Question: Thank you for the answer, I will like your response! :) REQUIRMENTS: MORE INFO: Surler Metal Products Company had the following balances, among others, at
Thank you for the answer, I will like your response! :)
REQUIRMENTS:
 MORE INFO:
MORE INFO:
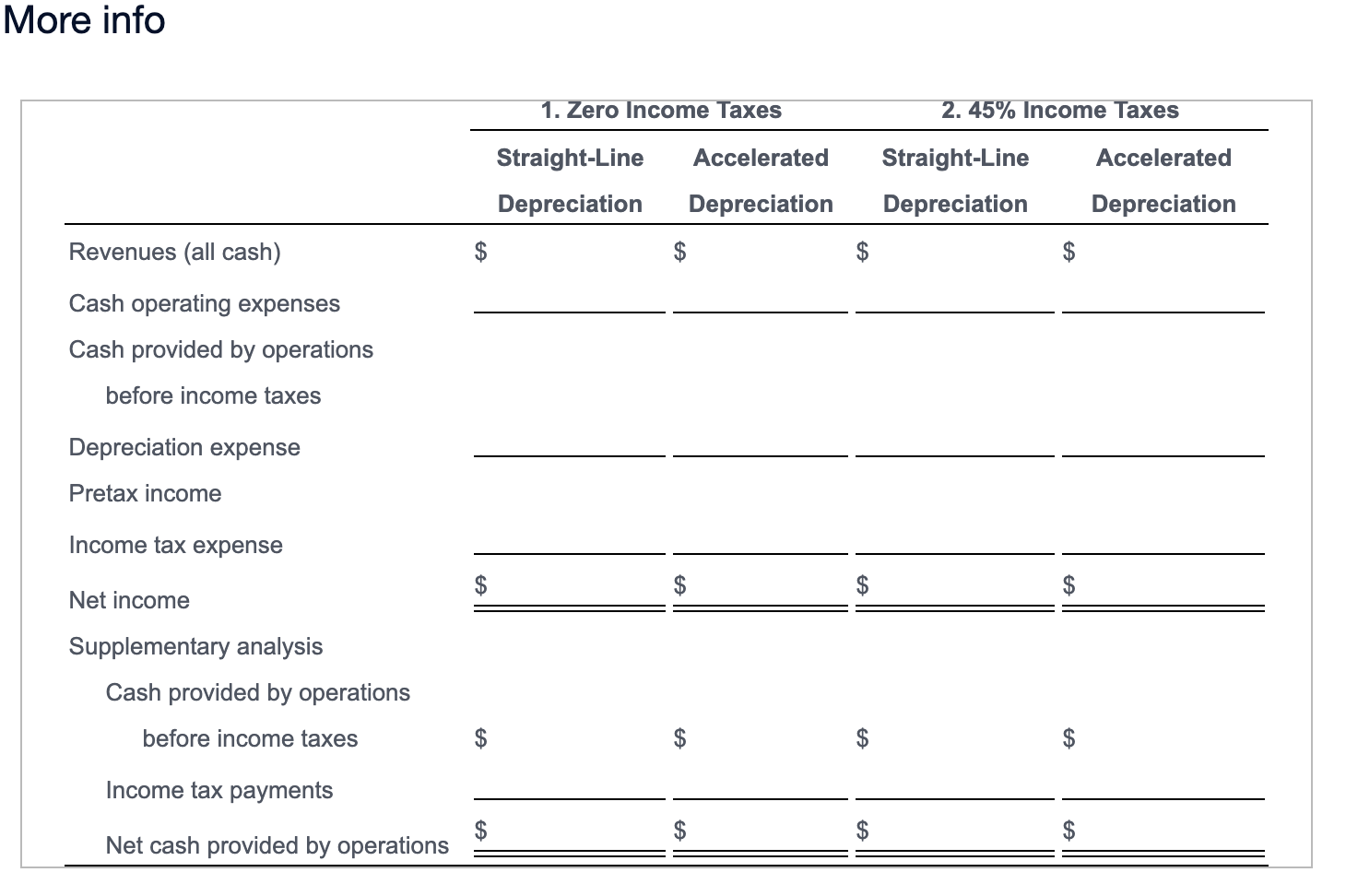
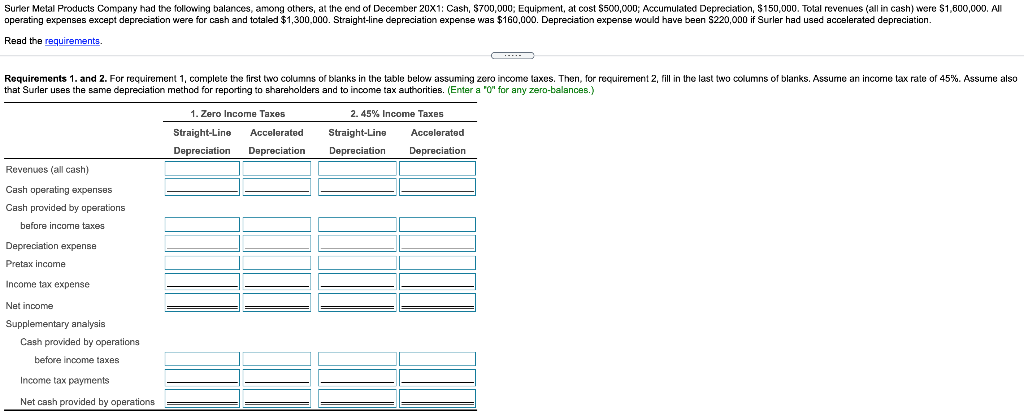
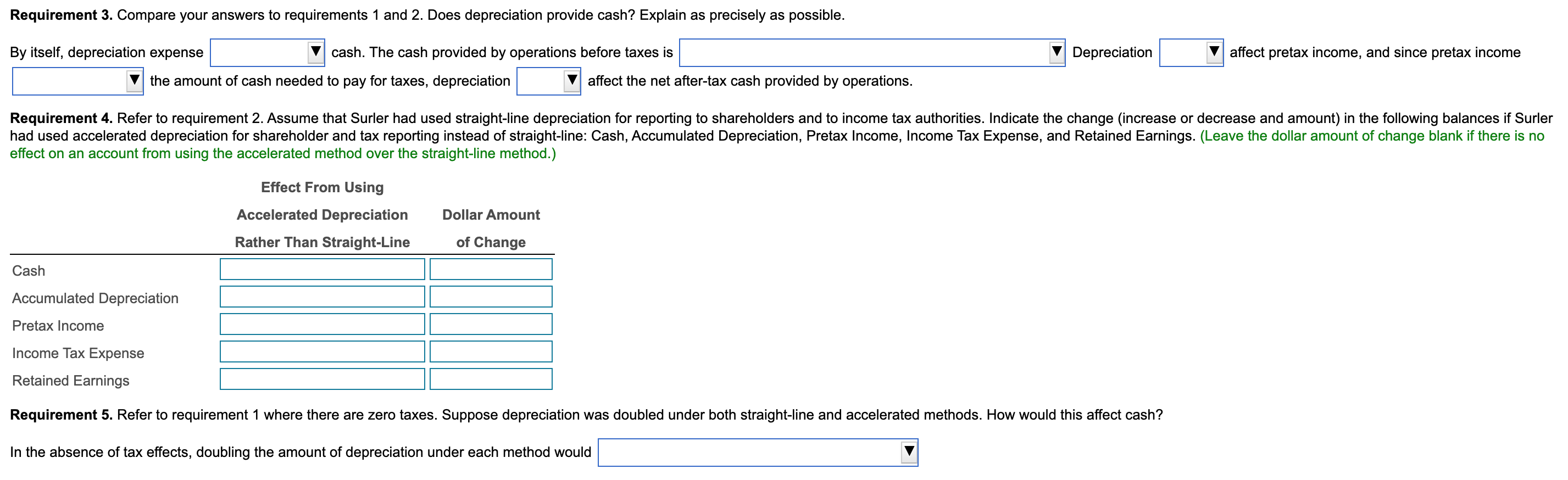
Surler Metal Products Company had the following balances, among others, at the end of December 20X1: Cash, $700,000; Equipment, at cost $500,000; Accumulated Depreciation, $150,000. Total revenues (all in cash) were $1,600,000. All operating expenses except depreciation were for cash and totaled $1,300,000. Straight-line depreciation expense was $160,000. Depreciation expense would have been $220,000 if Surler had used accelerated depreciation. Read the requirements. Requirements 1. and 2. For requirement 1, complete the first two columns of blanks in the table below assuming zero income taxes. Then, for requirement 2, fill in the last two columns of blanks. Assume an income tax rate of 45%. Assume also that Surler uses the same depreciation method for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. (Enter a "o" for any zero-balances.) 1. Zero Income Taxes Straight-Line Accelerated Depreciation Depreciation 2.45% Income Taxes Straight-Line Accelerated Depreciation Depreciation Revenues (all cash) Cash operating expenses Cash provided by operations before income taxes Depreciation expense Pretax income Income tax expense Net income Supplementary analysis Cash provided operations before income taxes Income tax payments Net cash provided by operations Requirement 3. Compare your answers to requirements 1 and 2. Does depreciation provide cash? Explain as precisely as possible. Depreciation affect pretax income, and since pretax income By itself, depreciation expense cash. The cash provided by operations before taxes is the amount of cash needed to pay for taxes, depreciation affect the net after-tax cash provided by operations. Requirement 4. Refer to requirement 2. Assume that Surler had used straight-line depreciation for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. Indicate the change (increase or decrease and amount) in the following balances if Surler had used accelerated depreciation for shareholder and tax reporting instead of straight-line: Cash, Accumulated Depreciation, Pretax Income, Income Tax Expense, and Retained Earnings. (Leave the dollar amount of change blank if there is no effect on an account from using the accelerated method over the straight-line method.) Effect From Using Accelerated Depreciation Rather Than Straight-Line Dollar Amount of Change Cash Accumulated Depreciation Pretax Income Income Tax Expense Retained Earnings Requirement 5. Refer to requirement 1 where there are zero taxes. Suppose depreciation was doubled under both straight-line and accelerated methods. How would this affect cash? In the absence of tax effects, doubling the amount of depreciation under each method would Requirements 1. Assume zero income taxes. Fill in the first two columns of blanks in the accompanying table. (Click the icon to view the table.) 