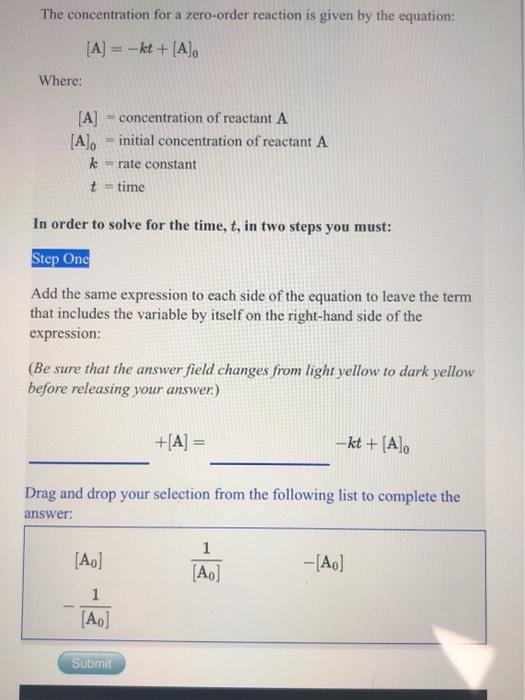
Question: The concentration for a zero-order reaction is given by the equation: [A] = -kt + [A] Where: [A] = concentration of reactant A [A]. -
![[A] = -kt + [A] Where: [A] = concentration of reactant A](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f9442e9c248_95066f9442e3b4c9.jpg)
The concentration for a zero-order reaction is given by the equation: [A] = -kt + [A] Where: [A] = concentration of reactant A [A]. - initial concentration of reactant A rate constant t = time In order to solve for the time, t, in two steps you must: Step One Add the same expression to each side of the equation to leave the term that includes the variable by itself on the right-hand side of the expression: (Be sure that the answer field changes from light yellow to dark yellow before releasing your answer) +[A] = --kt + [A] Drag and drop your selection from the following list to complete the answer: [A] 1 [A] -[A] 1 [AO] Submit The Gibbs Free Energy equation is given by the equation: AG = AH-TAS Where: AG Gibbs Free Energy change AH = Enthalpy change T temperature AS = Entropy change In order to solve for the Entropy change, AS, in two steps you must: Step Onc Add the same expression to each side of the equation to leave the term that includes the variable by itself on the right-hand side of the expression: (Be sure that the answer field changes from light yellow to dark yellow before releasing your answer) +AG = +AH-TAS Drag and drop your selection from the following list to complete the answer: 1 AH - 1 AH Submit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


