Question: When there are coefficients in the reaction formula, how does that change the integrated rate law? For example I know that in a 2nd-order reaction
When there are coefficients in the reaction formula, how does that change the integrated rate law? For example I know that in a 2nd-order reaction of 2A->B, the integrated rate law becomes 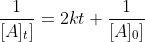 but what about when the coefficients are A->2B? What about reactions of other orders?
but what about when the coefficients are A->2B? What about reactions of other orders?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