2. Fill in the last two columns of blanks in the accompanying table. Assume an income tax rate of 45%. Assume also that Surler uses the same depreciation method for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. 3. Compare your answers to requirements 1 and 2. Does depreciation provide cash? Explain as precisely as possible. 4. Refer to requirement 2. Assume that Surler had used straight-line depreciation for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. Indicate the change (increase or decrease and amount) in the following balances if Surler had used accelerated depreciation for shareholder and tax reporting instead of straight-line: Cash, Accumulated Depreciation, Pretax Income, Income Tax Expense, and Retained Earnings. 5. Refer to requirement 1 where there are zero taxes. Suppose depreciation was doubled under both straight-line and accelerated methods. How would this affect cash? Be specific. More info 1. Zero Income Taxes 2. 45% Income Taxes Straight-Line Accelerated Accelerated Straight-Line Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Revenues (all cash) $ $ $ $ Cash operating expenses Cash provided by operations before income taxes Depreciation expense Pretax income Income tax expense $ $ $ $ Net income Supplementary analysis Cash provided by operations before income taxes $ $ $ $ Income tax payments $ $ $ $ Net cash provided by operations Surler Metal Products Company had the following balances, among others, at the end of December 20X1: Cash, $700,000; Equipment, at cost $500,000; Accumulated Depreciation, $150,000. Total revenues (all in cash) were $1,600,000. All operating expenses except depreciation were for cash and totaled $1,300,000. Straight-line depreciation expense was $160,000. Depreciation expense would have been $220,000 if Surler had used accelerated depreciation. Read the requirements. Requirements 1. and 2. For requirement 1, complete the first two columns of blanks in the table below assuming zero income taxes. Then, for requirement 2, fill in the last two columns of blanks. Assume an income tax rate of 45%. Assume also that Surler uses the same depreciation method for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. (Enter a "o" for any zero-balances.) 1. Zero Income Taxes Straight-Line Accelerated Depreciation Depreciation 2.45% Income Taxes Straight-Line Accelerated Depreciation Depreciation Revenues (all cash) Cash operating expenses Cash provided by operations before income taxes Depreciation expense Pretax income Income tax expense Net income Supplementary analysis Cash provided operations before income taxes Income tax payments Net cash provided by operations Requirement 3. Compare your answers to