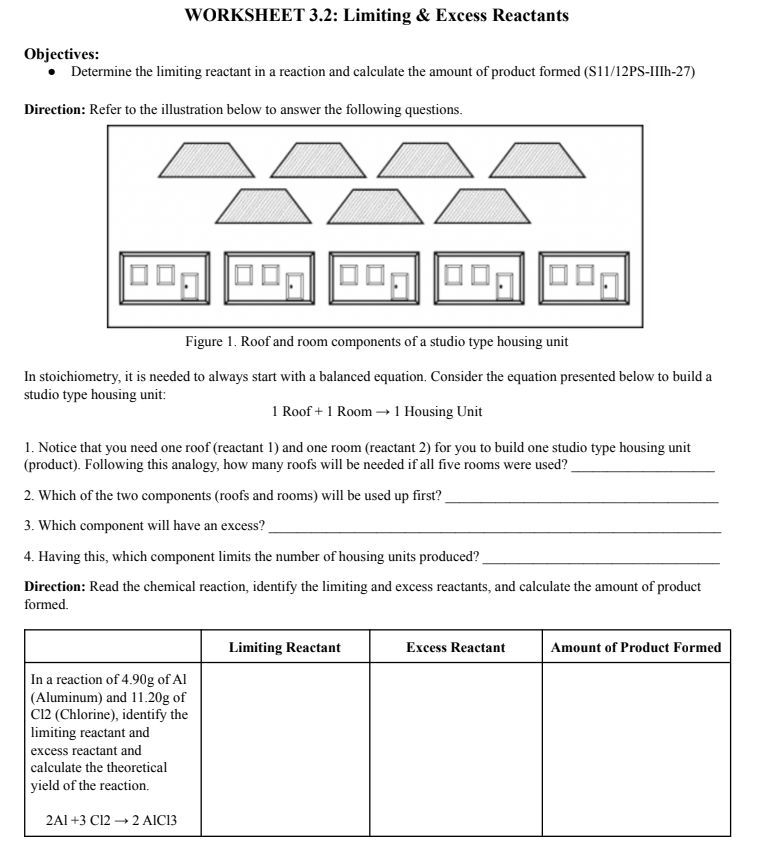
Part I - Predicting the Reaction Rates Directions: Assume that the substances below are the reactants for different reactions. Indicate if the reaction will be slower, faster, or have the same rate. Normal condition Changed condition Factor Reaction Rate 1. 276 K 315 K Temperature 2. A cube of sugar Powdered sugar Surface area 3. 5 sampaloc cubes in I sampaloc cube in 10mL 10mL of water of water Concentration 4. 500 K, 4.5% Barium 600 K, 4.5% Barium Temperature 5. 48g powdered Zinc 48g Zinc pellets Surface area 6. 3.68 x 1025 atoms of Li 9.25 x 10- atoms of Li Concentration 7. Crushed eggshell Uncrushed eggshell Surface area 8. Warm NazS203 Cold NazS203 Temperature 9. Starch + water Starch + water + amylase Catalyst 10. 2 H202 > 2 H20 + Addition of Iron (III) Oz Catalyst oxide Part II - Predicting the Reaction Rates Directions: Write T if the statement is correct and F if the statement is false. Write your answer on the space provided before each item. 1. The rate of reaction is independent on the character of the participating particles. 2. Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy needed for successful collision. 3. If the reactants concentration is doubled, the number of collisions is increased into half. 4. Chemical reactions occur faster at lower temperatures. 5. In collision theory an increase in surface area results in more particles available for collision. 6. Catalysts are substances added to a chemical reaction to increase reaction rate. 7. Catalyst alters the products of the reaction. 8. Reaction rate is a measure of how quickly a reactant is formed or a product is used up. 9. Reactant particles must collide with proper orientation to be effective. 10. Fruits and vegetables ripen slowly during summer when the temperature is much warmer.WORKSHEET 3.2: Limiting & Excess Reactants Objectives: . Determine the limiting reactant in a reaction and calculate the amount of product formed ($1 1/12PS-IIIh-27) Direction: Refer to the illustration below to answer the following questions. Figure 1. Roof and room components of a studio type housing unit In stoichiometry, it is needed to always start with a balanced equation. Consider the equation presented below to build a studio type housing unit: 1 Roof + 1 Room - 1 Housing Unit 1. Notice that you need one roof (reactant 1) and one room (reactant 2) for you to build one studio type housing unit (product). Following this analogy, how many roofs will be needed if all five rooms were used? 2. Which of the two components (roofs and rooms) will be used up first? 3. Which component will have an excess? 4. Having this, which component limits the number of housing units produced? Direction: Read the chemical reaction, identify the limiting and excess reactants, and calculate the amount of product formed. Limiting Reactant Excess Reactant Amount of Product Formed In a reaction of 4.90g of Al (Aluminum) and 11.20g of C12 (Chlorine), identify the limiting reactant and excess reactant and calculate the theoretical yield of the reaction. 2AI +3 C12 - 2 AIC13
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


