Question: A free-piston engine under development consists of a small piston in a cylinder. Each end of the cylinder behaves like a two-stroke engine, in which
A free-piston engine under development consists of a small piston in a cylinder. Each end of the cylinder behaves like a two-stroke engine, in which the following sequence of processes occurs repetitively:1. A fresh charge of fuel–air mixture is blown in when the cylinder volume is approaching its maximum.2. The fresh gas is compressed as the piston moves in one direction.3. The mixture is ignited when the cylinder volume is at its minimum, producing a sudden rise in pressure.4. The hot, high-pressure gas expands as the piston moves in the other direction.5. The products of combustion are exhausted when the cylinder volume is near its maximum.These processes happen in the two end volumes out of phase, with the gas at one end expanding while the gas at the other end is being compressed. There are no shafts in this engine. Instead, the piston is a lightweight ceramic magnet that moves back and forth inside a coil of wire surrounding the engine, generating AC electrical power directly.
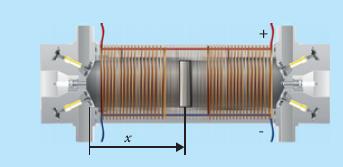
Energy transfer as work takes place between the piston and the electrons in the coil as a result of the force exerted by the electrons on the moving magnetic piston. Pressure measurements in the two cylinders as a function of the piston position x during the motion to the right are shown in the following figure.
The piston cross-sectional area is 0.01 m2.
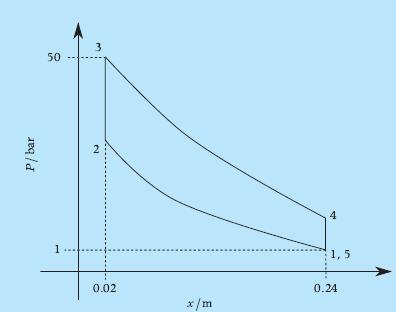
a. Calculate the work done (J) by the expanding left-side gas on the piston as it moves from one end to the other.b. Calculate the work done (J) by the piston on the right-side gas.c. Neglecting friction and electrical losses, calculate the power output of this engine (W), assuming that each one-way stroke takes 0.01 s.d. The density of the fresh charge (at the start of the compression) is 1 kg/m3. The measured temperature of the gas in the right side at the start of the compression is 300 K, and at the end of the compression, just before ignition, is 500 K. The internal energy of the fresh charge is given by
![]()
e. Calculate the energy transfer as heat (magnitude and direction) between the right side gas and the surrounding solid during the compression process. Make a sketch of the system and of the energy transfers.f. Suppose that the coil gets broken just as a stroke starts so that there is no force exerted on the piston by the electrons.Neglecting friction, assuming a piston mass of 0.8 kg, calculate the piston velocity at the end of the stroke, where normally the piston would be coming to rest at the other end. Make a sketch of the system and of the energy transfers.
x
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The work done by the expanding leftside gas on the piston can be calculated as the area under the pressurevolume curve for the left side of the cyli... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


