Question: The subject is Strategic Management EXERCISE 6E Construct an IFE Matrix for Nestl Purpose This exercise will give you experience developing an IFE matrix. Identifying
The subject is Strategic Management

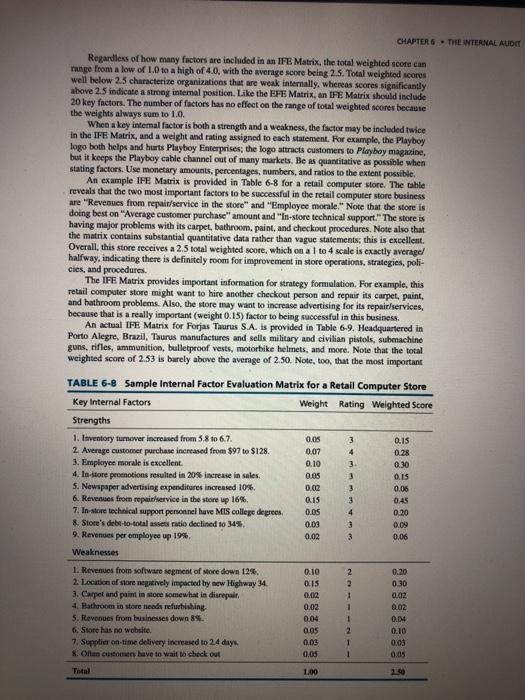
EXERCISE 6E Construct an IFE Matrix for Nestl Purpose This exercise will give you experience developing an IFE matrix. Identifying and prioritizing factors to include in an IFE matrix fosters communication among functional and divisional managers. Preparing an IFE matrix allows human resources,' marketing's, production/operations, finance/ accounting's, R&D's, and management information systems' managers to articulate their concerns and thoughts regarding the business condition of the firm. This results in an improved collective understanding of the business. Instructions Step 1 Join with two other individuals to form a three-person team. Develop an IFE matrix for Nestl. Step 2 Compare your team's IFE matrix with other teams' IFE matrices. Discuss any major differences. Step 3 What strategies do you think would allow Nestl to capitalize on its major strengths? What strategies would allow Nestl to improve upon its major weaknesses? The Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix A summary step in conducting an internal strategic-management audit is to construct an Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix. This strategy-formulation tool summarizes and evaluates the major strengths and weaknesses in the functional areas of a business, and it also provides a basis for identifying and evaluating relationships among those areas. Intuitive judgments are required in developing an IFE Matrix, so the appearance of a scientific approach should not be interpreted to mean this is an all-powerful technique. A thorough understanding of the factors included is more important than the actual numbers. Similar to the EFE Matrix and the Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) described in Chapter 7, an IFE Matrix can be developed in five steps: 1. List key internal factors as identified in the internal-audit process. Use a total of 20 internal factors, including both strengths and weaknesses. List strengths first and then weaknesses. Be as specific as possible, using percentages, ratios, and comparative numbers. Recall that Edward Deming said, "In God we trust. Everyone else bring data." Include action- able factors that can provide insight regarding strategies to pursue. For example, the factor "Our Quick Ratio is 2.1 versus industry average of 1.8" is not actionable, whereas the factor "Our chocolate division's ROI increased from 8 to 15 percent in South America" is actionable. Also, be as divisional as possible, because consolidated data oftentimes is not as revealing or useful in deciding among strategies as the underlying by-segment or division data. 2. Assign a weight that ranges from 0.0 (not important) to 1.0 (all-important) to each factor. The weight assigned to a given factor indicates the relative importance of the factor to being successful in the firm's industry. Regardless of whether a key factor is an internal strength or weakness, factors considered to have the greatest effect on organizational performance should be assigned the highest weights. The sum of all weights must equal 1.0. 3. Assign a 1 to 4 rating to each factor to indicate whether that factor represents a major weakness (rating = 1), a minor weakness (rating =2), a minor strength (rating =3), or a major strength (rating = 4). Note that strengths must receive a 3 or 4 rating and weaknesses must receive a 1 or 2 rating. Ratings are thus company-based, whereas the weights in step 2 are industry-based. 4. Multiply each factor's weight by its rating to determine a weighted score for each variable. 5. Sum the weighted scores for each variable to determine the total weighted score for the organization CHAPTER 6 - THE INTERNAL AUDIT Regardless of how many factors are included in an IFE Matrix, the total weighted score can range from a low of 1.0 to a high of 4.0, with the average score being 2.5. Total weighted scores well below 25 characterize organizations that are weak internally, whereas scores significantly above 2.5 indicate a strong internal position. Like the EFE Matrix, an IFE Matrix should include 20 key factors. The number of factors has no effect on the range of total weighted scores because the weights always sum to 1.0. When a key internal factor is both a strength and a weakness, the factor may be included twice in the IFE Matrix, and a weight and rating assigned to each statement. For example, the Playboy logo both helps and hurts Playboy Enterprises, the logo attracts customers to Playboy magazine, but it keeps the Playboy cable channel out of many markets. Be as quantitative as possible when stating factors. Use monetary amounts, percentages, numbers, and ratios to the extent possible. An example IFE Matrix is provided in Table 6-8 for a retail computer store. The table reveals that the two most important factors to be successful in the retail computer store business are "Revenues from repair/service in the store" and "Employee morale. Note that the store is doing best on "Average customer purchase amount and in-store technical support. The store is having major problems with its carpet, bathroom, paint, and checkout procedures. Note also that the matrix contains substantial quantitative data rather than vague statements, this is excellent. Overall, this store receives a 2.5 total weighted score, which on a I to 4 scale is exactly average halfway, indicating there is definitely room for improvement in store operations, strategies, poli- cies, and procedures. The IFE Matrix provides important information for strategy formulation. For example, this retail computer store might want to hire another checkout person and repair its carpet, paint, and bathroom problems. Also, the store may want to increase advertising for its repair/services, because that is a really important (weight 0.15) factor to being successful in this business. An actual IFE Matrix for Forjas Tuurus S.A. is provided in Table 6-9. Headquartered in Porto Alegre, Brazil, Taurus manufactures and sells military and civilian pistols, submachine guns, rifles, ammunition, bulletproof vests, motorbike helmets, and more. Note that the total weighted score of 2.53 is barely above the average of 2.50. Note, too, that the most important Q.IS 0.28 4 TABLE 6-8 Sample Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix for a Retail Computer Store Key Internal Factors Weight Rating Weighted Score Strengths 1. Inventory turnover increased from 5.8 to 6.7. 0.05 3 2 Average customer purchase increased from $97 to $128. 0.07 3. Employee morale is excellent 0.10 0.30 4. In-store promotions resulted in 20% increase in sales. 0.05 3 0.15 5. Newspaper advertising expenditures increased 10%. 0.02 3 0.06 6. Revenues from repair service in the store up 16%. 0.15 3 0.45 7. In-store technical support personnel have MIS college degrees 0.05 4 0.20 8. Store's debt-to-total assets ratio declined to 34% 0.03 0.09 9. Revenues per employee up 19% 3 0.06 Weaknesses 0.02 1. Revenues from software segment of More down 12%. 2. Location of store negatively impacted by new Highway 34 3. Carpet and paint in store somewhat in disrepair 4. Bathroom in store needs refurbishing, 5. Revenues from businesses down 8. 6. Store has no website. 7. Supplier on-time delivery increased to 24 days X. Often cacoes have to wait to check out 0.10 0.15 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.05 0.0 0.05 2 2 1 1 1 0.20 0.30 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.10 0.03 0.05 2 1 Total 1.00 250