requirements 1 and 2. Does depreciation provide cash? Explain as precisely as possible. Depreciation affect pretax income, and since pretax income By itself, depreciation expense cash. The cash provided by operations before taxes is the amount of cash needed to pay for taxes, depreciation affect the net after-tax cash provided by operations. Requirement 4. Refer to requirement 2. Assume that Surler had used straight-line depreciation for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. Indicate the change (increase or decrease and amount) in the following balances if Surler had used accelerated depreciation for shareholder and tax reporting instead of straight-line: Cash, Accumulated Depreciation, Pretax Income, Income Tax Expense, and Retained Earnings. (Leave the dollar amount of change blank if there is no effect on an account from using the accelerated method over the straight-line method.) Effect From Using Accelerated Depreciation Rather Than Straight-Line Dollar Amount of Change Cash Accumulated Depreciation Pretax Income Income Tax Expense Retained Earnings Requirement 5. Refer to requirement 1 where there are zero taxes. Suppose depreciation was doubled under both straight-line and accelerated methods. How would this affect cash? In the absence of tax effects, doubling the amount of depreciation under each method would Requirements 1. Assume zero income taxes. Fill in the first two columns of blanks in the accompanying table. (Click the icon to view the table.) 2. Fill in the last two columns of blanks in the accompanying table. Assume an income tax rate of 45%. Assume also that Surler uses the same depreciation method for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. 3. Compare your answers to requirements 1 and 2. Does depreciation provide cash? Explain as precisely as possible. 4. Refer to requirement 2. Assume that Surler had used straight-line depreciation for reporting to shareholders and to income tax authorities. Indicate the change (increase or decrease and amount) in the following balances if Surler had used accelerated depreciation for shareholder and tax reporting instead of straight-line: Cash, Accumulated Depreciation, Pretax Income, Income Tax Expense, and Retained Earnings. 5. Refer to requirement 1 where there are zero taxes. Suppose depreciation was doubled under both straight-line and accelerated methods. How would this affect cash? Be specific. More info 1. Zero Income Taxes 2. 45% Income Taxes Straight-Line Accelerated Accelerated Straight-Line Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Revenues (all cash) $ $ $ $ Cash operating expenses Cash provided by operations before income taxes Depreciation expense Pretax income Income tax expense $ $ $ $ Net income Supplementary analysis Cash provided by operations before income taxes $ $ $ $ Income tax payments $ $ $ $ Net cash provided by operations
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


