Question: Using the probit equations provided in Table 2-5: a. Determine the explosion overpressure (in psi) where 50% fatalities due to lung hemorrhage are expected. b.
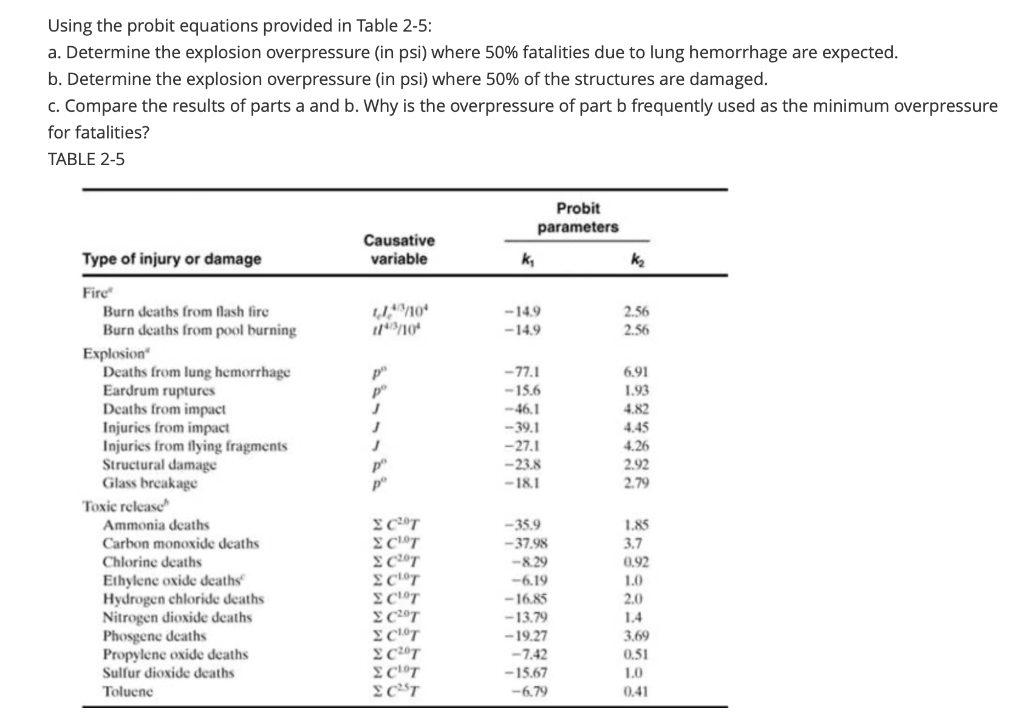
Using the probit equations provided in Table 2-5: a. Determine the explosion overpressure (in psi) where 50% fatalities due to lung hemorrhage are expected. b. Determine the explosion overpressure (in psi) where 50% of the structures are damaged. C. Compare the results of parts a and b. Why is the overpressure of part b frequently used as the minimum overpressure for fatalities? TABLE 2-5 Probit parameters Causative variable Type of injury or damage ky ka 19/10 1/43710 -149 -14.9 2.56 2.36 p p - 77.1 -15.6 -46.1 - 39.1 -27.1 - 23.8 -18.1 6.91 1.93 4.82 4.45 4.26 2.92 2.79 Fire Burn deaths from Nash fire Burn deaths from pool burning Explosion Deaths from lung hemorrhage Eardrum ruptures Deaths from impact Injuries from impact Injuries from flying fragments Structural damage Glass breakage Toxic release Ammonia deaths Carbon monoxide deaths Chlorine deaths Ethylenc oxide deaths Hydrogen chloride deaths Nitrogen dioxide deaths Phosgene deaths Propylene oxide deaths Sulfur dioxide deaths Toluene p p C0T C101 (20) CY C101 C20T C101 10207 C0T C251 -35.9 - 37.98 -8.29 -6.19 -16.85 -13.79 -19.27 -7.42 -15.67 -6,79 1.85 3.7 0.92 10 2.0 1.4 3.69 0.51 1.0 0.41
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


