Question: Open PowerWorld Simulator case Problem 6_49. This case is identical to Example 6.9, except that the transformer between buses 1 and 5 is now a
Open PowerWorld Simulator case Problem 6_49. This case is identical to Example 6.9, except that the transformer between buses 1 and 5 is now a tap-changing transformer with a tap range between 0.9 and 1.1 and a tap step size of 0.006 25 . The tap is on the high side of the transformer. As the tap is varied between 0.975 and 1.1, show the variation in the reactive power output of generator \(1, \mathrm{~V}_{5}, \mathrm{~V}_{2}\), and the total real power losses.
Example 6.9
Figure 6.2 shows a single-line diagram of a five-bus power system. Input data are given in Tables 6.1, 6.2, and 6.3. As shown in Table 6.1, bus 1, to which a generator is connected, is the swing bus. Bus 3, to which a generator and a load are connected, is a voltage-controlled bus. Buses 2, 4, and 5 are load buses. Note that the loads at buses 2 and 3 are inductive since \(\mathrm{Q}_{2}=-\mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{L} 2}=-2.8\) and \(-\mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{L} 3}=\) -0.4 are negative.
For each bus \(k\), determine which of the variables \(\mathrm{V}_{k}, \delta_{k}, \mathrm{P}_{k}\), and \(\mathrm{Q}_{k}\) are input data and which are unknowns. Also, compute the elements of the second row of \(\boldsymbol{Y}_{\text {bus }}\).
Figure 6.2
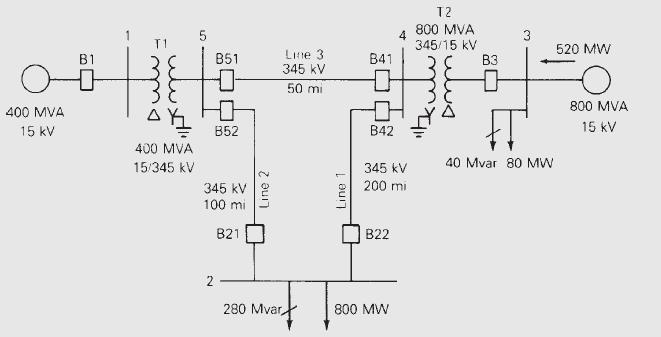
Table 6.1
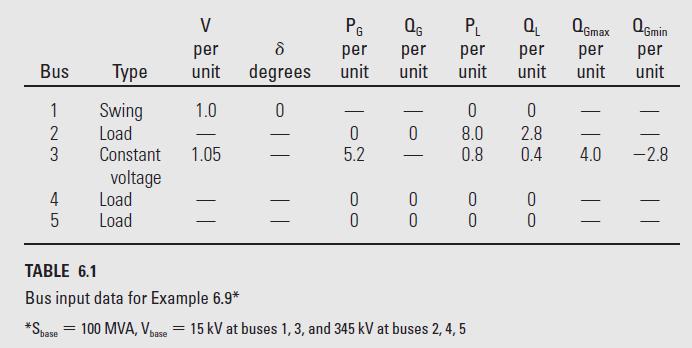
Table 6.2
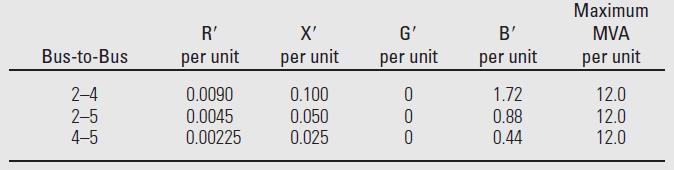
400 MVA 15 kV B1 400 MVA 15/345 KV 5 B51 2 B52 345 kV 100 mi B21 Line 3 345 kV 50 mi 280 Mvar, B41 B42 345 kV 200 mi B22 800 MW T2 800 MVA 345/15 kV B3 3 40 Mvar 80 MW 520 MW 800 MVA 15 kV
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


